Trump Enacts Law Banning China-Based Engineers from Pentagon IT Systems Amid Security Concerns
Published on: 2025-12-31
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
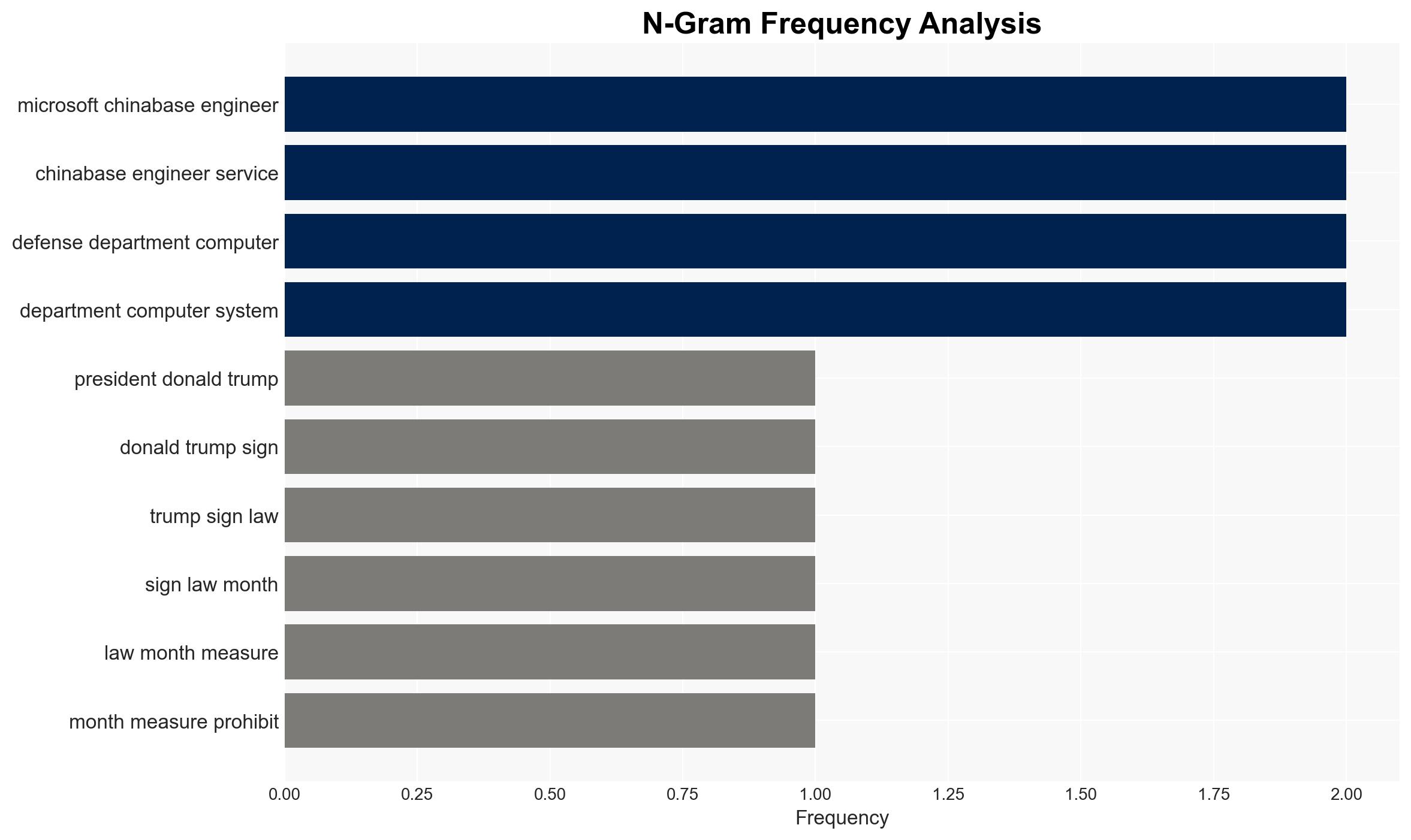
Intelligence Report: Trump Signs Defense Bill Prohibiting China-Based Engineers in Pentagon IT Work
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The recent defense bill signed by President Trump prohibits individuals based in China and other adversarial countries from accessing the Pentagon’s cloud systems, aiming to mitigate cybersecurity risks. This measure is a response to vulnerabilities exposed by foreign engineers’ involvement in sensitive U.S. defense IT systems. The most likely hypothesis is that this legislation will enhance national security by reducing potential cyber threats from adversarial nations. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate due to potential implementation challenges and unknowns about adversarial responses.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The prohibition of China-based engineers will significantly enhance the cybersecurity posture of the Pentagon’s IT systems by eliminating a direct vector for potential cyber-espionage. Supporting evidence includes the legislative action and prior vulnerabilities identified by ProPublica. However, uncertainties remain regarding the full extent of existing vulnerabilities and the effectiveness of U.S.-based oversight.
- Hypothesis B: The prohibition may have limited impact on cybersecurity due to potential alternative espionage methods and the possibility of insufficient domestic expertise to replace foreign engineers. This is supported by historical challenges in cybersecurity and the complexity of IT systems. Contradicting evidence includes the legislative intent and public statements from officials emphasizing security improvements.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct legislative action addressing identified vulnerabilities. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include reports of continued cybersecurity breaches or successful adaptation by adversaries to circumvent the new restrictions.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The legislation will be effectively implemented; U.S.-based personnel can adequately replace foreign engineers; adversarial nations lack immediate alternative access methods.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the implementation timeline and effectiveness of new oversight mechanisms; adversarial nations’ response strategies.
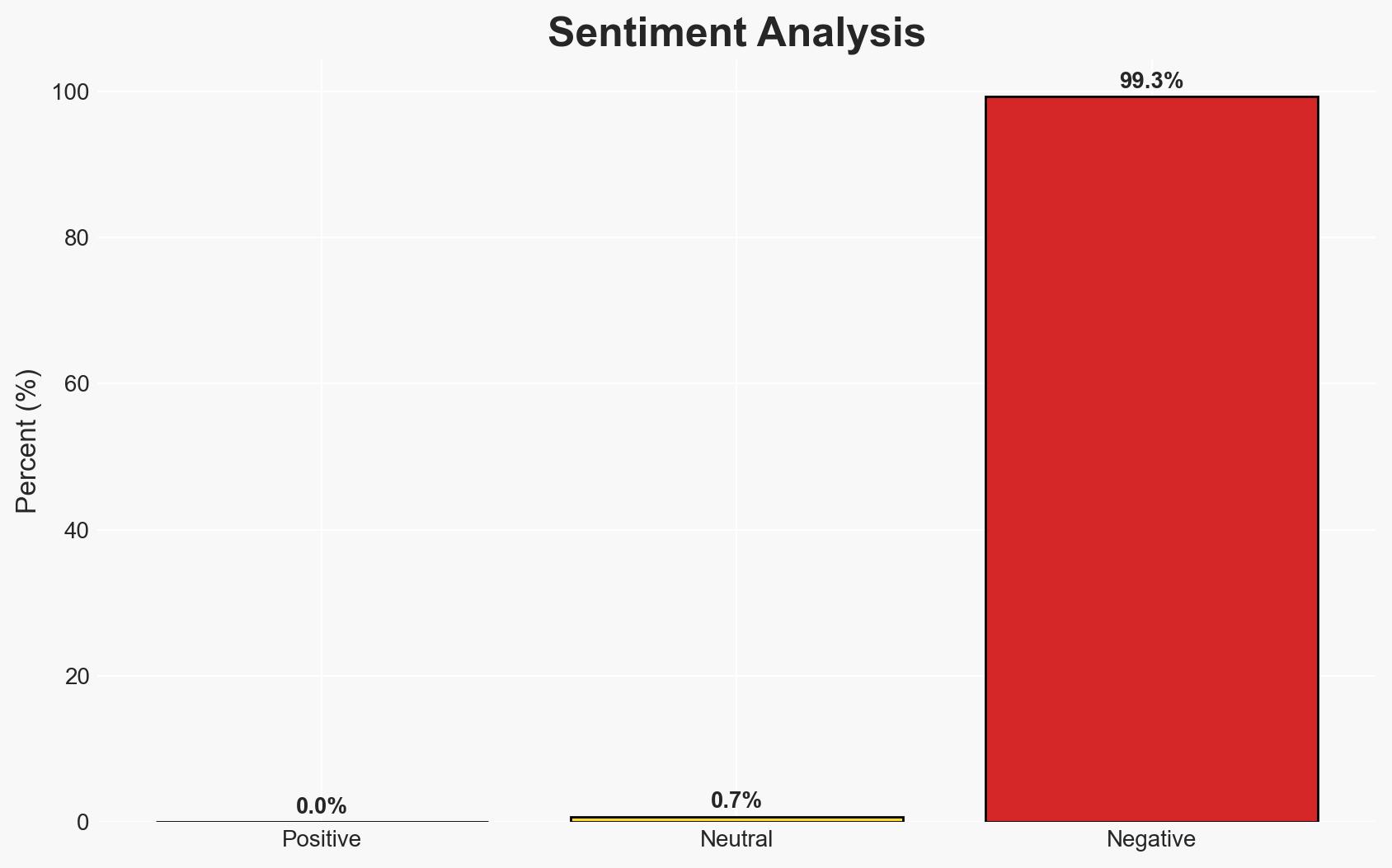
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting due to political motivations; risk of underestimating adversarial capabilities or overestimating domestic cybersecurity improvements.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a more secure Pentagon IT environment, but may also provoke adversarial nations to seek alternative espionage methods. The broader dynamics include potential shifts in international cyber strategies and defense collaborations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in cyber tensions with China and other adversarial nations; impact on U.S.-China relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced security posture may deter some cyber threats but could lead to increased sophistication in adversarial tactics.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber defense measures and innovation in response to new security requirements.
- Economic / Social: Possible impact on the tech industry’s workforce dynamics and international collaborations; potential economic repercussions from strained U.S.-China relations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor implementation of the legislation; assess potential adversarial responses; strengthen domestic cybersecurity training and recruitment.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with allied nations for cybersecurity collaboration; invest in advanced cyber defense technologies; evaluate the effectiveness of the new measures.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Significant reduction in cyber threats with effective implementation and international cooperation.
- Worst: Continued vulnerabilities due to insufficient domestic expertise and adaptive adversarial tactics.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in cybersecurity posture with ongoing challenges in implementation and adaptation by adversaries.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- President Donald Trump
- Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth
- Rep. Elise Stefanik
- Sen. Tom Cotton
- Microsoft Corporation
- ProPublica (investigative reporting entity)
7. Thematic Tags
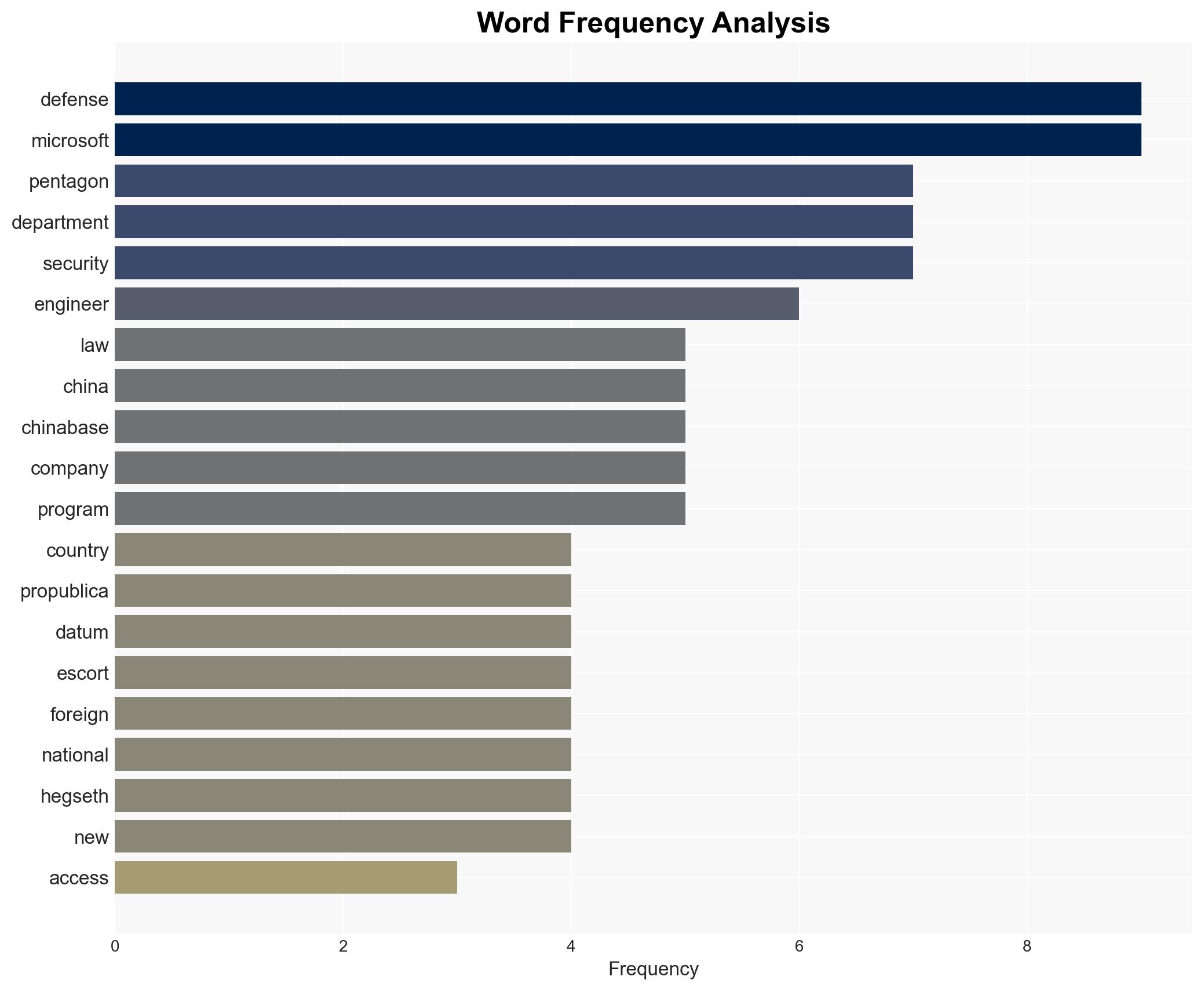
cybersecurity, national security, defense policy, U.S.-China relations, cloud computing, legislative action, espionage
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model hostile behavior to identify vulnerabilities.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us