Russia claims U.S. and Israel are instigating unrest in Iran amid escalating anti-government protests
Published on: 2026-01-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Russia warns of Western-backed color revolution in Iran as protests turn violent
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
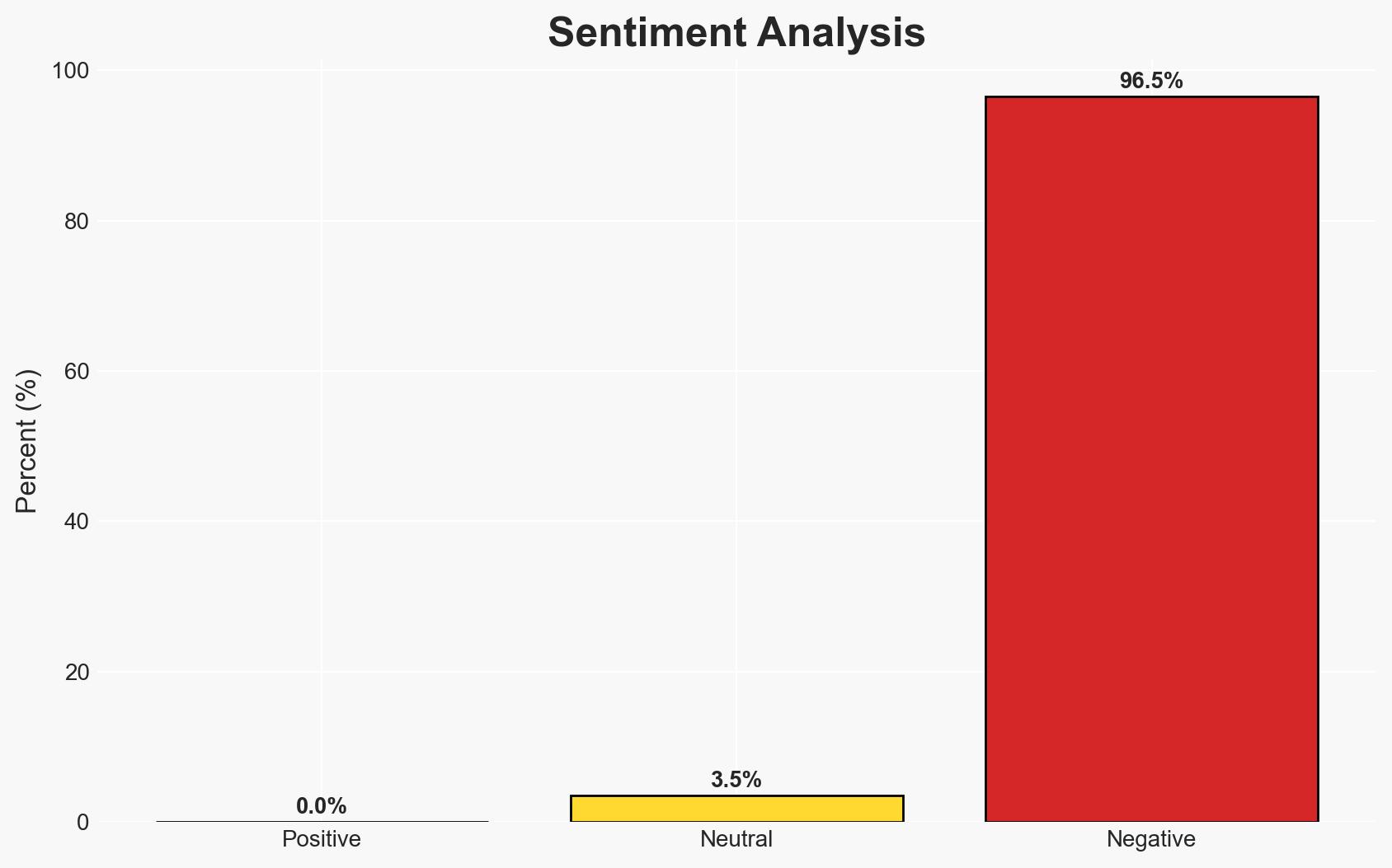
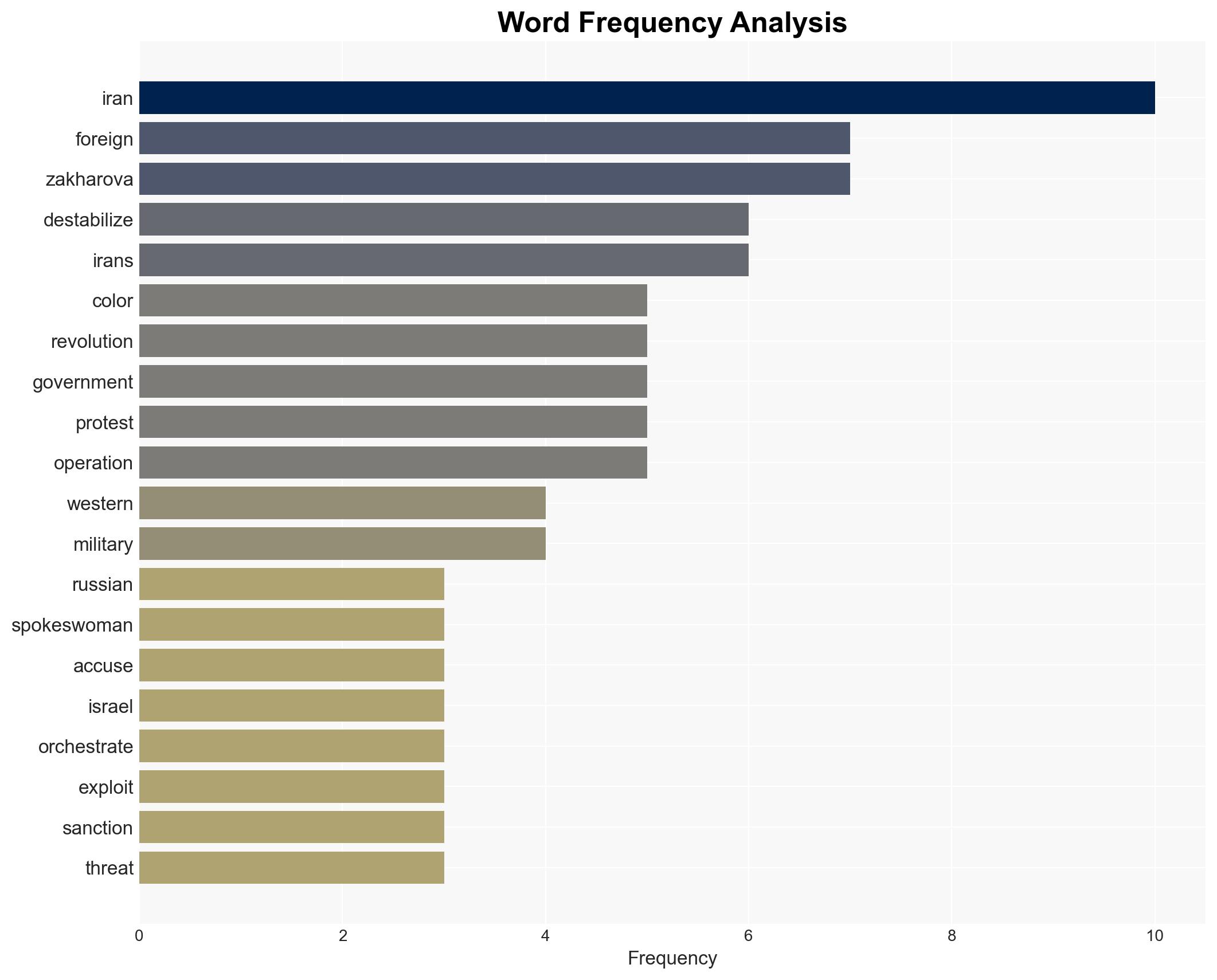
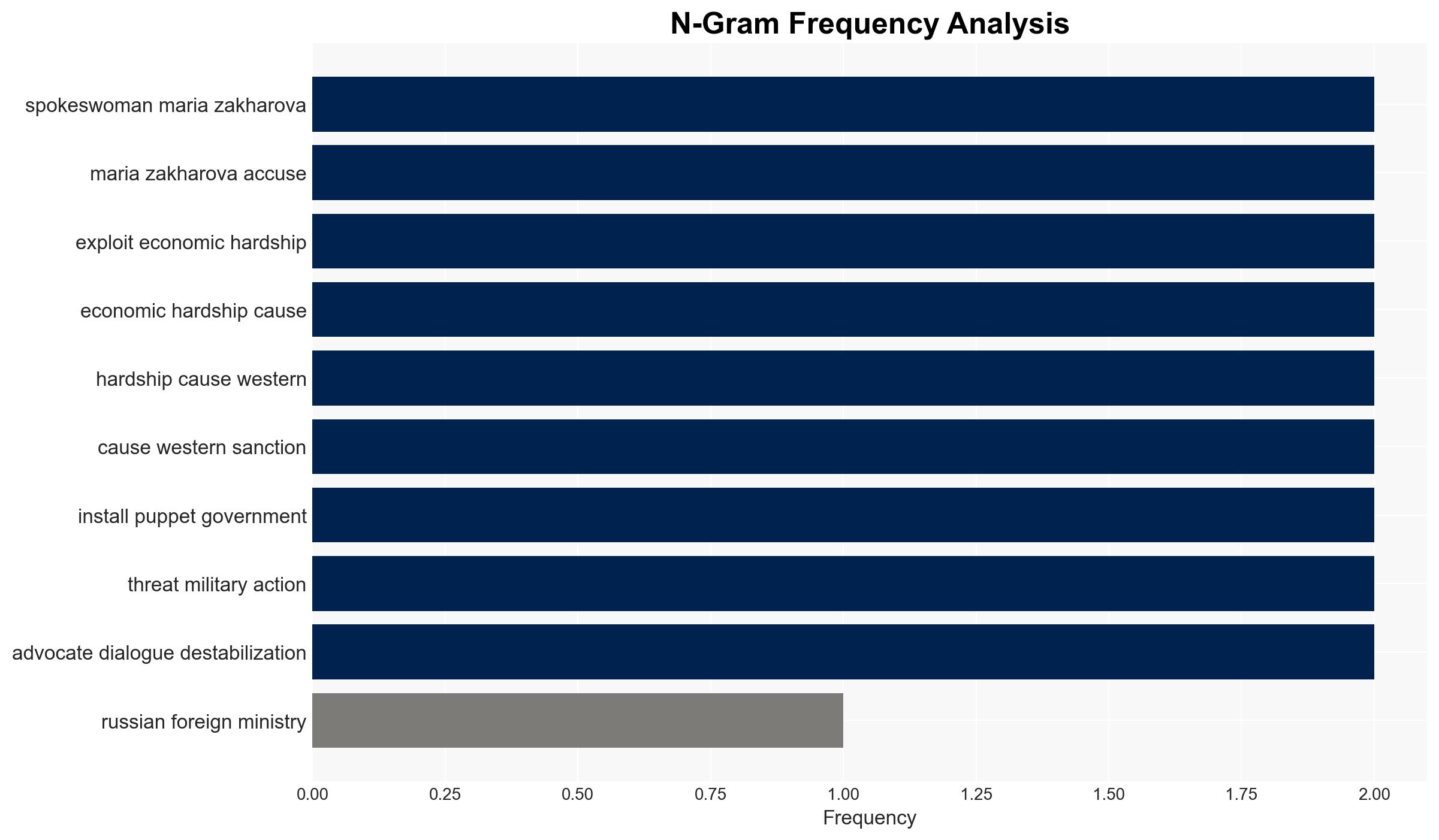
Russia has accused the U.S. and Israel of orchestrating a “color revolution” in Iran amid escalating protests triggered by economic hardship and currency collapse. The situation could destabilize the Middle East, with implications for geopolitical alignments and regional security. Current assessment leans towards external influence exacerbating internal dissent, with moderate confidence.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The protests in Iran are primarily a result of internal economic mismanagement and genuine grassroots dissent, with limited external influence. Evidence includes the timing of protests following economic downturns. Key uncertainties involve the extent of foreign involvement.
- Hypothesis B: The protests are significantly influenced by external actors, notably the U.S. and Israel, aiming to destabilize Iran through a “color revolution.” Supporting evidence includes public accusations by Russia and historical precedents. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of concrete proof of direct foreign orchestration.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the alignment of geopolitical narratives and historical patterns of foreign intervention in similar contexts. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include verified evidence of foreign operational support or significant shifts in protest dynamics.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Iranian government remains cohesive; U.S. and Israeli interests align in destabilizing Iran; economic sanctions are a significant protest driver.
- Information Gaps: Lack of direct evidence linking foreign entities to protest organization; unclear levels of popular support for the protests.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Russian statements due to geopolitical interests; risk of Iranian government exaggerating foreign involvement to delegitimize protests.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The protests in Iran could lead to broader regional instability, affecting geopolitical alliances and security dynamics. The situation may evolve with increased foreign intervention or internal repression.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased East-West tensions; realignment of regional alliances.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of internal conflict and cross-border terrorism.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely increase in cyber operations and information warfare targeting Iranian and foreign entities.
- Economic / Social: Continued economic decline could exacerbate social unrest and weaken state structures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence collection on protest dynamics and foreign involvement; engage in diplomatic channels to de-escalate tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional partnerships to mitigate spillover effects; develop resilience measures against economic and cyber threats.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diplomatic resolution and stabilization of Iran’s economy.
- Worst: Escalation into regional conflict involving multiple state actors.
- Most-Likely: Prolonged unrest with intermittent foreign influence and regional tensions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Maria Zakharova, Russian Foreign Ministry spokeswoman
- U.S. Government, unspecified entities
- Israeli Government, Mossad
- Iranian Government, unspecified entities
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, color revolution, geopolitical tensions, Middle East stability, foreign intervention, economic sanctions, protest dynamics, intelligence operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us