Saudi Arabia and UAE Clash in Yemen: A Decade of Alliances Unravels Amidst Escalating Tensions
Published on: 2026-01-02
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Two of the Middle East’s most powerful countries are facing off in Yemen Here’s what to know CNN
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
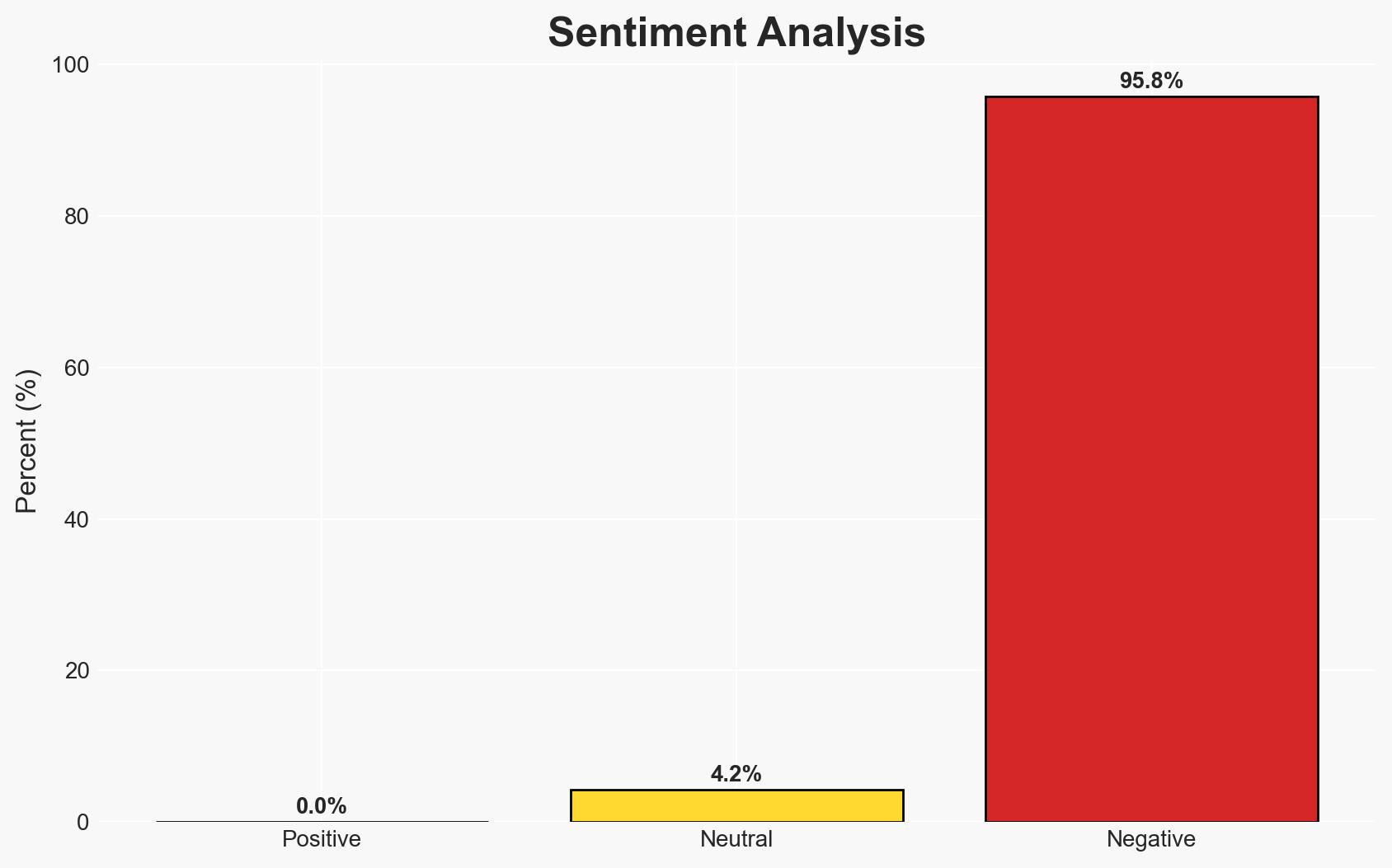
The current conflict in Yemen has escalated into a proxy confrontation between Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), two former allies, due to diverging interests and support for rival factions. This development could destabilize the region further and complicate efforts to resolve the Yemeni civil war. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The rift between Saudi Arabia and the UAE is primarily due to strategic divergences over Yemen, with each nation backing different factions to secure their own regional influence. Evidence includes the recent military actions and public accusations. However, the extent of these divergences and their impact on broader regional alliances remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The conflict between Saudi Arabia and the UAE is a temporary tactical disagreement rather than a strategic realignment, driven by immediate operational needs in Yemen. This hypothesis is less supported due to the public nature of the dispute and the strategic implications of the military actions.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the public escalation and strategic nature of the actions taken by both countries. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in diplomatic rhetoric or military cooperation between the two nations.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Saudi Arabia and the UAE are primarily motivated by regional influence; the Houthis will continue to act as an Iranian proxy; the Yemeni conflict remains a focal point for regional power dynamics.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the internal decision-making processes of Saudi and UAE leadership; the full extent of Iranian support to the Houthis.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential source bias from media outlets with vested interests; possibility of strategic misinformation from involved parties to manipulate perceptions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to further fragmentation of Yemen, complicating peace efforts and potentially drawing in more regional actors. The rivalry may also affect broader Middle Eastern alliances and U.S. interests in the region.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential realignment of regional alliances and increased Iranian influence in Yemen.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of terrorist exploitation of the conflict and regional instability.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations and propaganda campaigns by involved states.
- Economic / Social: Further economic destabilization in Yemen, exacerbating humanitarian crises and refugee flows.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence collection on Saudi-UAE interactions; increase diplomatic engagement to de-escalate tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for regional allies; foster dialogue among Yemeni factions to reduce external influence.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diplomatic resolution between Saudi Arabia and UAE, leading to a unified approach in Yemen.
- Worst: Escalation into a broader regional conflict involving direct military engagements.
- Most-Likely: Continued proxy conflict with intermittent diplomatic efforts, maintaining regional instability.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
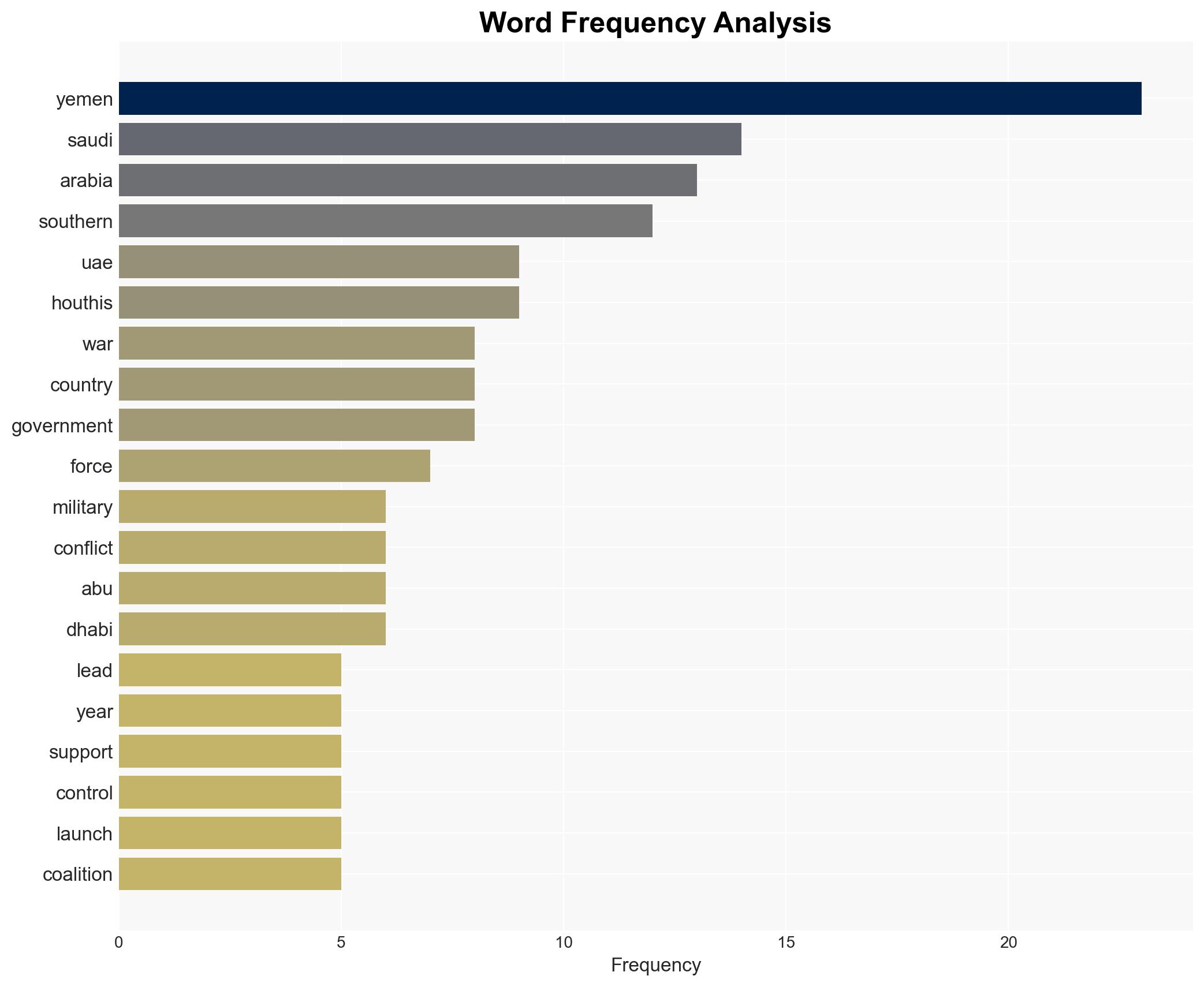
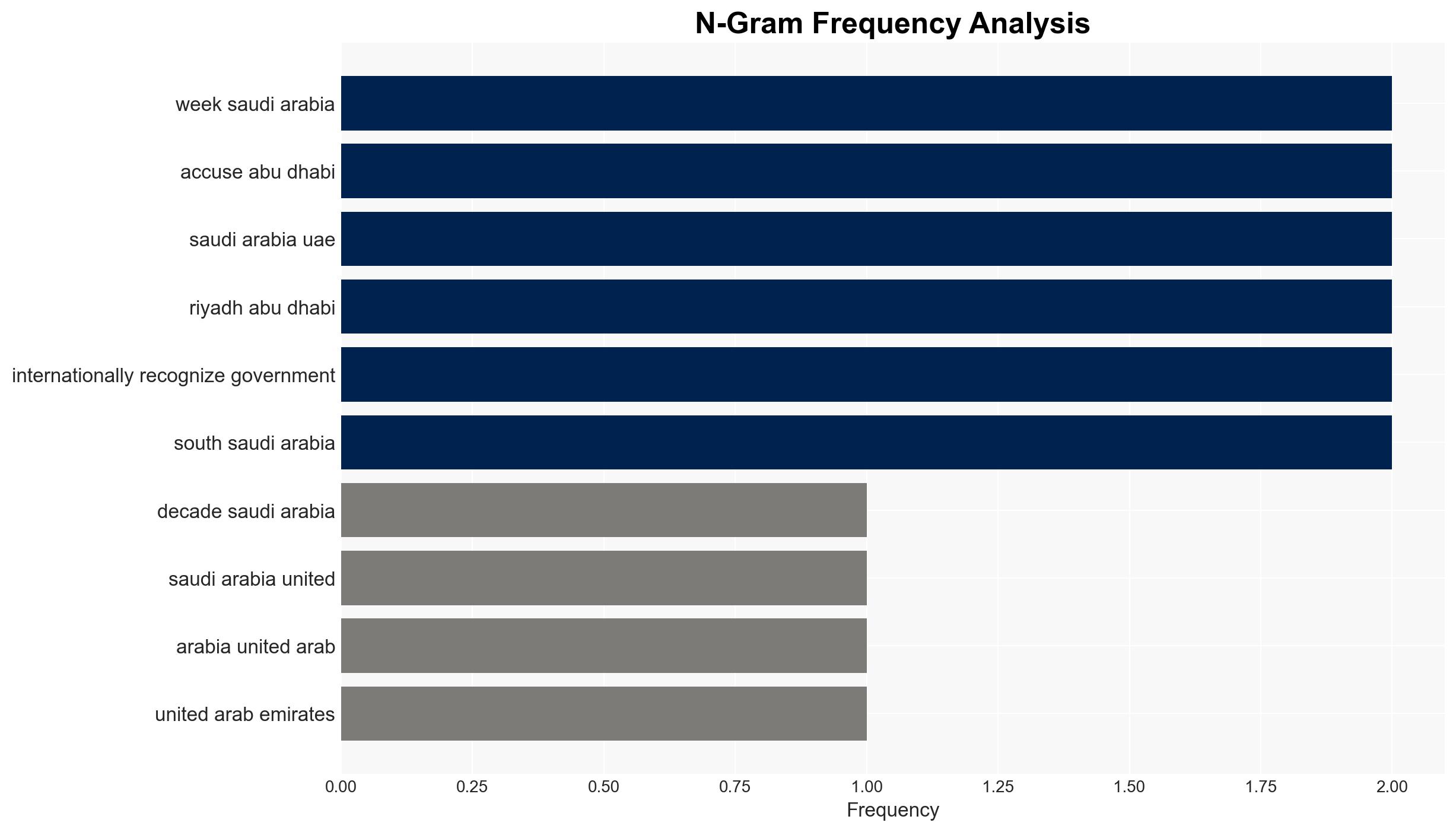
regional conflicts, regional conflict, proxy war, Middle East alliances, Yemen civil war, Saudi-UAE relations, Iranian influence, geopolitical instability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us