Neglected digital assets could lead to security breaches; here’s how to mitigate the risks.
Published on: 2026-01-11
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Idle infrastructure might cause your next breach heres how to stop it
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
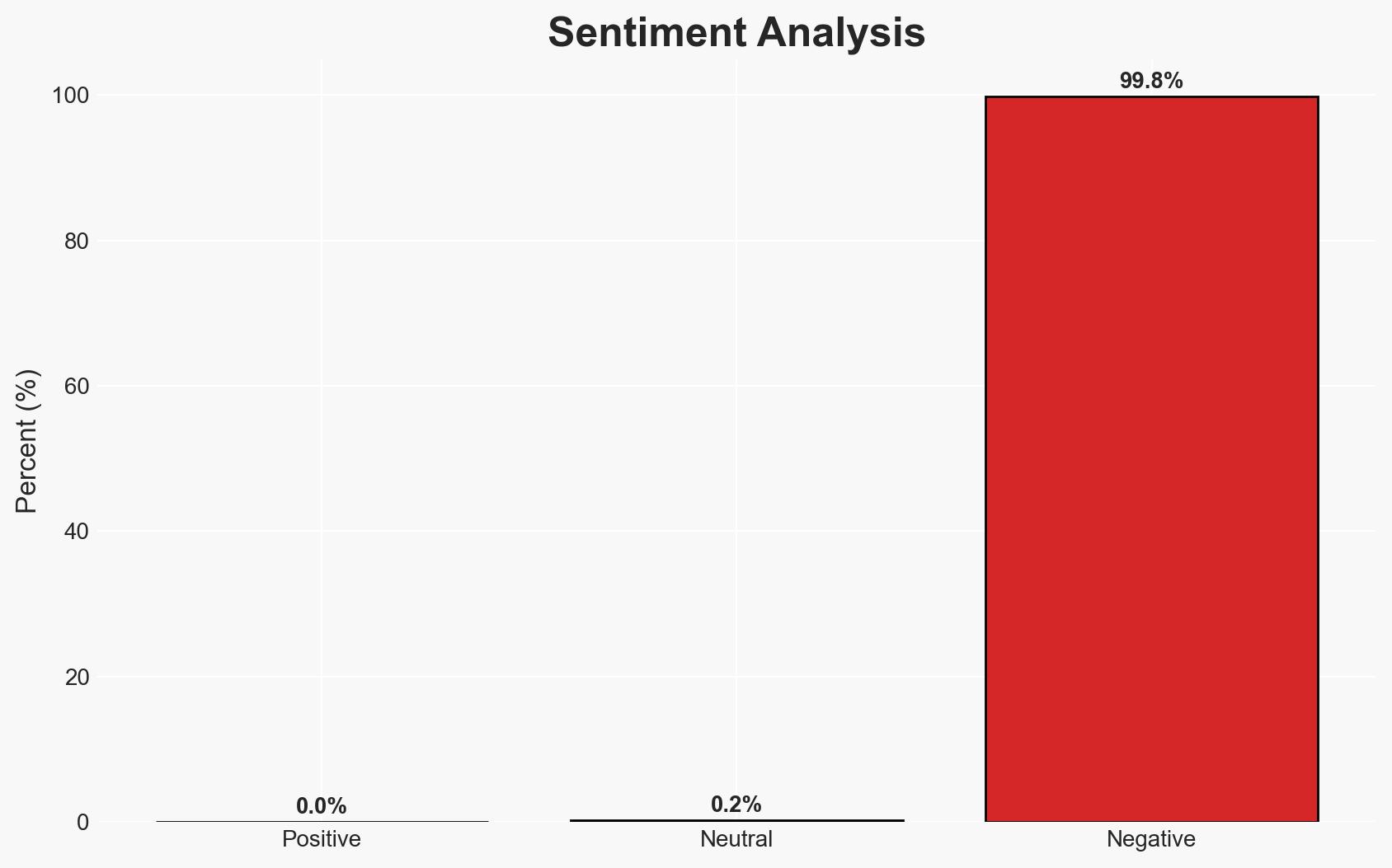
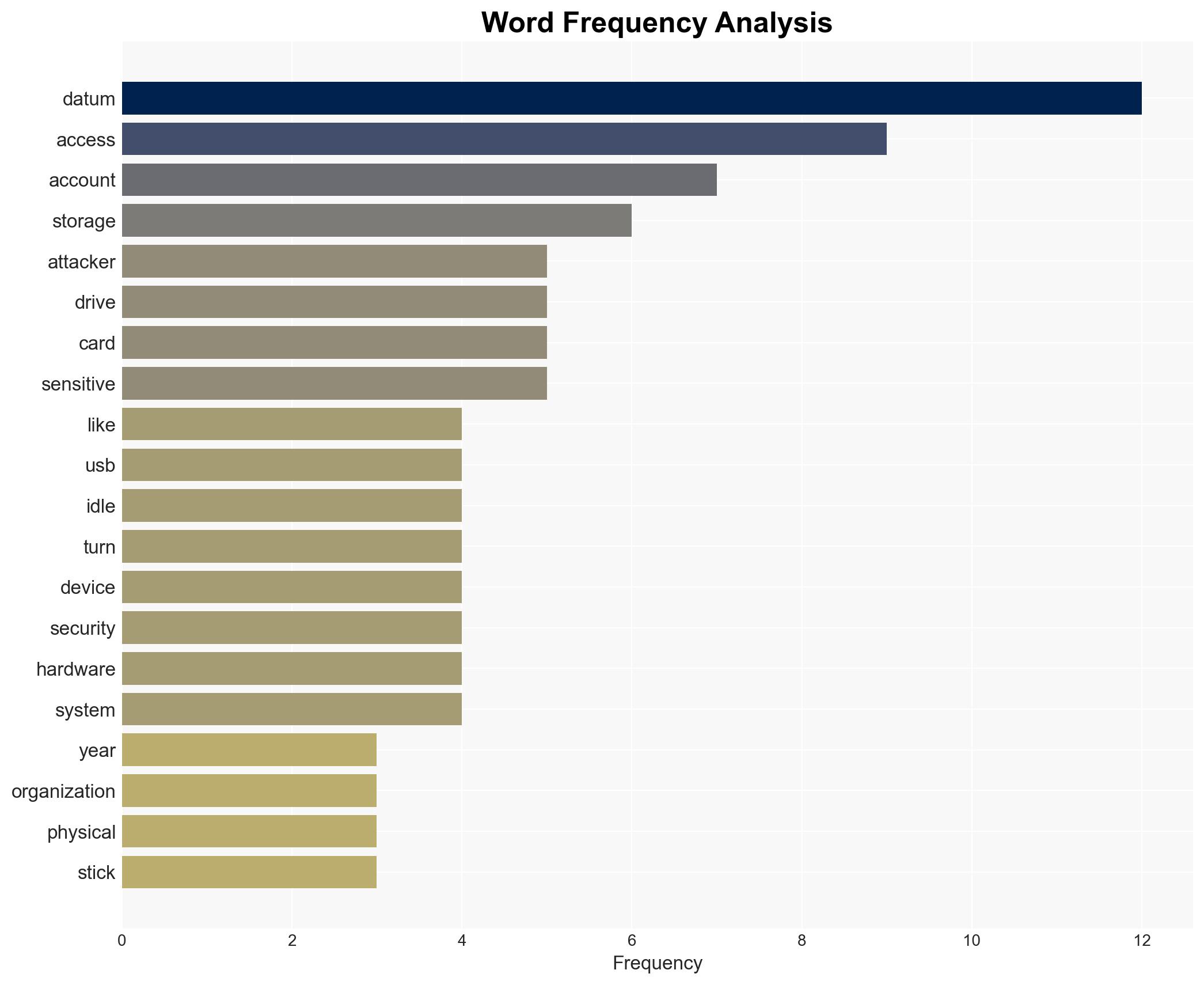
The exploitation of idle digital and physical infrastructure poses a significant cyber threat to organizations across various sectors. The most likely hypothesis is that attackers leverage inactive accounts and unsecured physical media to gain unauthorized access, facilitated by operational convenience over security. This affects sectors including retail, automotive, healthcare, and education. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the prevalence of such vulnerabilities and the regularity of reported incidents.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Cybercriminals are primarily exploiting idle digital and physical infrastructure due to poor security practices, such as non-expiring credentials and unsecured data storage. This is supported by the reported increase in cyber incidents and the commonality of such vulnerabilities. However, uncertainties include the specific methods used by attackers and the extent of organizational awareness of these risks.
- Hypothesis B: The rise in cyber incidents is driven more by sophisticated attack techniques such as AI-driven malware and zero-day exploits, rather than idle infrastructure. This is contradicted by the focus on inactive accounts and unsecured data storage as primary vulnerabilities, suggesting that while advanced techniques are a concern, they are not the primary vector in these cases.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct link between idle infrastructure and the ease of unauthorized access. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of widespread use of advanced attack techniques in these incidents or significant improvements in organizational security practices.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations have not fully addressed idle infrastructure vulnerabilities; attackers prefer low-effort entry points; operational convenience often outweighs security considerations.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the frequency and impact of breaches directly attributable to idle infrastructure; detailed case studies of exploited vulnerabilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting frequency of incidents; possible underreporting of advanced attack techniques; deception by attackers to mask true entry methods.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and demand for enhanced cybersecurity measures. Organizations may face reputational damage and financial losses from breaches, driving a shift towards more robust security postures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for international tensions if state-sponsored actors are involved or if breaches affect critical infrastructure.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cyber-terrorism as vulnerabilities are exploited for broader strategic objectives.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened focus on cybersecurity innovation and the development of solutions to secure idle infrastructure.
- Economic / Social: Economic impacts from data breaches could affect consumer trust and market stability, particularly in affected sectors.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct comprehensive audits of digital and physical infrastructure to identify and secure idle assets; implement stricter access controls and regular credential updates.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance threat detection capabilities; invest in employee training on data security best practices.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Organizations successfully mitigate idle infrastructure risks, reducing breach incidents.
- Worst: Continued exploitation leads to significant breaches, prompting regulatory intervention.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security practices reduce, but do not eliminate, vulnerabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, digital infrastructure, data breaches, operational security, cyber threats, information security, risk management
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us