Jihadist Control Tightens in Sahel as Mali Faces Strategic Siege and Threat of Regional Collapse
Published on: 2026-01-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: West Africas unchecked siege Jihadist forces tighten stranglehold over the Sahel threatening regional collapse
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
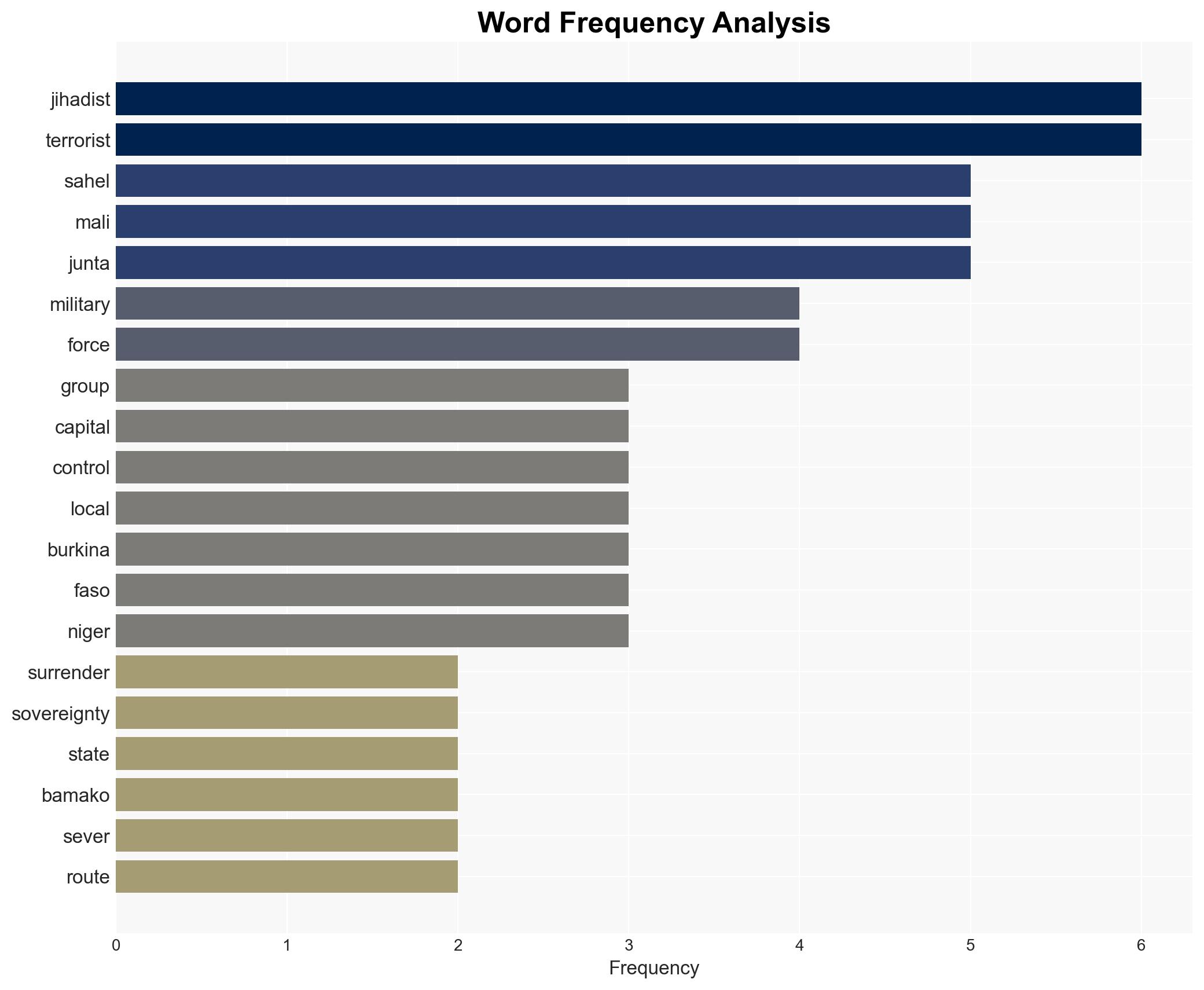
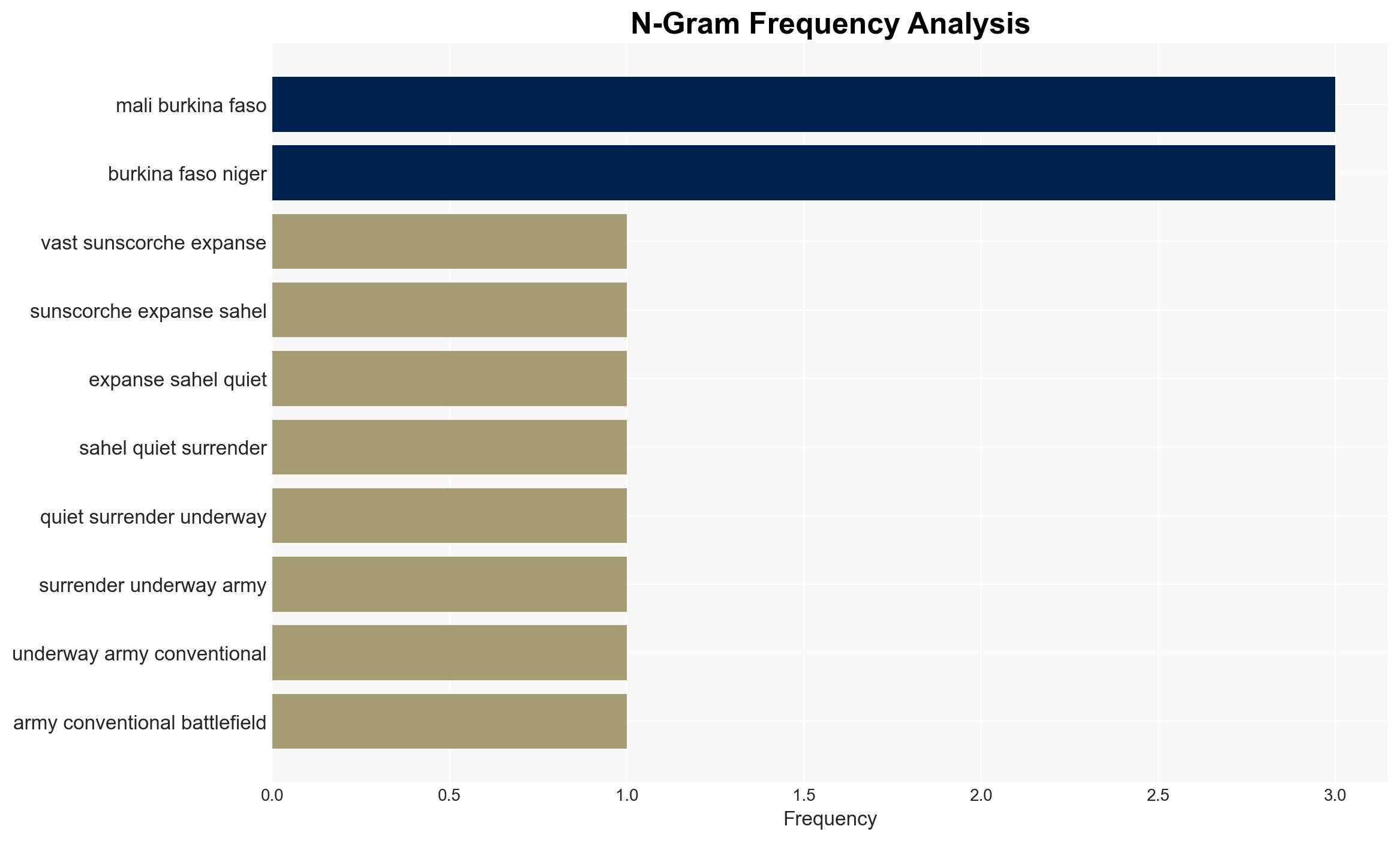
Jihadist groups, particularly Al-Qaeda’s Sahel branch JNIM, are systematically undermining state sovereignty in Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger, with potential spillover into coastal West African nations. The expulsion of French forces and reliance on Russian mercenaries have exacerbated the situation. This assessment is made with moderate confidence, acknowledging significant information gaps and potential biases in available data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: JNIM’s actions are primarily driven by ideological goals to establish a regional caliphate. This is supported by their imposition of Sharia law and collection of jizyah. However, the involvement of local ethnic groups and criminal networks suggests mixed motivations.
- Hypothesis B: The jihadist expansion is opportunistic, exploiting weak governance and economic desperation rather than a cohesive ideological campaign. The reliance on local grievances and criminal activities supports this view, though the strategic targeting of capitals indicates a broader agenda.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the diverse composition of jihadist ranks and the pragmatic nature of their territorial control. Indicators such as increased coordination among ethnic and criminal groups could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The military juntas lack capacity to effectively counter jihadist advances; Russian mercenaries are ineffective in the Sahel context; JNIM’s control over supply routes is sustainable.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the internal dynamics of jihadist groups; the extent of Russian mercenary operations; local population support or resistance levels.
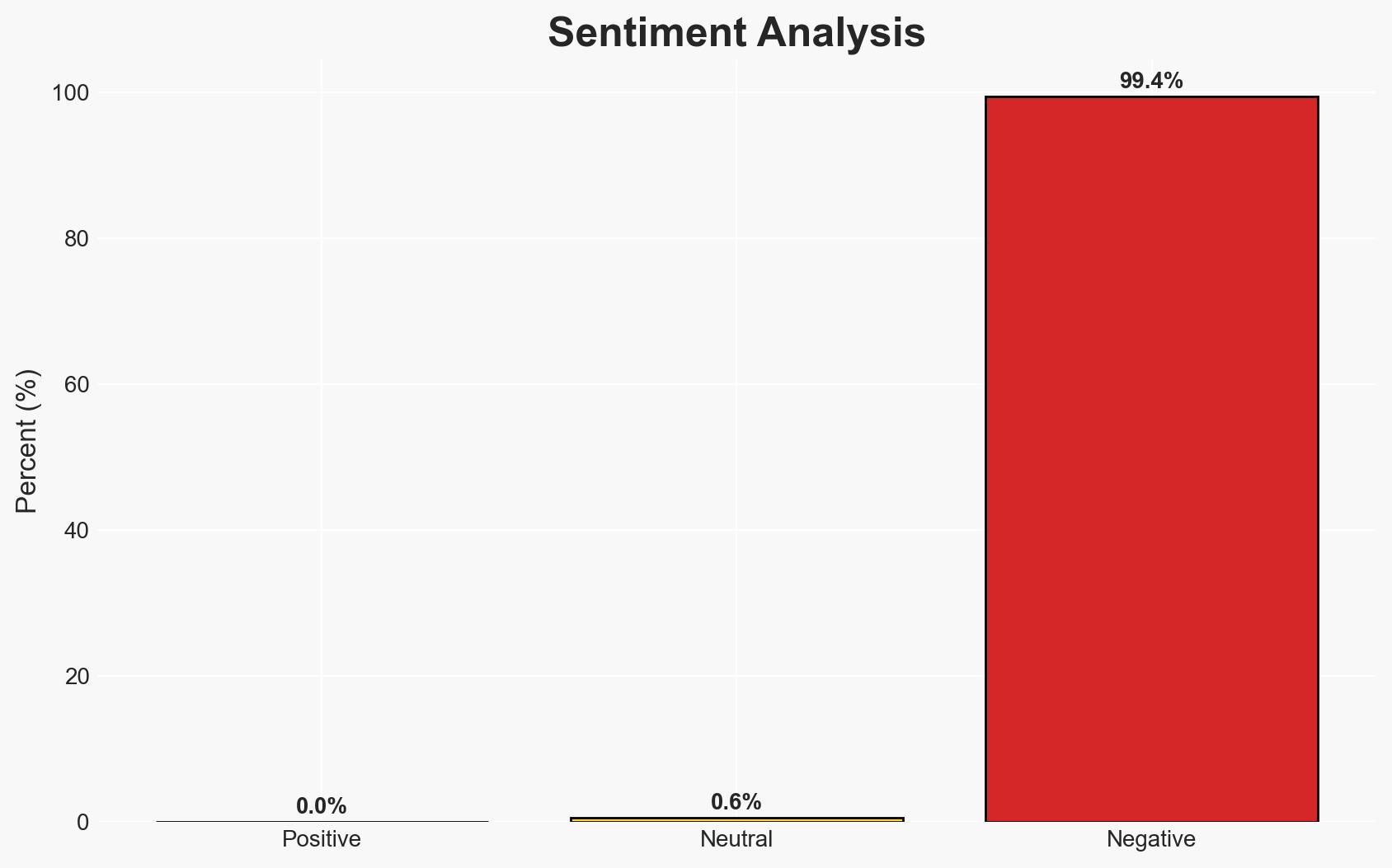
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underestimation of local support for jihadists; overreliance on sources with anti-Russian sentiment; manipulation by jihadist propaganda.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The jihadist expansion in the Sahel could destabilize the region further, with potential impacts on global security and economic interests. The situation may evolve into a broader conflict involving regional and international actors.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased regional instability could lead to international intervention or a shift in alliances, particularly with coastal nations at risk.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Escalation of jihadist activities may necessitate enhanced counter-terrorism operations and intelligence sharing among affected nations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased jihadist propaganda and recruitment efforts online, targeting disaffected populations.
- Economic / Social: Disruption of trade routes and local economies could exacerbate poverty and drive further recruitment into jihadist ranks.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence collection on jihadist networks; engage with regional partners to assess security needs; monitor Russian mercenary activities closely.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for affected nations; strengthen regional security partnerships; support local governance and economic initiatives.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Regional cooperation leads to stabilization and rollback of jihadist gains.
- Worst: Jihadist control expands, leading to regional collapse and humanitarian crisis.
- Most-Likely: Continued instability with sporadic international intervention and limited success in containment.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Jama’a Nusrat ul-Islam wa al-Muslimin (JNIM)
- Military juntas of Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger
- Russian mercenary groups (e.g., Wagner Group)
- Local ethnic groups (e.g., Tuareg, Fulani)
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, counter-terrorism, regional instability, jihadist expansion, mercenary operations, geopolitical dynamics, Sahel security, economic disruption
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us