Former US Navy sailor sentenced to 16 years for selling military secrets to Chinese intelligence officer
Published on: 2026-01-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: US sailor sentenced to 16 years in prison in Chinese espionage case
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
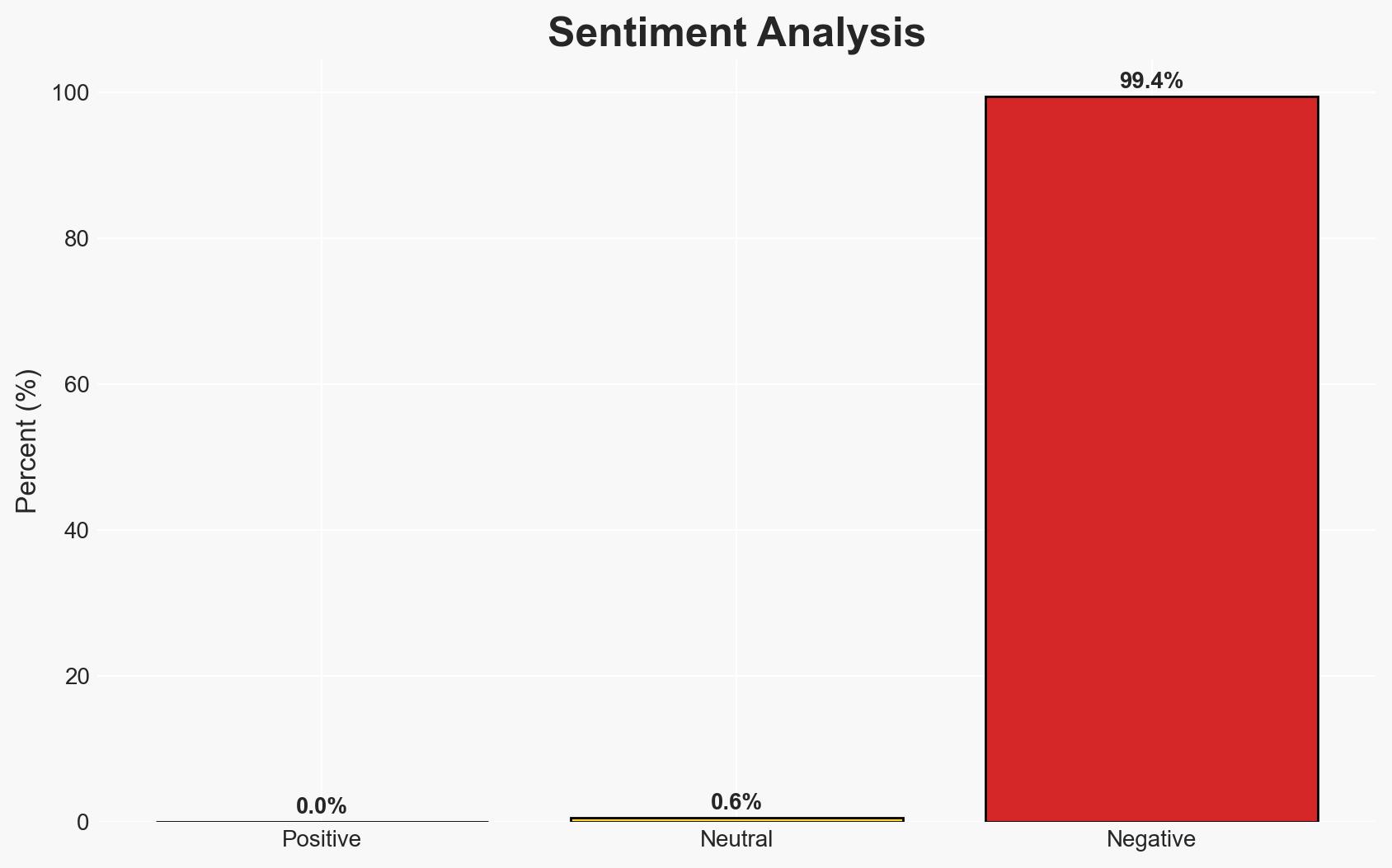
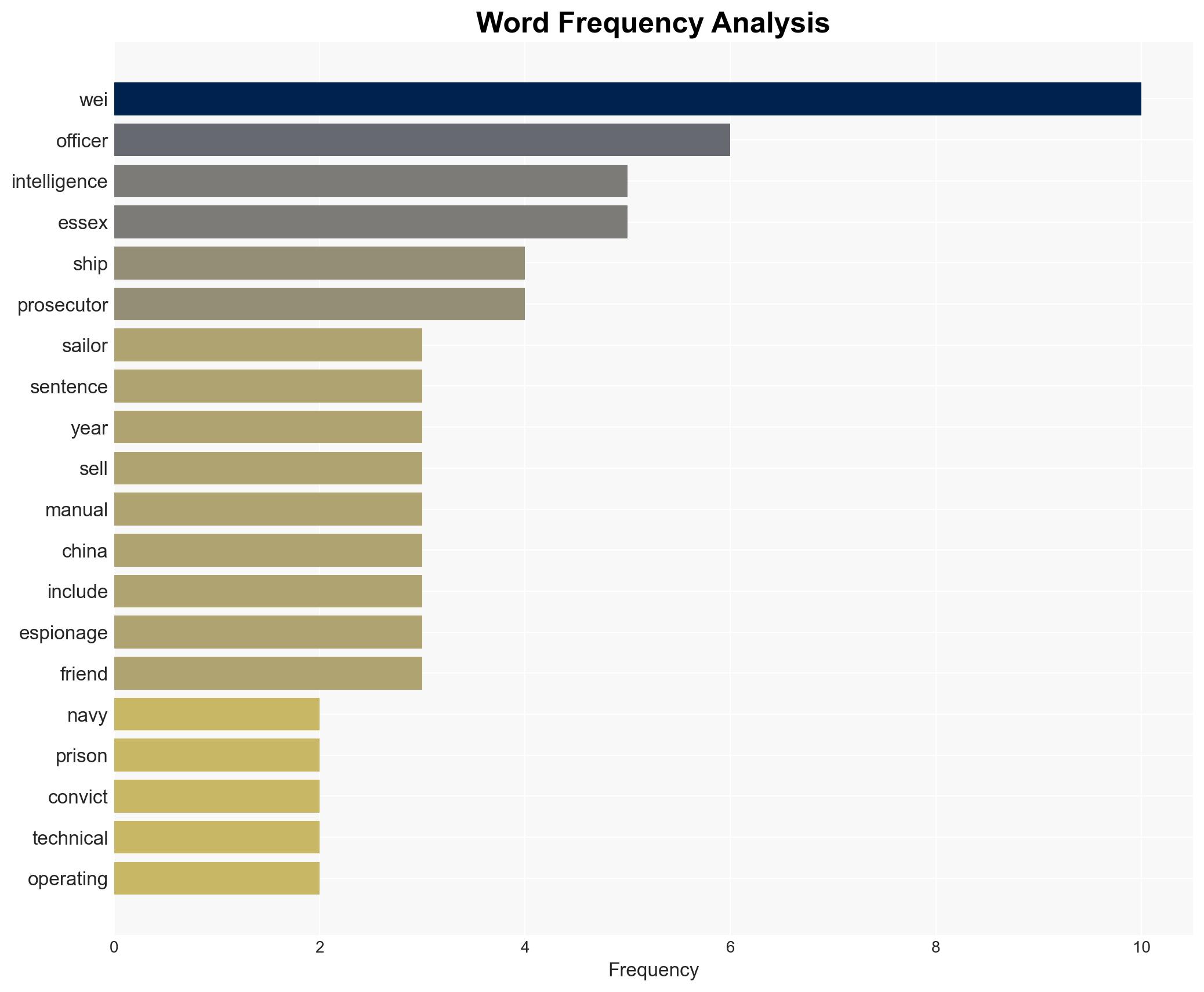
A US Navy sailor, Jinchao Wei, has been sentenced to 16 years for espionage activities involving China, highlighting vulnerabilities in military personnel recruitment and information security. The case underscores the persistent espionage threat posed by China. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to limited information on the broader network and recruitment methods.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Wei acted primarily out of personal financial motivation, exploiting his position to sell sensitive information for monetary gain. Supporting evidence includes the payment received and his disregard for warnings. However, uncertainties remain about any ideological motivations or coercion.
- Hypothesis B: Wei was ideologically motivated or coerced into espionage activities, with financial compensation being secondary. This is less supported due to lack of evidence of ideological statements or coercion, but cannot be ruled out without further intelligence.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported by the evidence of financial transactions and Wei’s own admission of poor judgment due to loneliness. Indicators such as additional financial transactions or communications could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Wei acted independently without a broader network; financial gain was the primary motivator; the information sold was not further disseminated beyond the initial recipient.
- Information Gaps: Details on the extent of Wei’s network, potential co-conspirators, and the full scope of information compromised.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Wei’s statements due to self-preservation; risk of underestimating the sophistication of Chinese recruitment tactics.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This case may lead to increased scrutiny on military personnel and information security protocols, potentially affecting US-China relations and military operational security.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic tensions between the US and China, with possible retaliatory measures or increased espionage activities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened security measures within the military to prevent similar breaches, possibly impacting operational readiness.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on cyber security and counter-intelligence measures to protect sensitive information.
- Economic / Social: Limited direct economic impact, but potential social implications for military personnel trust and morale.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a thorough review of information security protocols and personnel vetting processes; increase monitoring of communications for suspicious activities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with allied intelligence agencies to share insights on espionage threats; enhance training programs for personnel on counter-espionage awareness.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Strengthened security measures prevent future breaches, and diplomatic channels mitigate tensions.
- Worst Case: Escalation in espionage activities leads to significant operational compromises and diplomatic fallout.
- Most Likely: Incremental improvements in security with ongoing espionage attempts requiring continuous vigilance.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Jinchao Wei – Former US Navy sailor, convicted of espionage.
- Wenheng Zhao – Co-conspirator, sentenced for related charges.
- China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation – Entity associated with the intelligence officer.
- US Department of Justice – Prosecuting authority.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, espionage, military security, US-China relations, information security, counter-intelligence, personnel vetting, cyber security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us