Lockheed Martin to Increase Patriot Missile Production Capacity to 2,000 Annually Amid Rising Global Demand
Published on: 2026-01-06
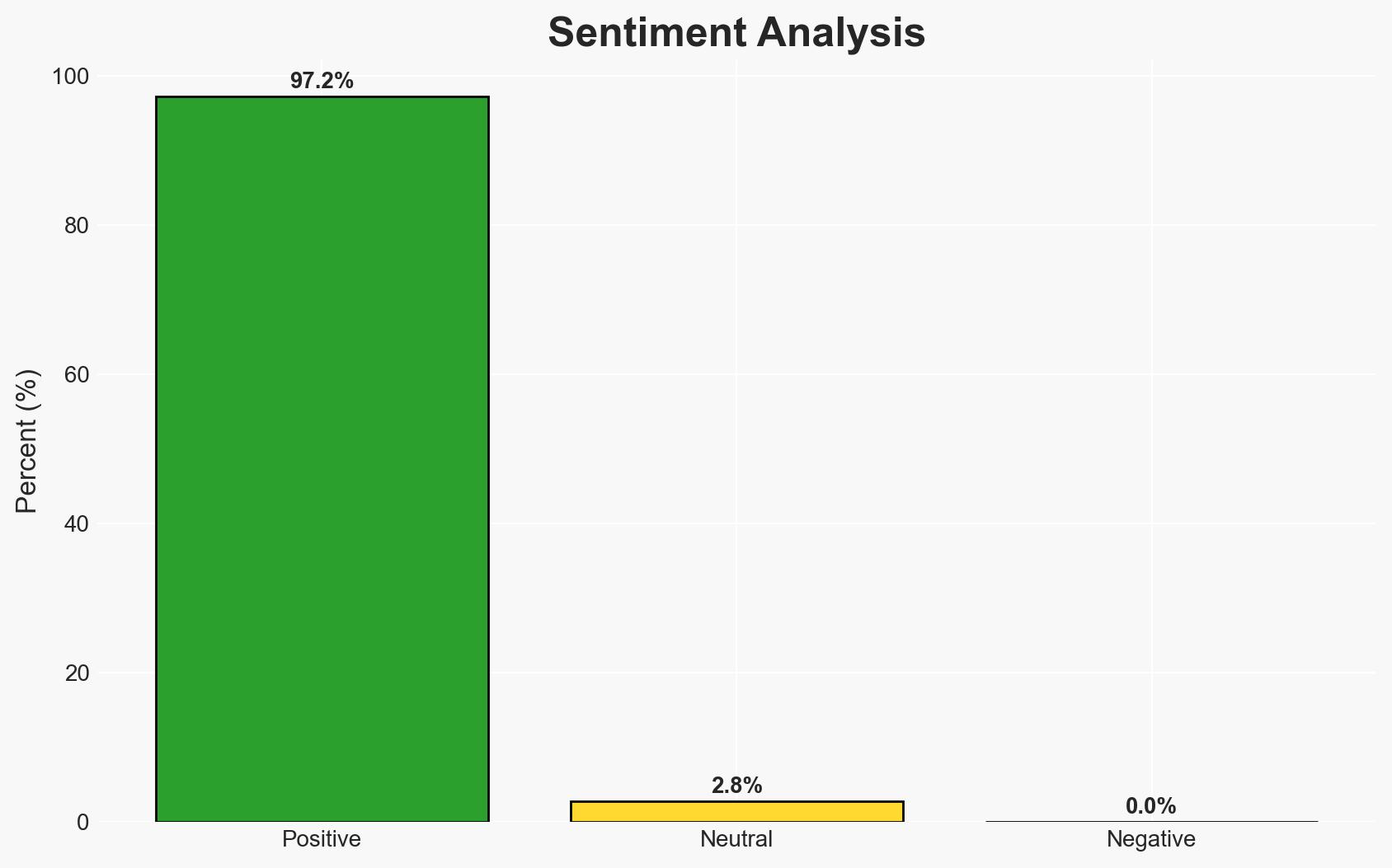
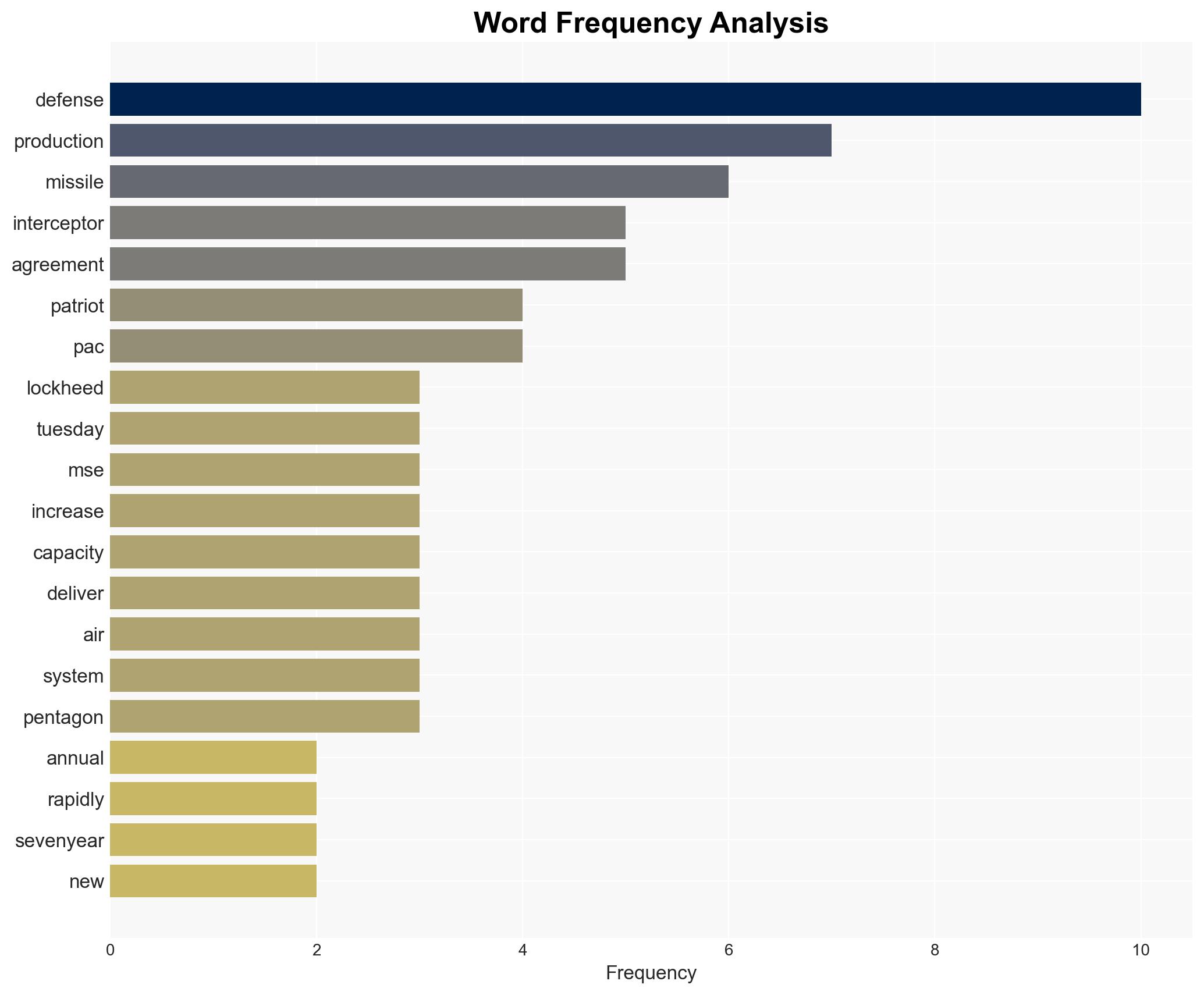
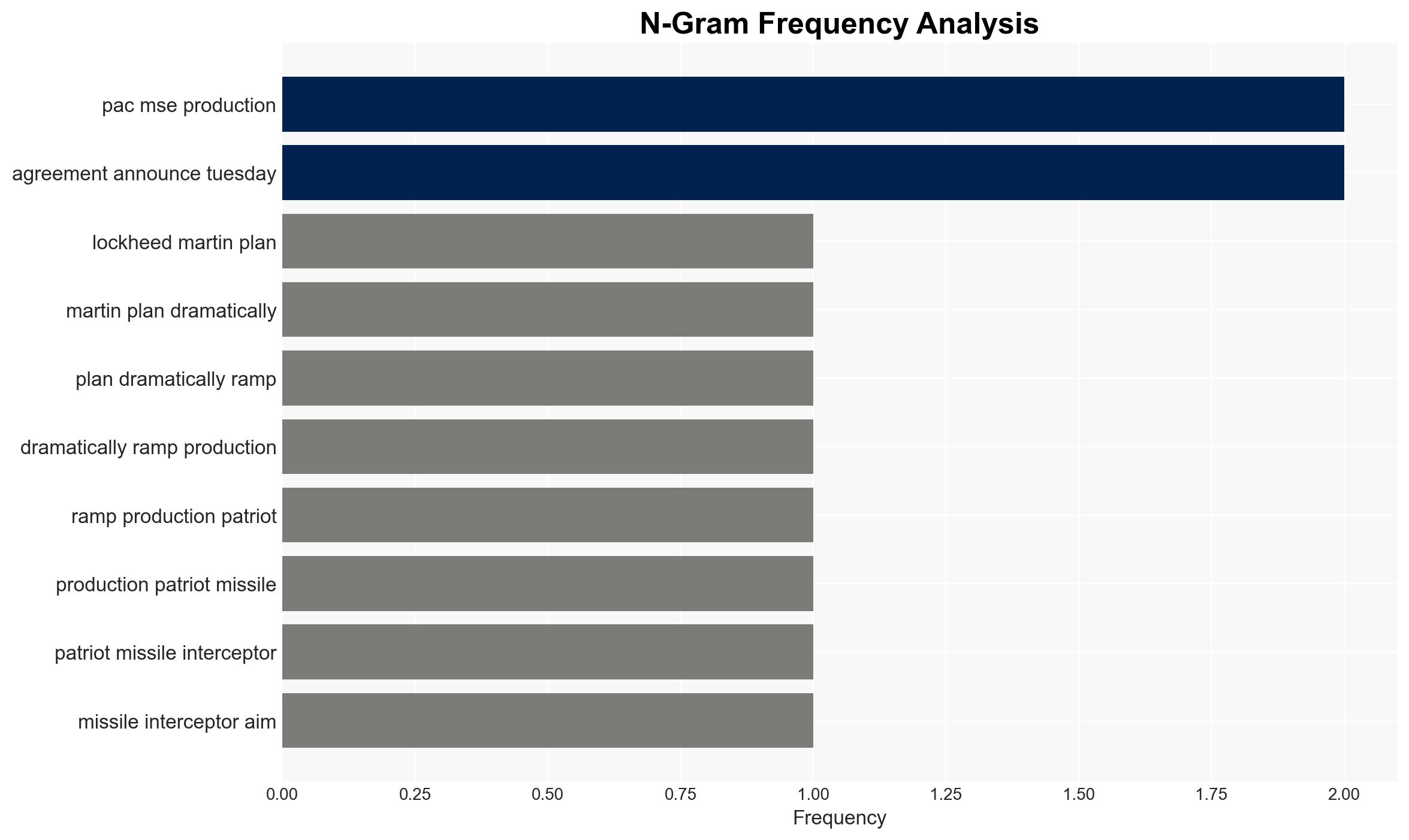
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Lockheed says it plans to dramatically turn up Patriot missile production
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Lockheed Martin’s plan to significantly increase the production of Patriot missile interceptors is likely to enhance the air defense capabilities of the US and its allies, addressing rising global demand due to ongoing conflicts. This development is supported by a new agreement with the US Department of Defense. Overall, there is moderate confidence in the assessment that this production increase will be realized as planned, contingent on Congressional approval.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Lockheed Martin will successfully increase production to 2,000 interceptors annually, enhancing US and allied defense capabilities. This is supported by the agreement with the Department of Defense and the existing increase in production capacity. Key uncertainties include potential supply chain disruptions and Congressional approval.
- Hypothesis B: Lockheed Martin may face challenges in achieving the planned production increase due to unforeseen logistical, financial, or political obstacles. While the agreement sets a framework, it is contingent on Congressional approval and assumes stable supply chains.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the formal agreement with the Department of Defense and past increases in production capacity. Indicators that could shift this judgment include delays in Congressional approval or significant supply chain issues.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The US Congress will approve the framework agreement; supply chains will remain stable; global demand for air defense systems will continue to rise.
- Information Gaps: Details on potential supply chain vulnerabilities and the specific terms of the Congressional approval process are missing.
- Bias & Deception Risks: There is a risk of over-reliance on optimistic projections from Lockheed Martin and the Department of Defense, which may have vested interests in portraying the agreement positively.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could significantly impact global defense postures, particularly in regions experiencing heightened missile threats. The increased production capacity may alter strategic balances and provoke responses from adversaries.
- Political / Geopolitical: The US and its allies may gain a strategic advantage, potentially escalating tensions with adversaries like Russia and Iran.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced interceptor availability could improve defense against missile threats, potentially reducing the effectiveness of adversary missile strategies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased production may attract cyber threats targeting supply chains or production facilities.
- Economic / Social: The initiative could boost the US defense industrial base, but may also strain resources if not managed effectively.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor Congressional proceedings related to the agreement and assess supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen partnerships with allied nations to ensure coordinated deployment of interceptors; invest in supply chain resilience.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Production increase proceeds smoothly, enhancing defense capabilities without geopolitical escalation.
- Worst: Congressional disapproval or supply chain disruptions delay production, weakening defense postures.
- Most-Likely: Incremental production increases occur, with some delays, but ultimately bolster defense capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Lockheed Martin
- US Department of Defense
- Jim Taiclet, Chairman and CEO of Lockheed Martin
- Pete Hegseth, Secretary of Defense
- Michael Duffey, Undersecretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, defense production, missile interceptors, US Department of Defense, Lockheed Martin, air defense systems, geopolitical tensions, supply chain resilience
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us