Web Skimming Operation Targets Major Payment Networks, Compromising Online Checkout Security
Published on: 2026-01-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Long-Running Web Skimming Campaign Steals Credit Cards From Online Checkout Pages
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
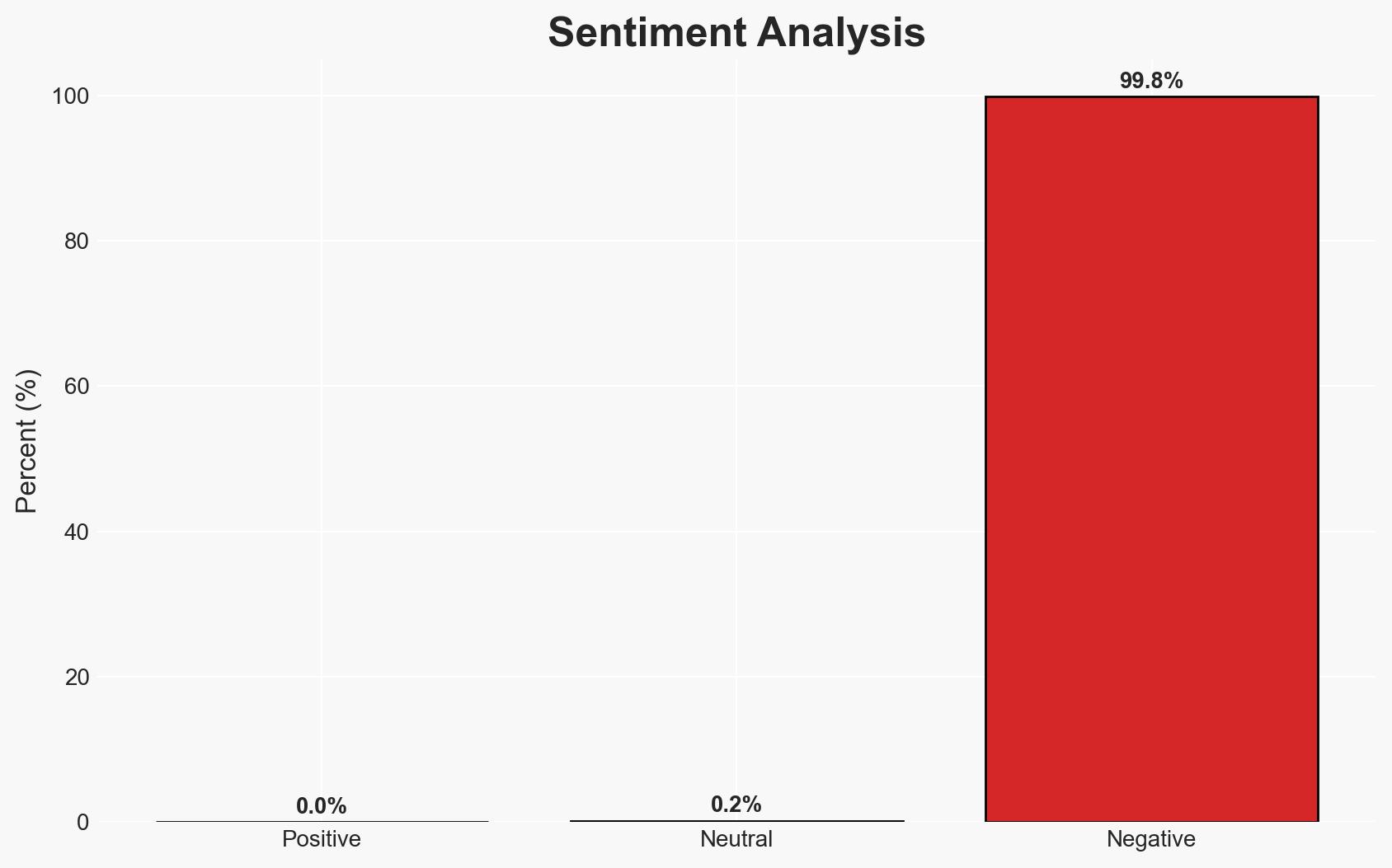
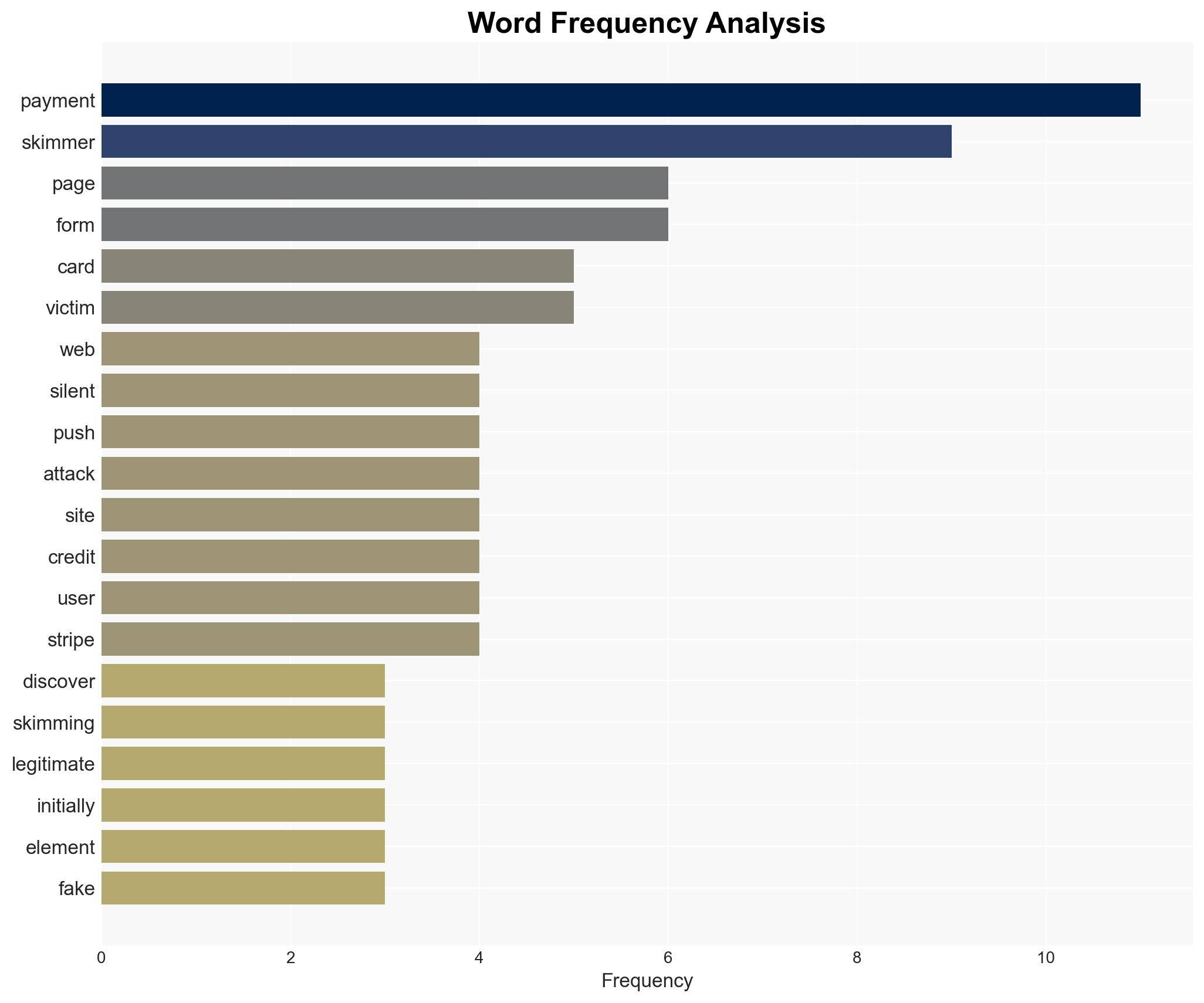
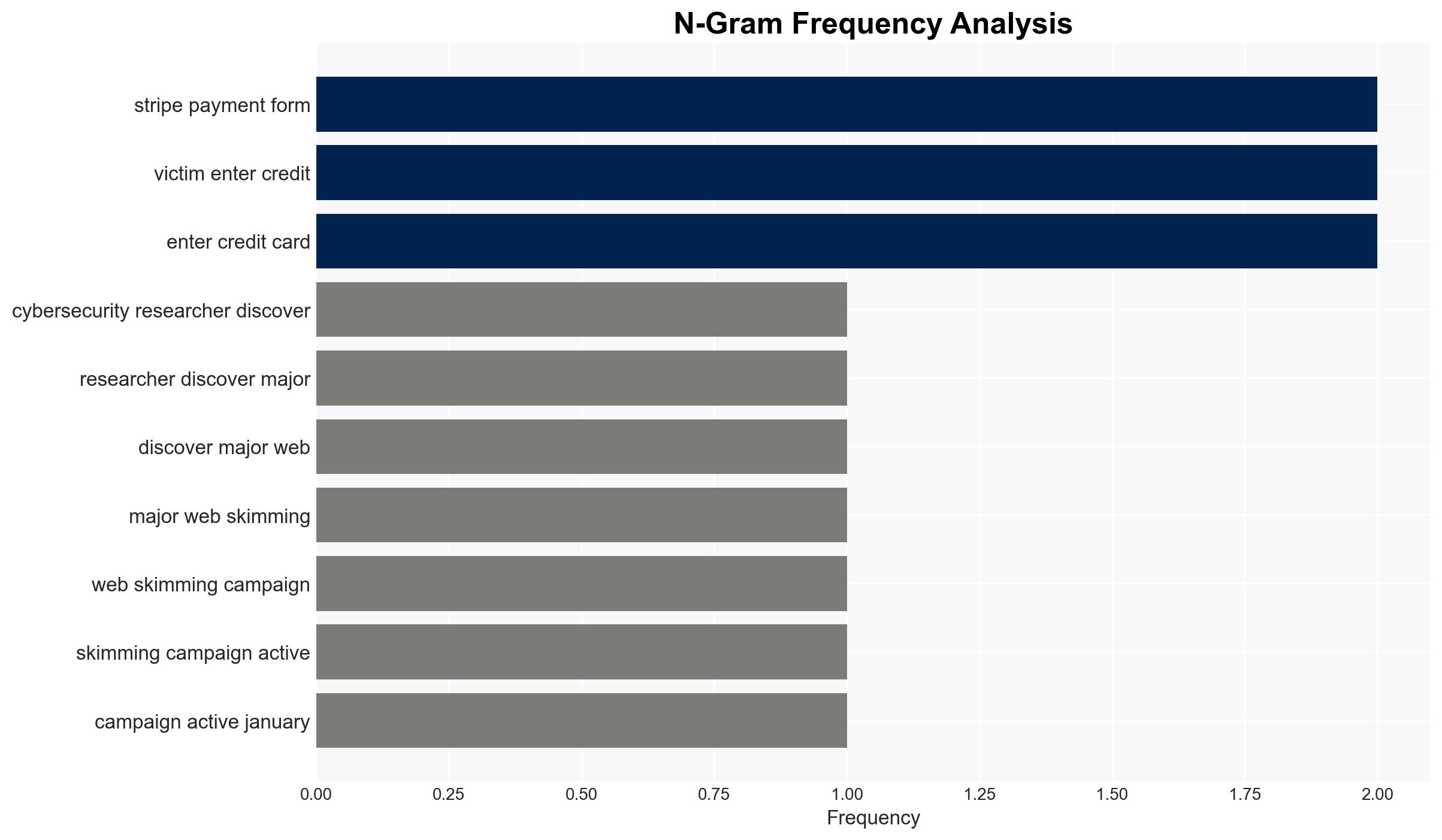
A sophisticated web skimming campaign has been targeting major payment networks since January 2022, compromising e-commerce sites to steal credit card information. The campaign exploits vulnerabilities in online checkout pages, affecting enterprise organizations using these payment networks. The most likely hypothesis is that the campaign is driven by financially motivated cybercriminals using advanced evasion techniques. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The campaign is orchestrated by a financially motivated cybercriminal group leveraging advanced techniques to evade detection. This is supported by the use of obfuscated JavaScript and the targeting of high-value payment networks. Key uncertainties include the identity and location of the perpetrators.
- Hypothesis B: The campaign is a state-sponsored operation aimed at economic disruption, using financial theft as a cover. The involvement of sanctioned entities could suggest state-level involvement. However, the primary focus on financial gain contradicts typical state-sponsored objectives.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the financial nature of the campaign and the use of techniques typical of organized cybercriminal groups. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of political motivations or state sponsorship.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The campaign is primarily financially motivated; the use of sanctioned entities is a tactical choice rather than a strategic alignment; the skimming techniques are adaptable to various e-commerce platforms.
- Information Gaps: The identity of the actors behind the campaign; the full scope of affected organizations; the specific vulnerabilities exploited in the e-commerce platforms.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in attributing the campaign to cybercriminals; reliance on potentially biased sources such as cybersecurity firms with vested interests.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of e-commerce security practices and potentially impact consumer trust in online transactions. If linked to state actors, it could escalate geopolitical tensions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased sanctions or diplomatic actions if state involvement is confirmed.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness and response from law enforcement and cybersecurity agencies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing payment gateways and e-commerce platforms; potential for copycat attacks.
- Economic / Social: Possible decline in consumer confidence in online shopping, impacting e-commerce revenue.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of e-commerce sites for suspicious activity; collaborate with cybersecurity firms to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships between payment networks and cybersecurity agencies; invest in advanced threat detection capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Campaign is dismantled through coordinated international efforts, leading to improved e-commerce security.
- Worst: Campaign evolves with more sophisticated techniques, causing widespread financial damage.
- Most-Likely: Continued targeting of e-commerce sites with gradual improvements in detection and mitigation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Silent Push (Cybersecurity firm)
- Stark Industries (Sanctioned bulletproof hosting provider)
- PQ.Hosting (Parent company of Stark Industries)
- THE[.]Hosting (Rebranded entity)
- WorkTitans B.V. (Dutch entity controlling THE[.]Hosting)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, financial crime, e-commerce, sanctions evasion, cyber-espionage, threat detection, payment networks
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us