U.S. Invasion of Venezuela Signals Shift Toward Aggressive Hegemony Under Trump Administration
Published on: 2026-01-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Trump Has Started Carving Up the World Now Its Putin and Xis Turn
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
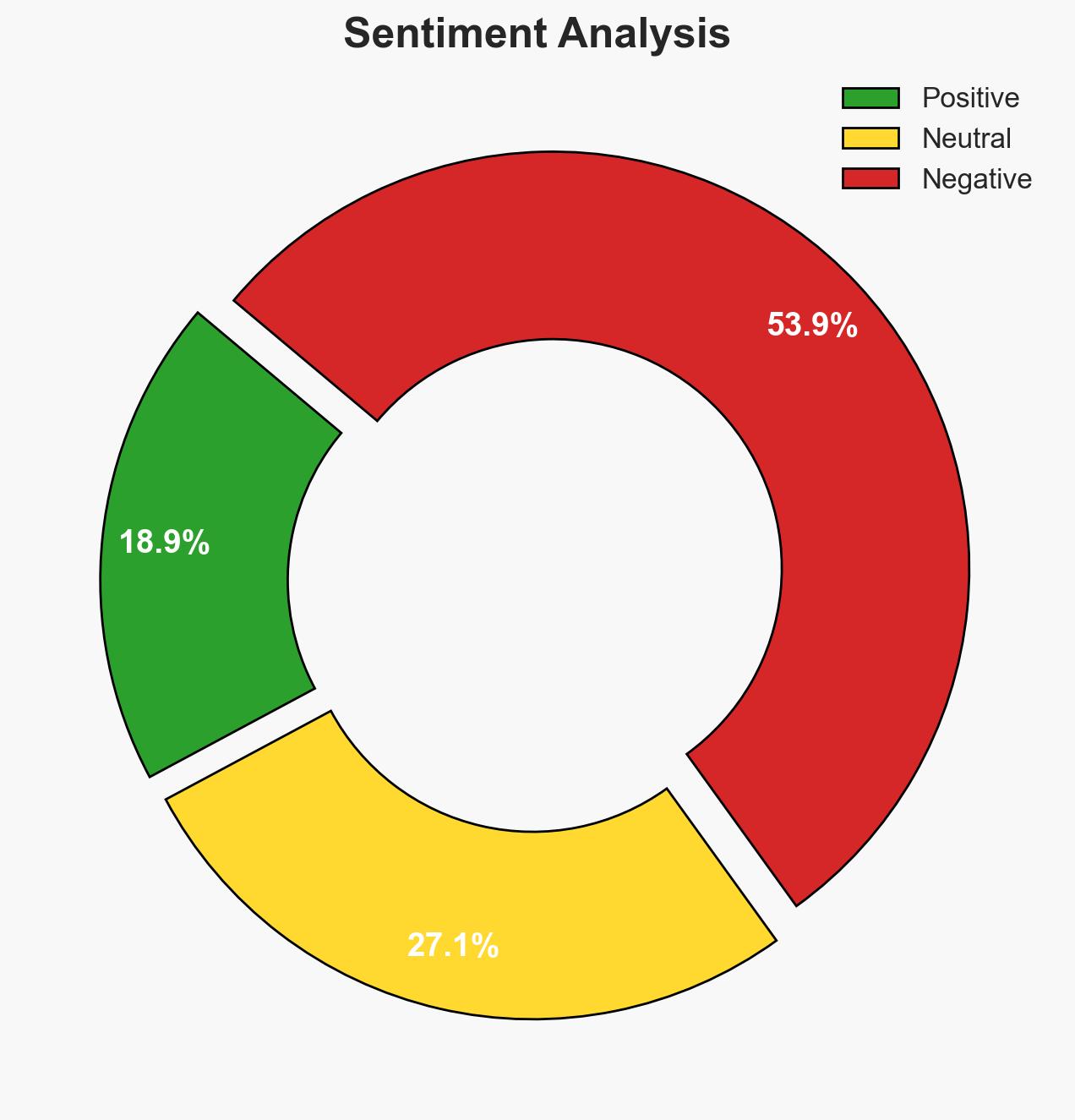
The U.S. invasion of Venezuela represents a significant shift in American foreign policy, characterized by unilateral military action without congressional approval, aimed at exploiting Venezuelan oil resources. This development could destabilize the region and alter global geopolitical dynamics, with moderate confidence in the assessment that the U.S. lacks a coherent long-term strategy.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. invasion of Venezuela is primarily motivated by economic interests, specifically the control and exploitation of oil resources. Supporting evidence includes Trump’s declaration to “take control” of Venezuelan oil. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of a clear long-term strategy and potential geopolitical backlash.
- Hypothesis B: The invasion is a strategic move to counter perceived threats from other global powers and assert U.S. dominance in the Western Hemisphere. Supporting evidence includes historical U.S. interventions in the region. Contradicting evidence includes the absence of immediate threats from Venezuela and the lack of international support.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to explicit statements regarding oil exploitation and the absence of a coherent strategic framework. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in U.S. military posture or diplomatic engagements with other global powers.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. aims to install a favorable regime in Venezuela; Venezuelan public sentiment is largely against foreign intervention; U.S. actions will face minimal immediate military resistance.
- Information Gaps: Details on the U.S. military’s operational plans in Venezuela; Venezuelan internal political dynamics and potential resistance; international reactions, particularly from Russia and China.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in interpreting U.S. motivations as purely economic; risk of underestimating Venezuelan and international responses; possible misinformation from involved parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased regional instability and strain U.S. relations with other global powers. The absence of a clear strategy raises the risk of prolonged conflict and unintended consequences.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for regional alliances against U.S. actions; escalation of tensions with Russia and China.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of insurgency and asymmetric warfare in Venezuela; potential for retaliatory actions against U.S. interests.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely increase in cyber operations targeting U.S. and Venezuelan infrastructure; information warfare to shape narratives.
- Economic / Social: Disruption of Venezuelan oil markets; potential humanitarian crisis and refugee flows; internal U.S. political backlash.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence gathering on Venezuelan military and political responses; engage with regional allies to assess diplomatic options; monitor cyber threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop contingency plans for potential insurgency; strengthen regional partnerships to mitigate instability; enhance cyber defenses.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Quick stabilization and installation of a cooperative regime.
- Worst Case: Prolonged conflict with regional and global escalation.
- Most-Likely: Ongoing instability with limited U.S. control and international condemnation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Donald Trump (U.S. President)
- Nicolás Maduro (Venezuelan Leader)
- Delcy Rodríguez (Venezuelan Vice President)
- U.S. Oil Companies (Unnamed)
7. Thematic Tags
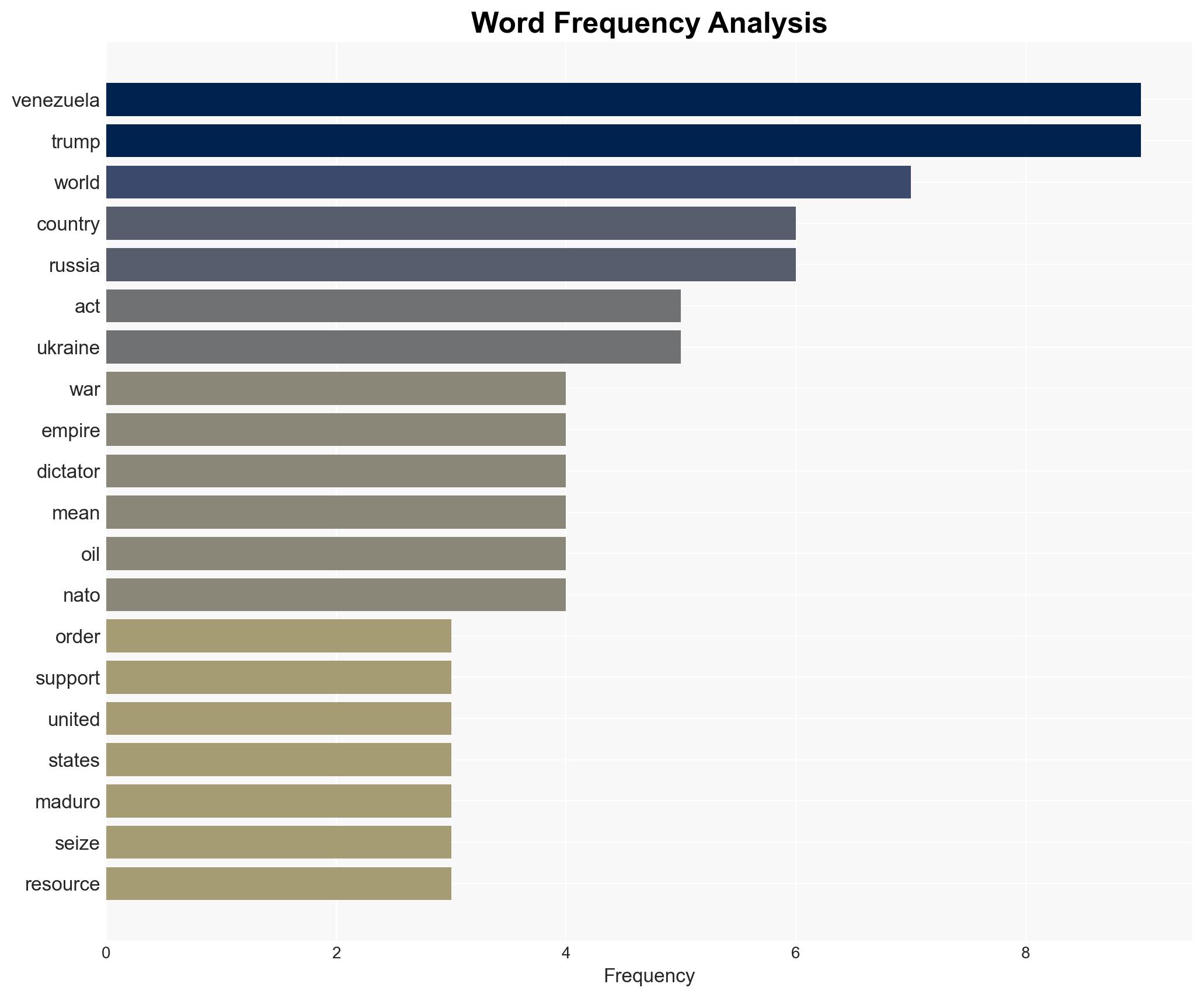
regional conflicts, geopolitics, military intervention, oil resources, U.S. foreign policy, regional stability, international relations, economic exploitation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us