Western arms manufacturers adapt weapon designs for rapid battlefield changes in Ukraine.
Published on: 2026-01-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Arms makers say that the fast-moving war in Ukraine is changing how they design and upgrade weapons
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine is catalyzing a shift in military technology development towards modular and software-first designs, enabling faster adaptation to battlefield changes. This trend affects Western arms manufacturers and has implications for military readiness and innovation. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the evolving nature of the conflict and technological advancements.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The shift towards modular and software-first designs in military technology is primarily driven by the immediate needs of the Ukraine conflict. Supporting evidence includes statements from industry leaders emphasizing rapid adaptation and modularity as responses to battlefield conditions. Key uncertainties include the extent to which these changes will persist post-conflict.
- Hypothesis B: The evolution towards modular and software-first designs is part of a broader, pre-existing trend in defense technology, merely accelerated by the Ukraine conflict. Evidence includes prior movements in defense technology towards flexibility and adaptability. Contradicting evidence is the specific urgency cited by manufacturers due to the Ukraine war.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to direct statements from industry leaders linking the shift to the Ukraine conflict. However, indicators such as continued investment in modular designs post-conflict could shift this assessment towards Hypothesis B.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The conflict in Ukraine will continue to influence military technology development; modular designs will remain cost-effective; software upgrades will keep pace with tactical needs.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the long-term strategic plans of arms manufacturers; specific feedback from end-users in the field regarding the effectiveness of modular systems.
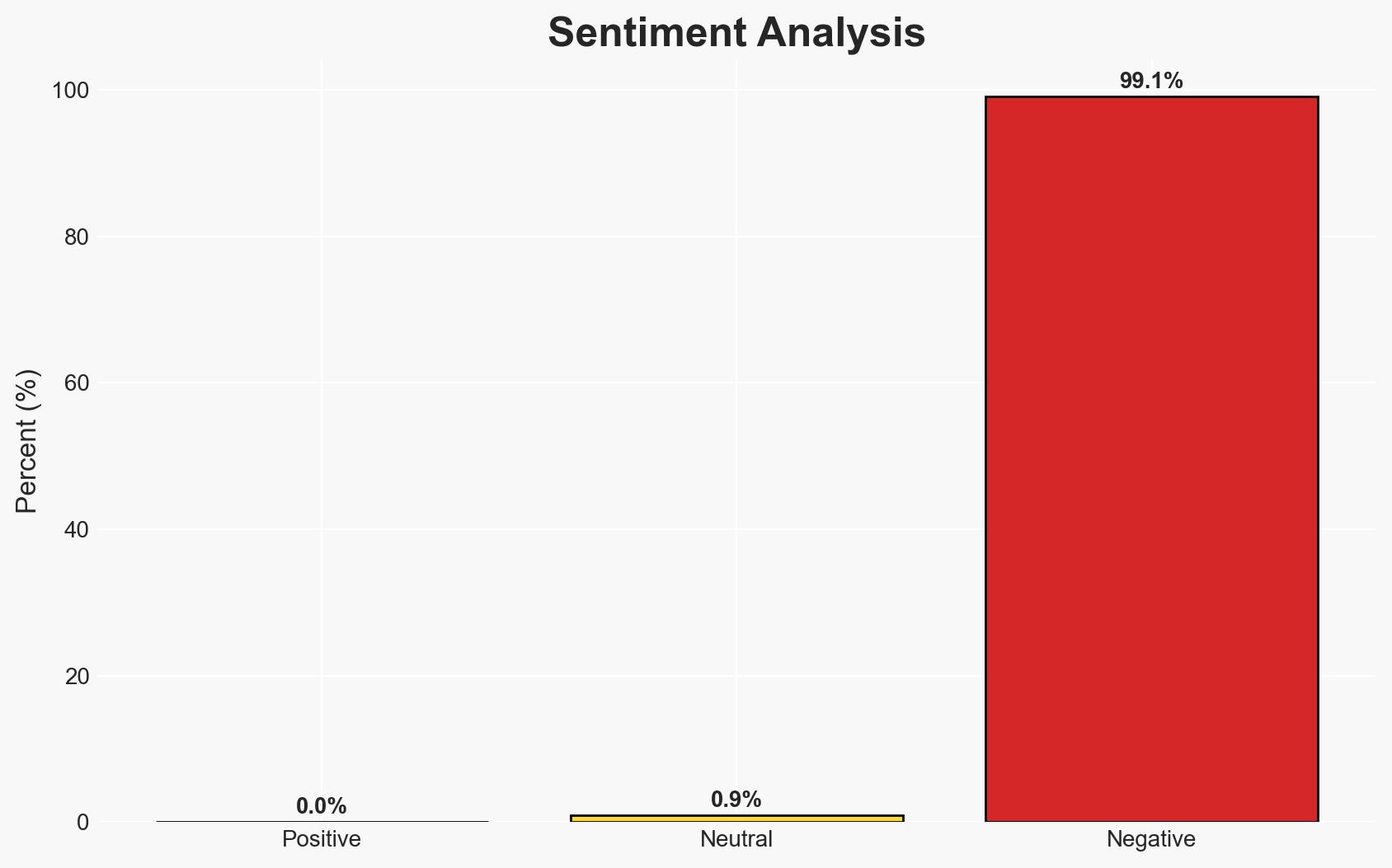
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from industry sources emphasizing the benefits of their products; risk of overestimating the impact of modular designs due to limited battlefield data.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The shift towards modular and software-first military technology could lead to significant changes in defense procurement and operational strategies. This development may influence global arms competition and technological innovation.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased arms competition and potential shifts in alliances as countries seek to acquire adaptable technologies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced military readiness and adaptability could alter threat environments and operational tactics.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater reliance on software increases vulnerability to cyber threats and necessitates robust cybersecurity measures.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic benefits from increased demand for modular systems; social impacts from shifts in defense industry employment.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor developments in modular technology deployments in Ukraine; assess cybersecurity measures for new systems.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with technology firms to enhance modular capabilities; invest in training for rapid adaptation to new systems.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Adoption of modular systems leads to enhanced military capabilities. Worst: Over-reliance on new technologies without adequate cybersecurity leads to vulnerabilities. Most-Likely: Gradual integration of modular systems with ongoing cybersecurity enhancements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Patrick Shepherd, Milrem Robotics
- Matt McCrann, DroneShield
- Gediminas Guoba, Granta Autonomy
- Achi, Ark Robotics
7. Thematic Tags
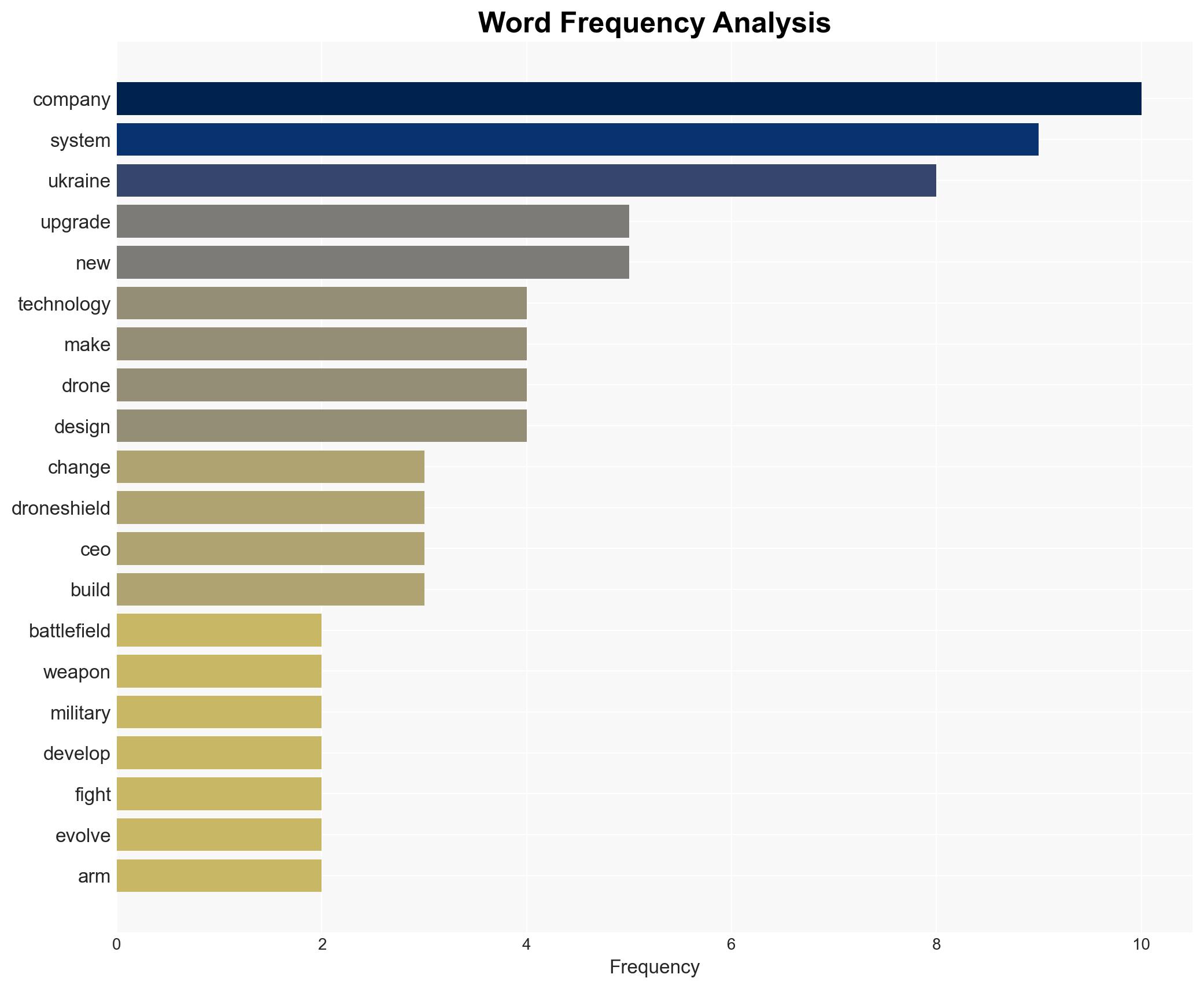
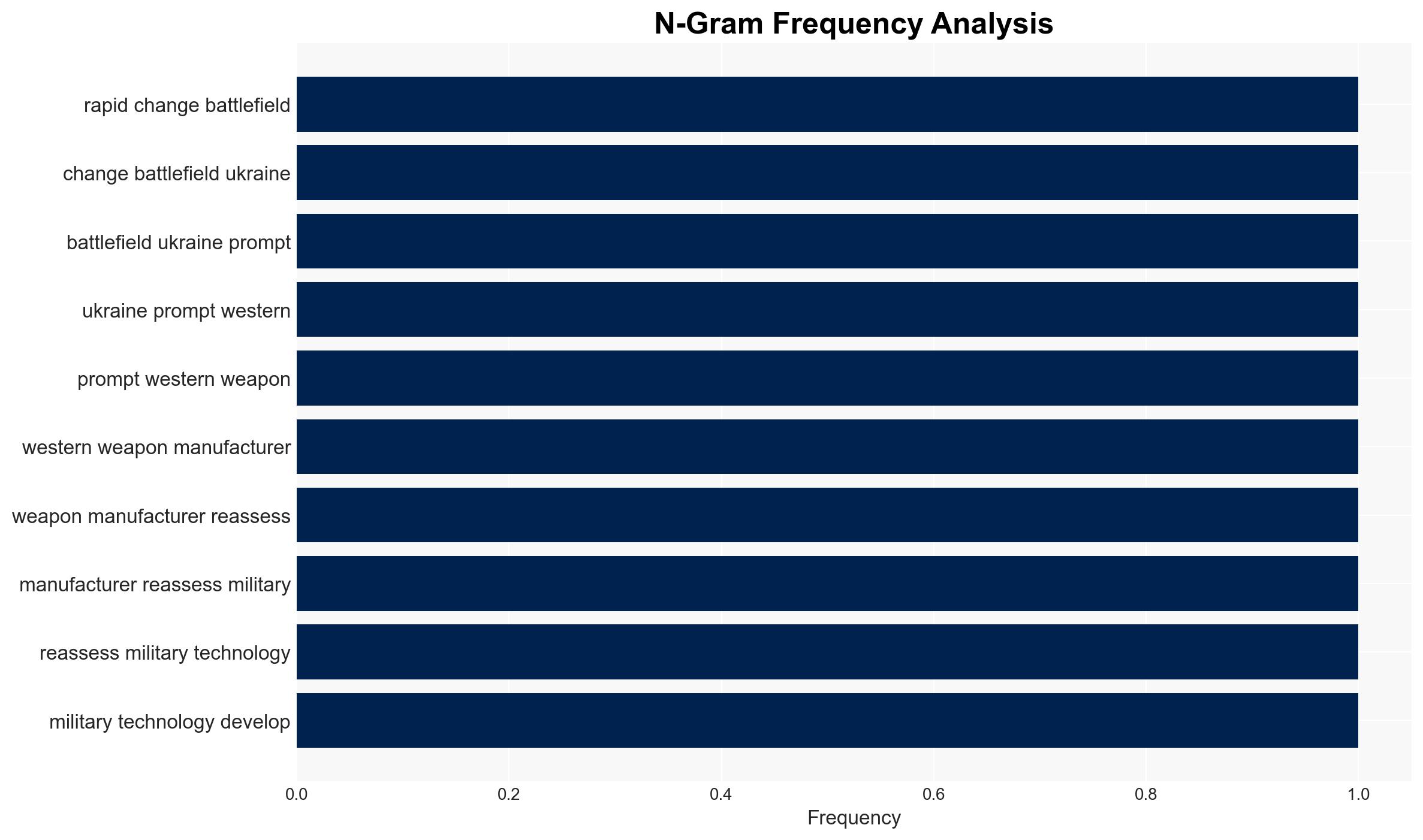
regional conflicts, military technology, modular design, Ukraine conflict, defense innovation, cybersecurity, arms industry, battlefield adaptation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us