CISA mandates federal agencies to address critical Gogs RCE vulnerability linked to zero-day exploits
Published on: 2026-01-12
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
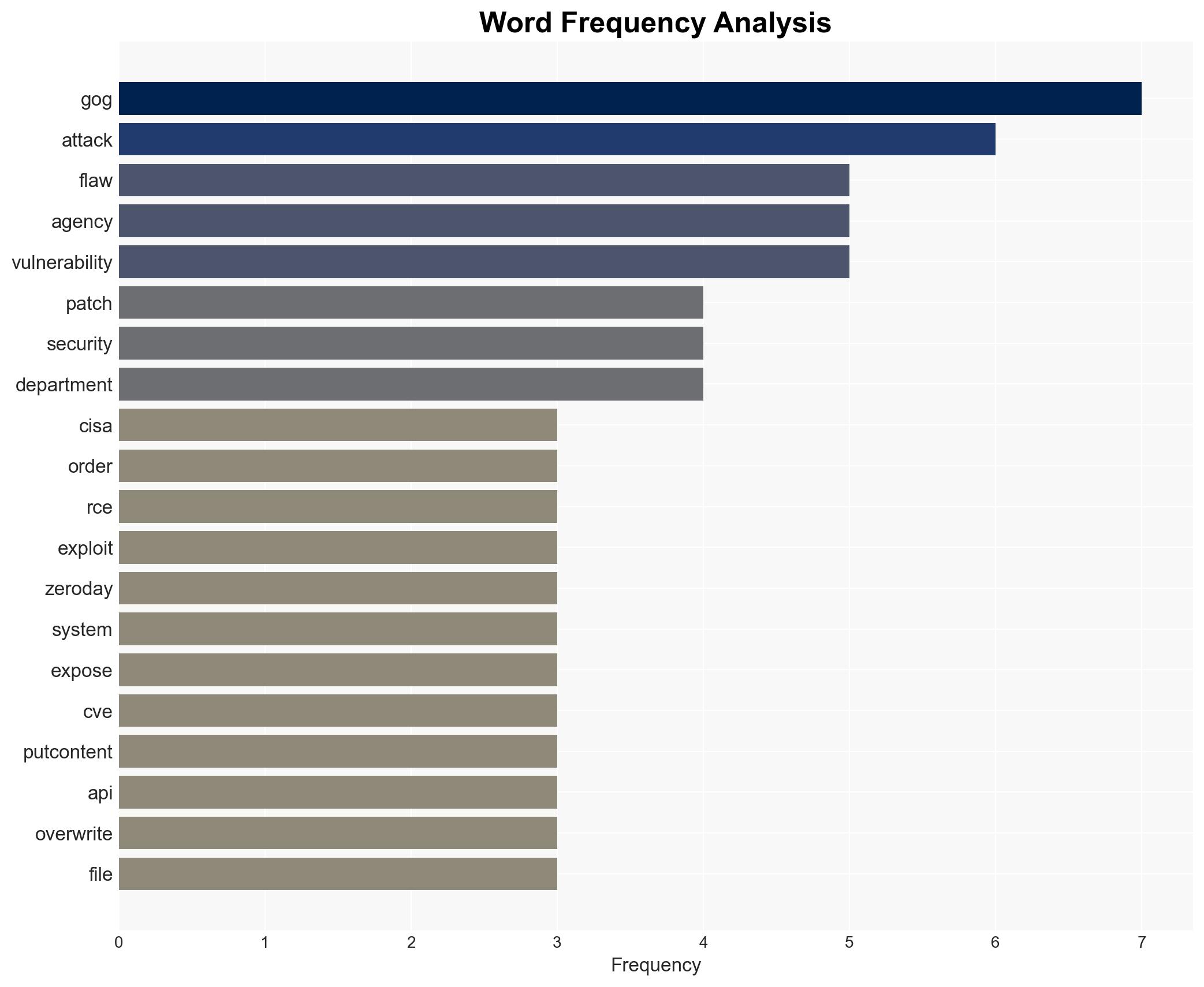
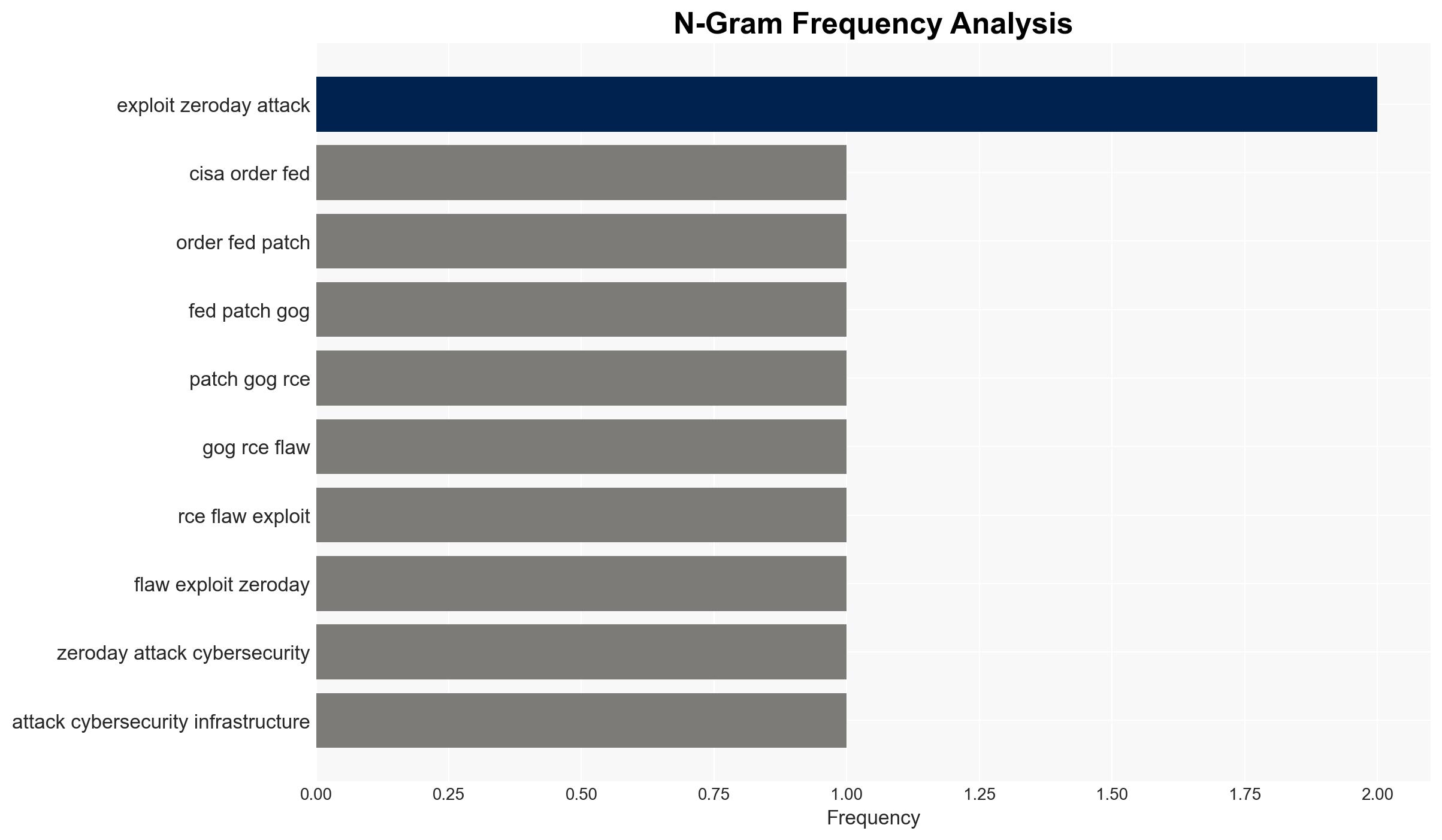
Intelligence Report: CISA orders feds to patch Gogs RCE flaw exploited in zero-day attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
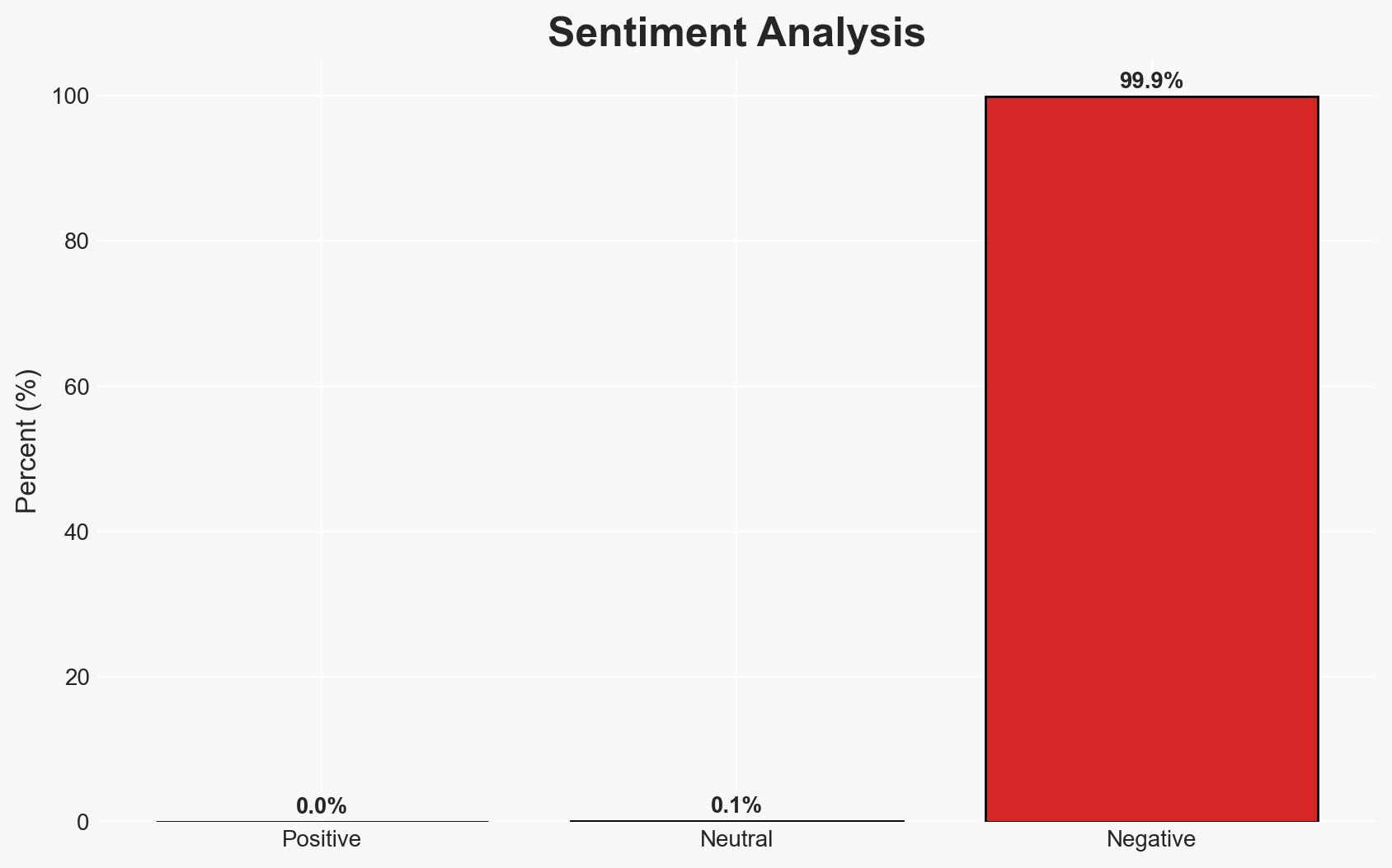
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has mandated federal agencies to patch a critical Gogs RCE vulnerability, CVE-2025-8110, which has been exploited in zero-day attacks. This vulnerability poses significant risks to federal systems and has already compromised numerous Gogs servers. The most likely hypothesis is that threat actors will continue exploiting this flaw until patches are universally applied. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability will be rapidly patched across federal systems, significantly reducing the threat. Supporting evidence includes CISA’s directive and the availability of patches. Contradicting evidence is the historical lag in patch implementation across large bureaucracies.
- Hypothesis B: Threat actors will continue to exploit the vulnerability due to slow patch adoption and widespread exposure of Gogs servers. Supporting evidence includes the ongoing exploitation observed and the number of unpatched servers. Contradicting evidence is the proactive stance by CISA and the availability of mitigation strategies.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the observed second wave of attacks and the significant number of exposed and compromised servers. Indicators that could shift this judgment include rapid patch adoption and a decrease in reported compromises.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Agencies will comply with CISA’s directive; the vulnerability is primarily exploited by non-state actors; patching will effectively mitigate the threat.
- Information Gaps: Specific identities and motivations of the threat actors; the full extent of compromised systems within federal agencies.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underreporting of compromises by affected entities; reliance on vendor-provided mitigation effectiveness.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of software supply chain security and influence future cybersecurity policy. The vulnerability’s exploitation may persist, impacting federal operations and data integrity.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state actors are implicated; pressure on inter-agency cooperation.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for cyber threats; possible diversion of resources from other security priorities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing open-source software; potential for further zero-day discoveries.
- Economic / Social: Minimal immediate economic impact; potential long-term effects on trust in digital collaboration tools.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Ensure compliance with CISA’s patch directive; monitor for signs of compromise; engage with Gogs maintainers for updates.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for open-source software vulnerabilities; enhance inter-agency information sharing.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid patch adoption and no further compromises. Worst: Continued exploitation leading to significant data breaches. Most-Likely: Gradual patching with intermittent exploitation attempts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Wiz Research
- Gogs maintainers
- CISA
- Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, zero-day vulnerability, federal agencies, open-source software, threat mitigation, CISA, remote code execution
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us