Vulnerabilities in Fast Pair Protocol Expose Millions of Audio Devices to Hacking and Tracking Risks
Published on: 2026-01-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Hundreds of Millions of Audio Devices Need a Patch to Prevent Wireless Hacking and Tracking
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
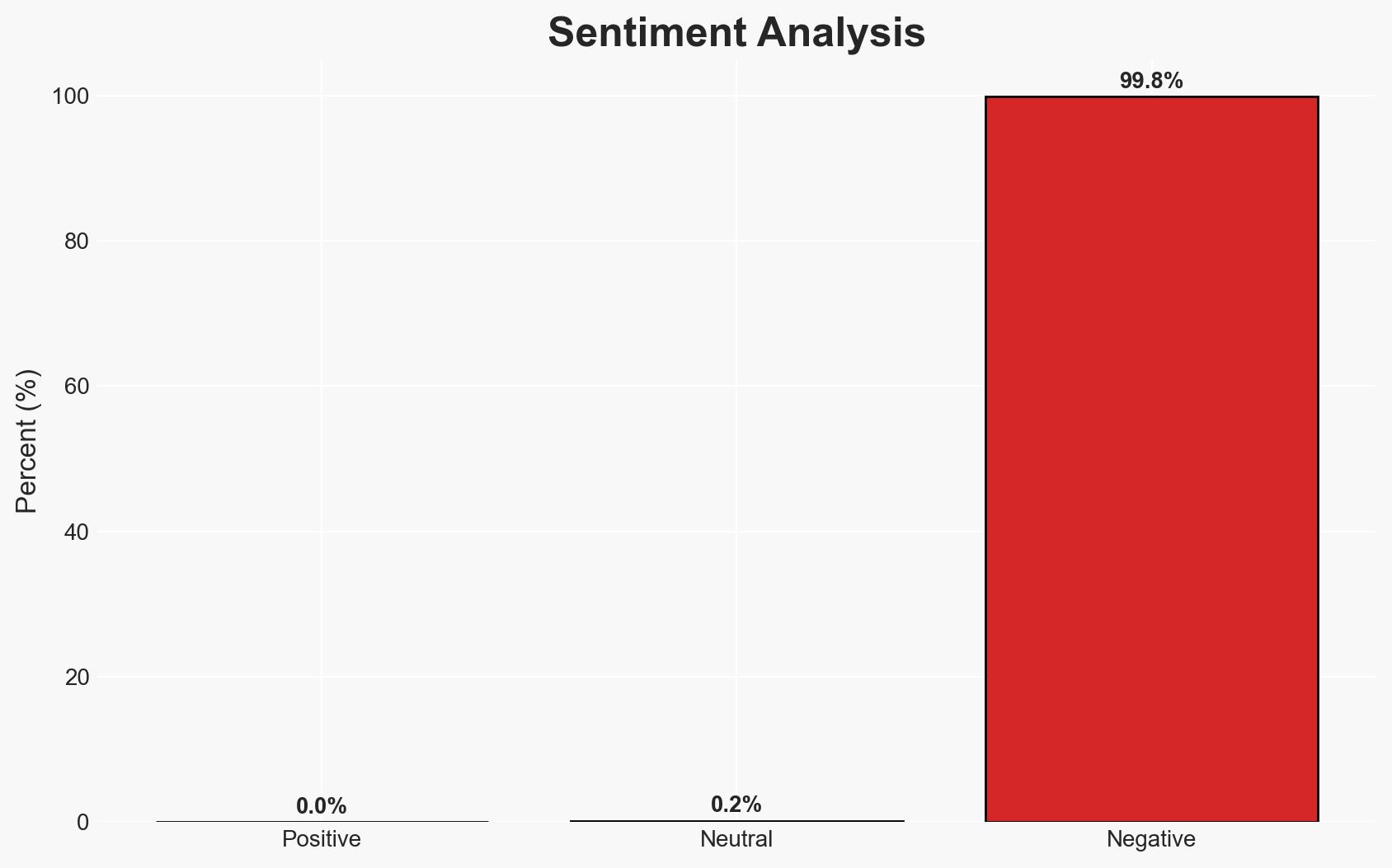
The discovery of vulnerabilities in the Fast Pair protocol affects hundreds of millions of audio devices, posing significant risks of unauthorized access and tracking. The vulnerabilities could allow attackers to hijack devices and track users, impacting both Android and non-Android users. The situation requires urgent attention to mitigate potential security breaches. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the current evidence and ongoing patching efforts.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerabilities in the Fast Pair protocol are primarily due to oversight in security design, which can be rectified through software updates. Supporting evidence includes Google’s acknowledgment and ongoing patching efforts. However, the assumption that all devices will be updated promptly is uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerabilities are indicative of a systemic flaw in the Fast Pair protocol that may require a more fundamental redesign rather than simple patches. This hypothesis is supported by the widespread nature of the issue across multiple manufacturers, suggesting a deeper protocol-level issue.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to Google’s active response and the availability of patches. However, if vulnerabilities persist despite updates, Hypothesis B may gain credence. Key indicators include the effectiveness of patches and any continued reports of exploitation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Fast Pair vulnerabilities can be mitigated through software updates; users will apply updates; the issue is not being exploited at scale.
- Information Gaps: The extent of user awareness and compliance with updates; detailed technical specifics of the vulnerabilities; potential exploitation incidents.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Confirmation bias in assuming patches will be universally effective; potential underreporting of exploitation due to reputational concerns by affected companies.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The vulnerabilities could lead to increased scrutiny of Bluetooth protocols and IoT device security, influencing regulatory and industry standards. Failure to address these issues could erode consumer trust and impact market dynamics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for regulatory action or international scrutiny on tech companies’ security practices.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of espionage or targeted surveillance using compromised devices.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential exploitation by cybercriminals or state actors for data collection or disruption.
- Economic / Social: Possible consumer backlash affecting sales and brand reputation; increased demand for secure alternatives.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage rapid deployment of patches; increase user awareness campaigns; monitor for exploitation reports.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for enhanced security protocols; invest in research for secure IoT frameworks; engage with regulators on standards.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Swift patch adoption and no significant exploitation incidents.
- Worst: Persistent vulnerabilities leading to widespread exploitation and regulatory backlash.
- Most-Likely: Gradual patch adoption with isolated incidents of exploitation prompting ongoing security enhancements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Sony
- Jabra
- JBL
- Marshall
- Xiaomi
- Nothing
- OnePlus
- Soundcore
- Logitech
- KU Leuven University Computer Security and Industrial Cryptography group
- Sayon Duttagupta (Researcher)
- Nikola Antonijević (Researcher)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, IoT vulnerabilities, Bluetooth protocol, consumer electronics, software patching, cyber-espionage, device tracking
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us