Lessons from 2025: How Attackers Enhanced Traditional Tactics with AI Efficiency
Published on: 2026-01-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: What Should We Learn From How Attackers Leveraged AI in 2025
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
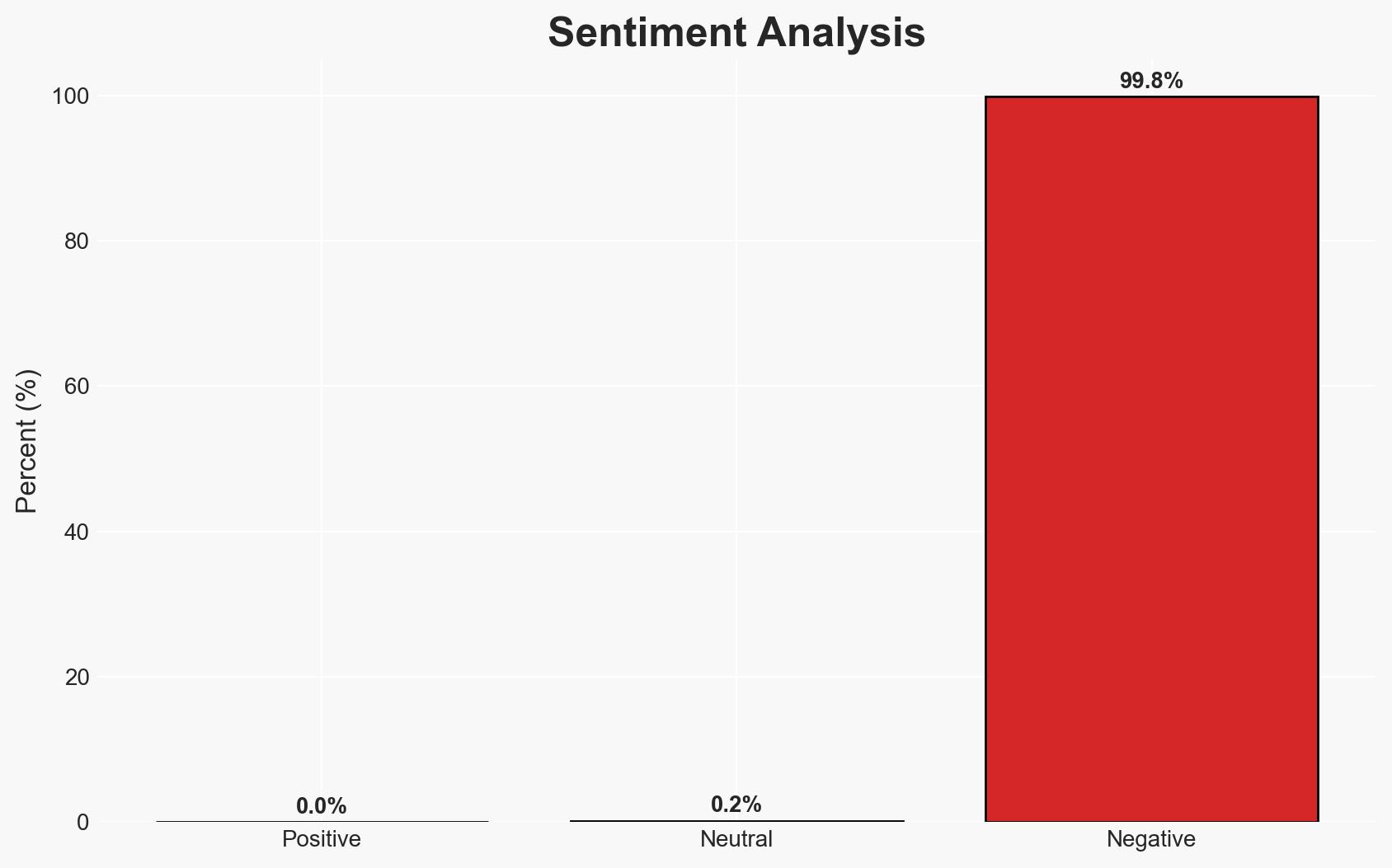
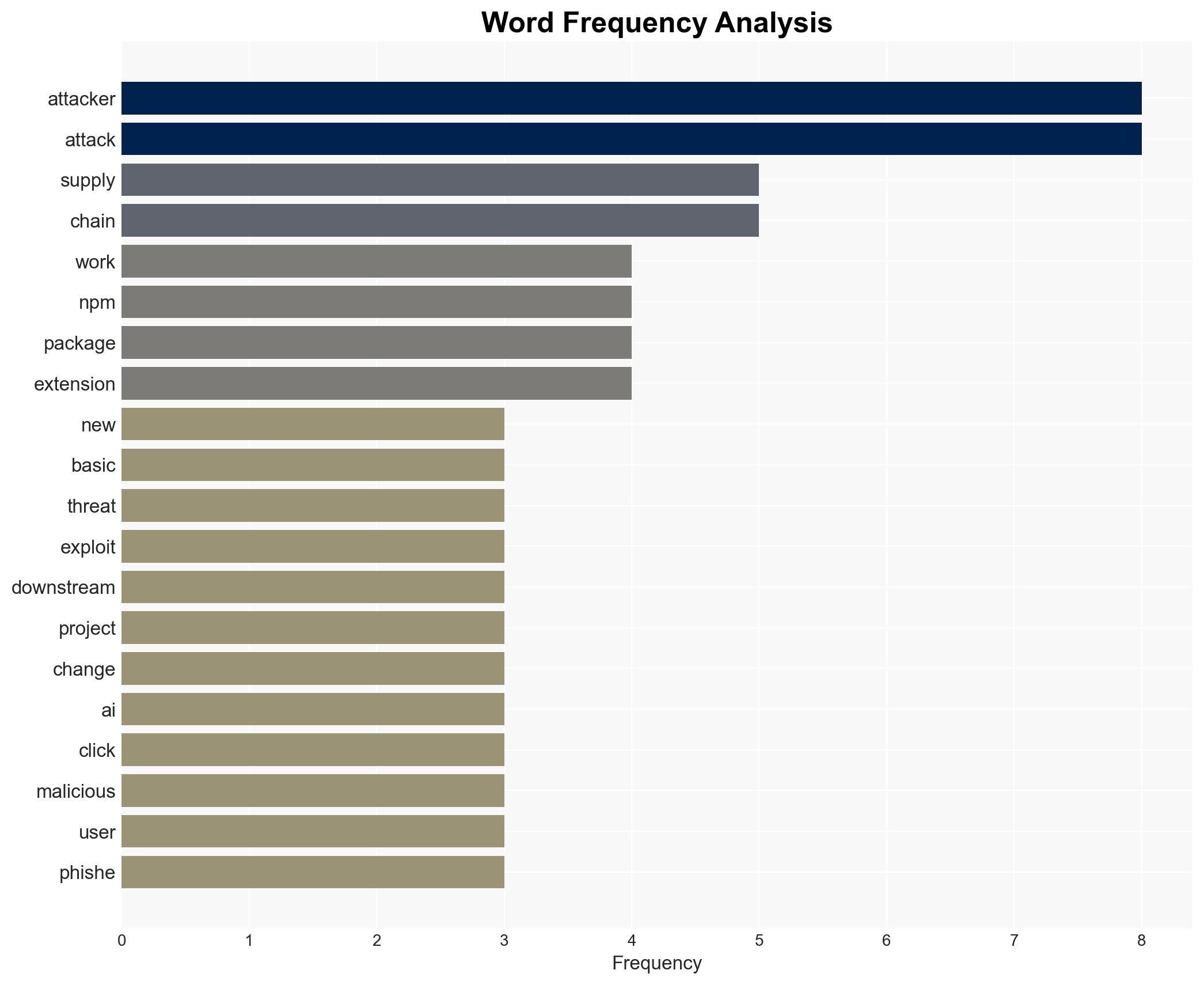
In 2025, cyber attackers have optimized traditional attack methods using AI, significantly enhancing their efficiency and scale. The most likely hypothesis is that AI has lowered the barrier to entry for cybercriminals, enabling even small teams or individuals to execute sophisticated attacks. This development affects software supply chains, phishing vulnerabilities, and the security of official app stores. Overall, there is moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Attackers are primarily leveraging AI to enhance traditional attack vectors, leading to more efficient and scalable operations. This is supported by evidence of AI enabling smaller, less organized groups to conduct attacks that previously required larger operations. However, the extent of AI’s role in these operations remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The observed increase in attack efficiency is due to improved attacker coordination and resource allocation, rather than AI advancements. This hypothesis is contradicted by the evidence of AI’s role in reducing the complexity and resource requirements for executing attacks.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented role of AI in simplifying and scaling attack operations. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of significant non-AI-related improvements in attacker coordination or resource allocation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI capabilities are accessible and usable by a broad range of actors; traditional attack vectors remain effective; defenders are not significantly outpacing attackers in innovation.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the specific AI tools and techniques used by attackers; comprehensive analysis of defender responses and their effectiveness.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential cognitive bias towards overestimating AI’s role due to its current prominence in discourse; source bias from industry stakeholders emphasizing AI threats for commercial reasons.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of AI-enhanced cyber attacks could lead to increased frequency and impact of security breaches, challenging existing defense mechanisms and policies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions between states over cyber attribution and response measures.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment as smaller actors gain capabilities previously limited to state-level entities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater difficulty in securing digital infrastructure and maintaining trust in digital communications.
- Economic / Social: Potential disruptions to economic stability due to compromised supply chains and loss of consumer trust in digital platforms.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of AI-related cyber threats; prioritize patching and securing supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop AI-driven defensive tools; foster international cooperation on cyber threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid adaptation of defensive measures mitigates AI-driven threats.
- Worst: Widespread disruptions due to unchecked AI-enhanced attacks.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in defense lead to a continued cat-and-mouse dynamic.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI, supply chain attacks, phishing, digital infrastructure
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us