BRICS Coalition to Conduct ‘Will for Peace 2026’ Military Exercises Amid Rising Tensions with the U.S.
Published on: 2026-01-09
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Anti-American BRICS Group Announces War Games for ‘Peace’ in 2026
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
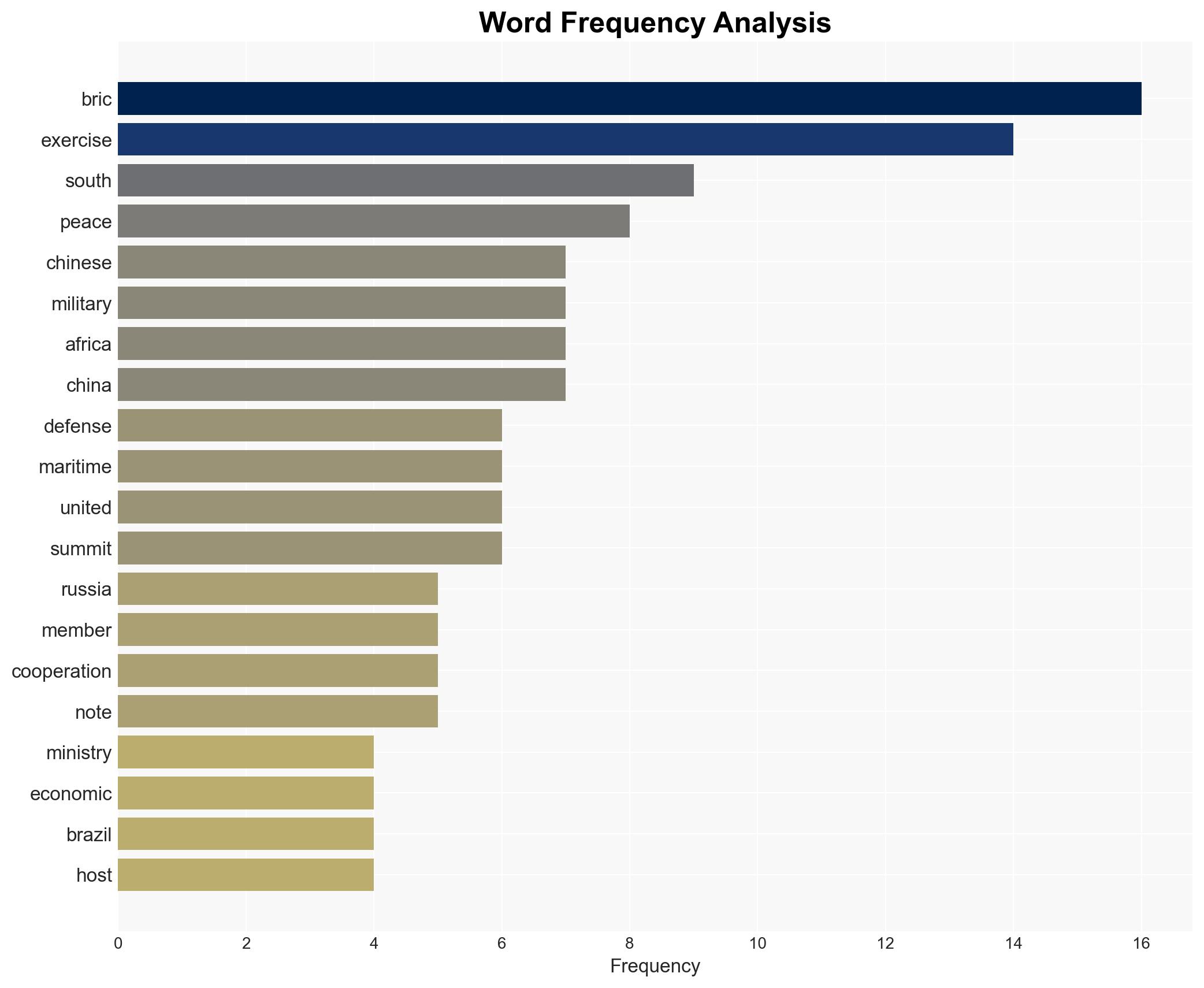
The announcement of the “Will for Peace 2026” military exercises by China, Russia, and South Africa under the BRICS framework represents a strategic shift towards military cooperation within the bloc. This development may signal an attempt to counter U.S. influence and assert geopolitical presence, particularly in maritime security. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the limited participation of BRICS members and potential for strategic signaling.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The exercises are primarily a strategic move by China and Russia to challenge U.S. influence and demonstrate military capabilities. Supporting evidence includes the timing following U.S. actions against BRICS members and the focus on maritime security. Contradicting evidence is the limited participation of other BRICS nations, which could indicate a less unified front.
- Hypothesis B: The exercises are genuinely aimed at enhancing maritime security and cooperation among participating nations, with no direct intent to counter U.S. influence. Supporting evidence includes the stated objectives of counter-terrorism and rescue operations. However, the geopolitical context and exclusion of most BRICS members suggest a potential strategic undercurrent.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the geopolitical context and historical patterns of China and Russia using military exercises as strategic signaling. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include increased participation from other BRICS members or explicit diplomatic statements aligning with U.S. interests.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The exercises are intended to enhance military cooperation; China and Russia are leveraging BRICS for strategic purposes; U.S. actions have influenced BRICS dynamics.
- Information Gaps: Details on the involvement of “BRICS Plus” countries; specific objectives and outcomes expected from the exercises.
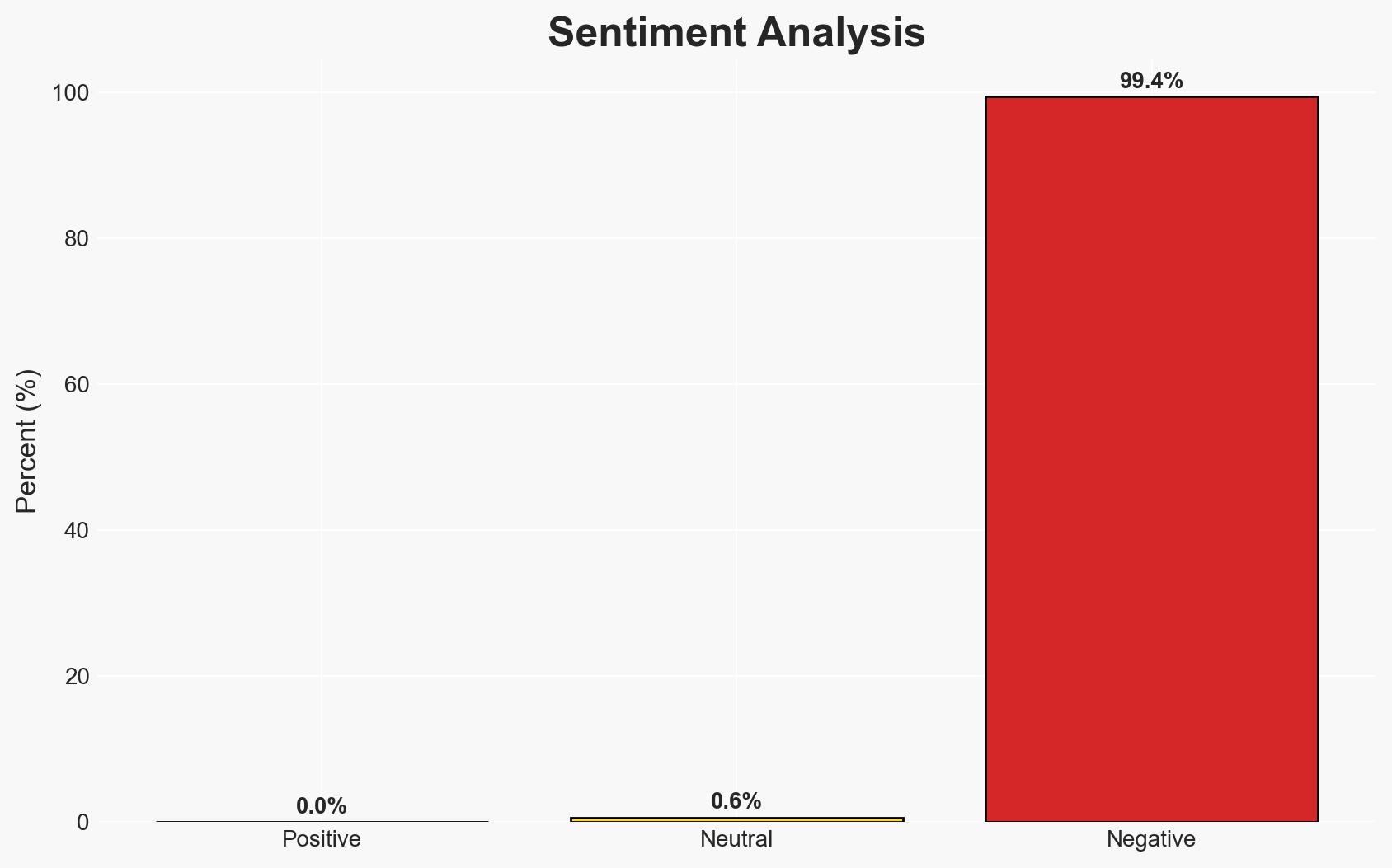
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Chinese state media reporting; strategic deception by China and Russia in framing the exercises as purely cooperative.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased geopolitical tensions, particularly in maritime regions of strategic interest. The exercises may embolden BRICS nations to pursue more assertive policies, potentially leading to regional instability.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in U.S.-BRICS tensions; increased alignment among BRICS members against Western influence.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced military capabilities and cooperation among participating nations; potential shifts in regional security dynamics.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in cyber operations targeting maritime infrastructure; information warfare to shape narratives around the exercises.
- Economic / Social: Potential impact on global trade routes and economic stability if tensions escalate; domestic political implications for participating nations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence monitoring of the exercises; engage diplomatically with BRICS nations to clarify intentions; assess potential impacts on maritime trade routes.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen alliances with regional partners; enhance maritime security capabilities; develop contingency plans for potential geopolitical escalations.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Exercises conclude without incident, leading to improved maritime security cooperation.
- Worst: Exercises lead to increased geopolitical tensions and military confrontations.
- Most-Likely: Exercises serve as strategic signaling, with limited immediate impact but potential long-term shifts in regional alignments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
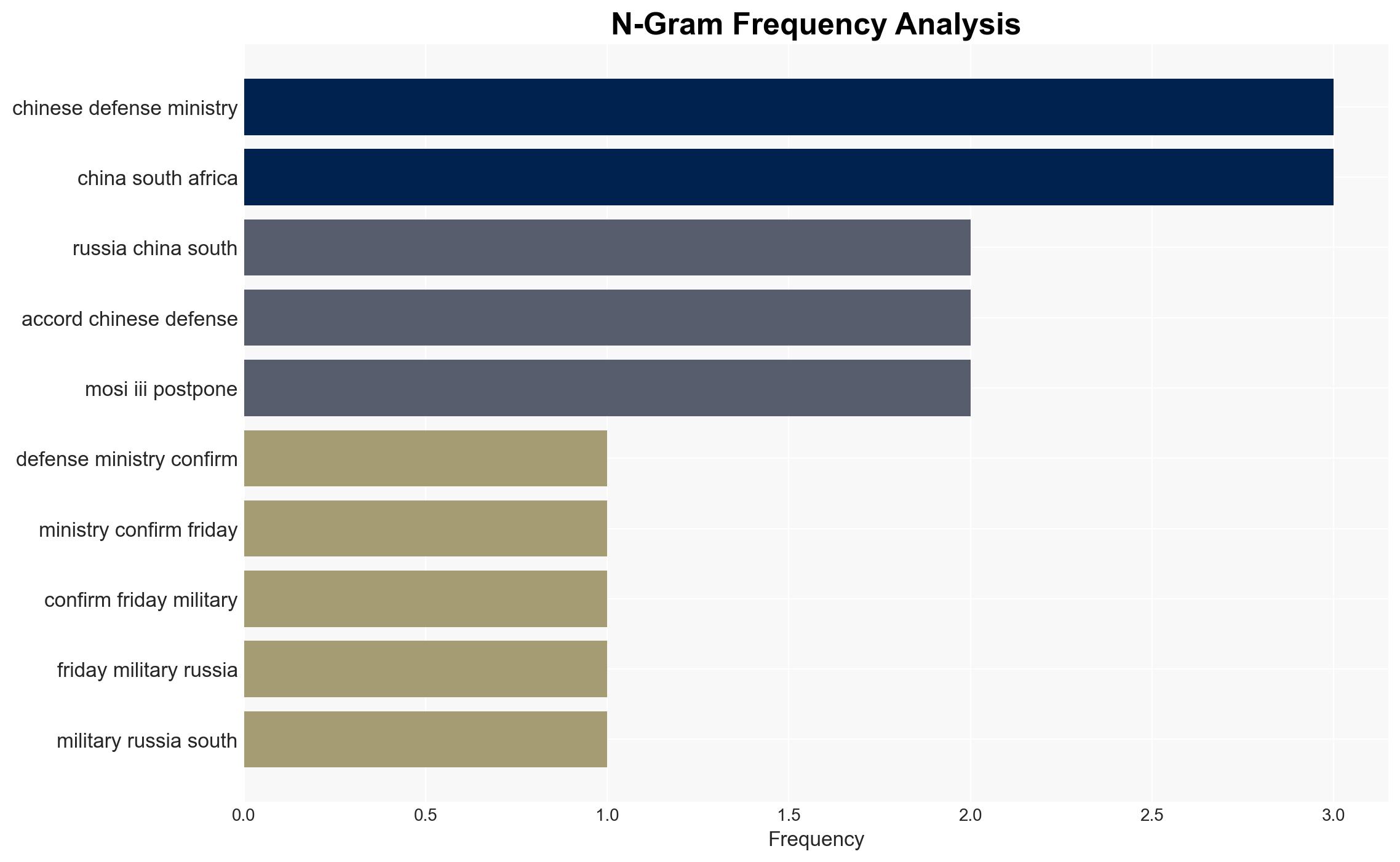
- Chinese Defense Ministry
- Global Times (Chinese state media)
- President Donald Trump
- President Cyril Ramaphosa
- BRICS nations (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa)
- BRICS Plus countries (Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, UAE, Indonesia)
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, BRICS, military exercises, maritime security, U.S.-China relations, geopolitical tensions, strategic signaling, international cooperation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us