China-Linked Cyberattacks on Taiwan’s Critical Infrastructure Surge, NSB Reports Significant Increase in Inci…
Published on: 2026-01-08
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: China-linked groups intensify attacks on Taiwans critical infrastructure NSB warns
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
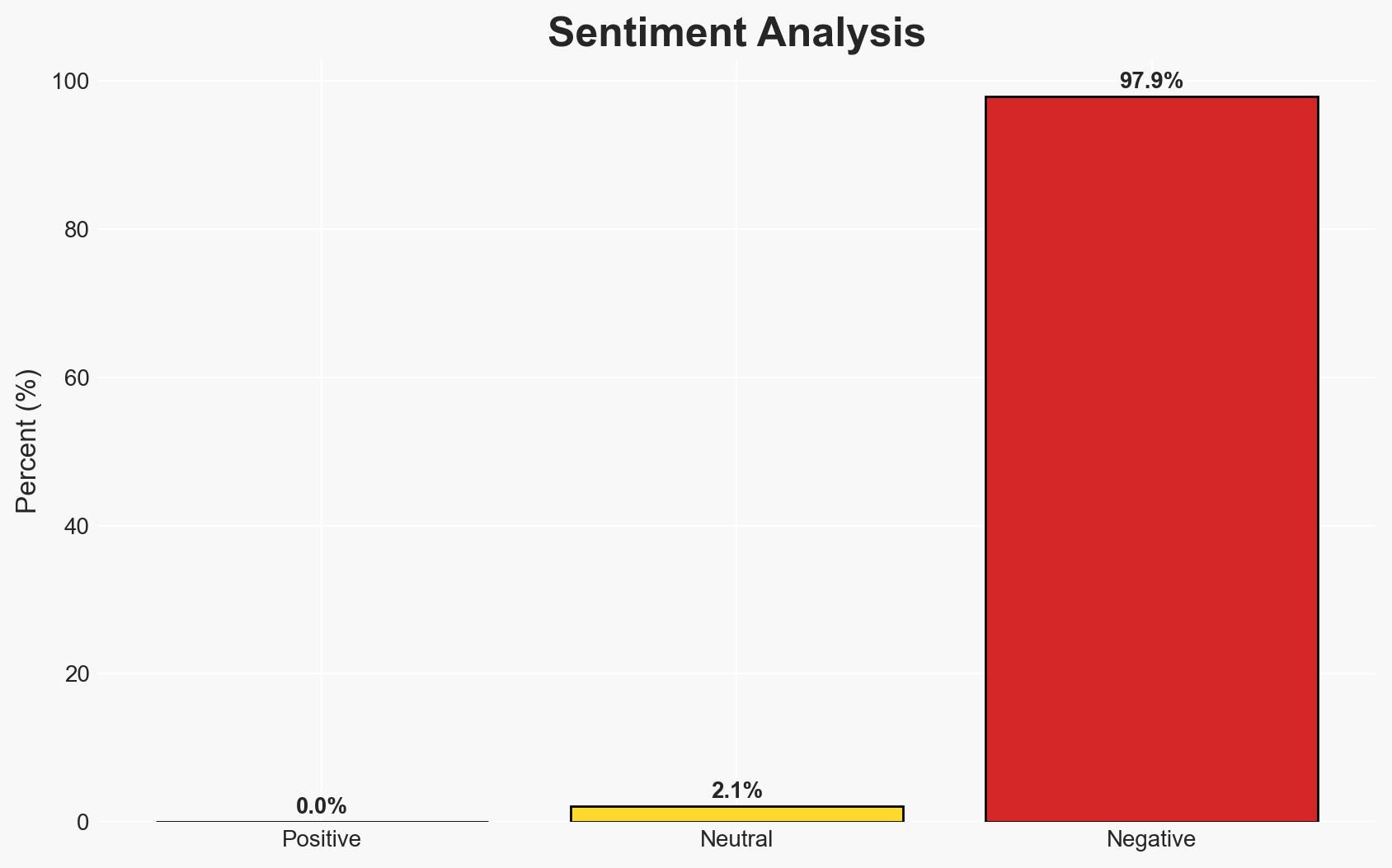
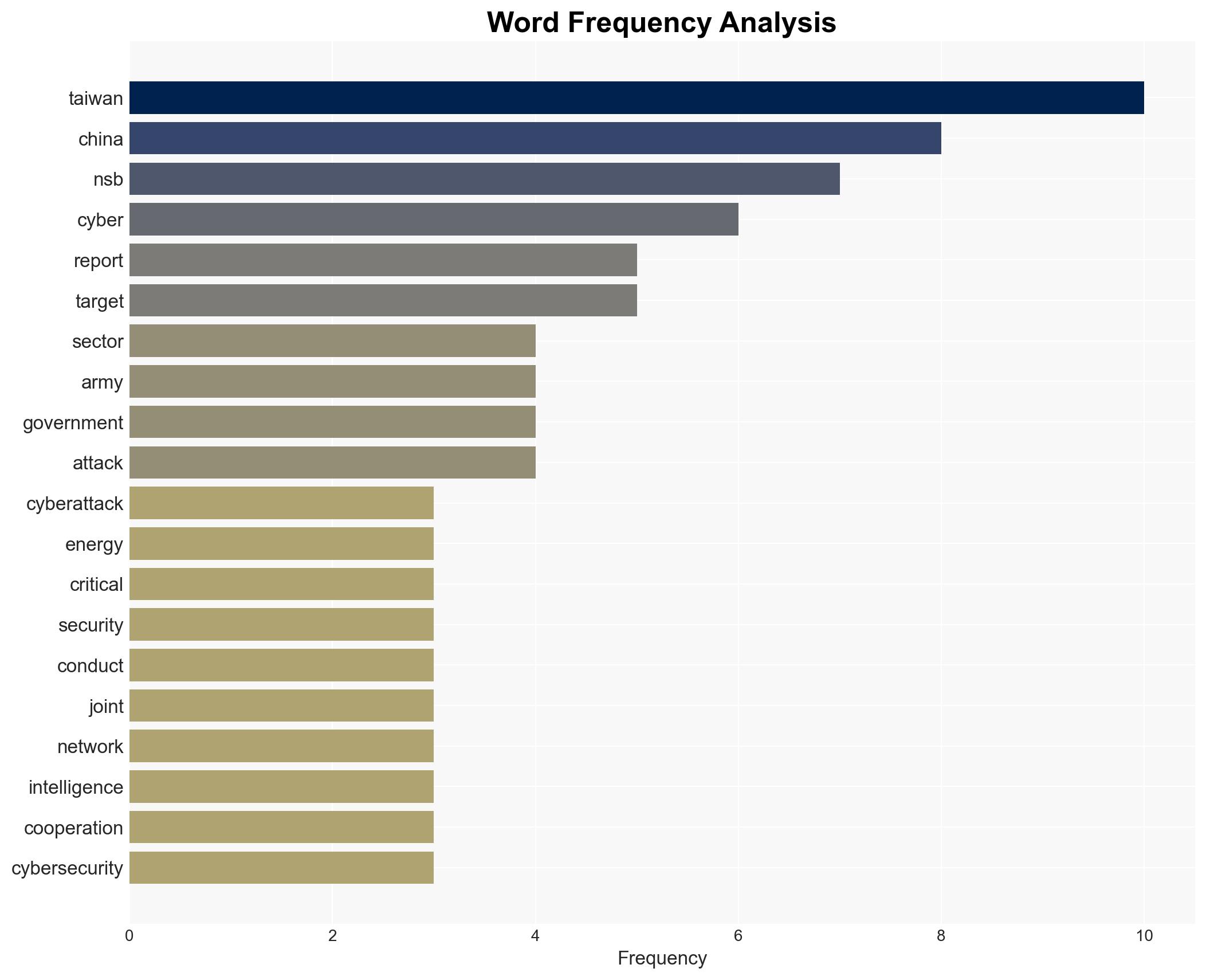
China-linked cyber groups have significantly increased their attacks on Taiwan’s critical infrastructure, particularly targeting the energy and healthcare sectors. These attacks coincide with political and military activities, suggesting a coordinated strategy. The most likely hypothesis is that these cyber operations are part of a broader coercive campaign by China. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to existing information gaps and potential biases.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The cyberattacks are part of a coordinated campaign by China to exert political and military pressure on Taiwan. This is supported by the timing of attacks with political events and military activities, and the targeting of critical infrastructure. However, uncertainties remain regarding the full extent of coordination and specific strategic objectives.
- Hypothesis B: The cyberattacks are primarily opportunistic actions by independent or semi-autonomous Chinese cyber groups, not directly coordinated by the state. While the involvement of known groups like APT41 and Mustang Panda suggests state-level capabilities, the lack of direct evidence linking these actions to specific state directives weakens this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the correlation between cyberattacks and China’s political and military maneuvers. Indicators such as increased attack frequency during significant Taiwanese events could further validate this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Taiwan’s critical infrastructure remains vulnerable to cyberattacks; China’s cyber capabilities are state-supported; political tensions between China and Taiwan will persist.
- Information Gaps: Specific motives behind each cyberattack, the degree of state control over cyber groups, and the full scope of compromised systems.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Taiwanese reporting due to national security interests; possibility of Chinese misinformation to obscure true attack origins.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The intensification of cyberattacks on Taiwan could escalate geopolitical tensions and provoke stronger international responses. This development could also lead to increased cyber defense collaboration among Taiwan and its allies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased diplomatic tensions and retaliatory measures by Taiwan or its allies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment requiring enhanced cybersecurity measures and intelligence sharing.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber defense initiatives and potential for retaliatory cyber operations by Taiwan.
- Economic / Social: Possible disruptions to critical services and economic activities, impacting public confidence and social stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cyber threats, increase public awareness campaigns, and strengthen cybersecurity protocols across critical sectors.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop international partnerships for cyber defense, invest in cybersecurity infrastructure, and conduct joint cyber exercises with allies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: De-escalation of cyber activities with increased international cooperation.
- Worst: Escalation to physical conflict due to cyber-induced disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued cyber skirmishes with gradual strengthening of Taiwan’s cyber defenses.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, Taiwan-China relations, critical infrastructure, cyber-espionage, geopolitical tensions, cyber defense, international cooperation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us