Ransomware Attack Hits South Korean Conglomerate Kyowon, Disrupting Operations and Potentially Exposing Data
Published on: 2026-01-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: A ransomware attack disrupted operations at South Korean conglomerate Kyowon
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
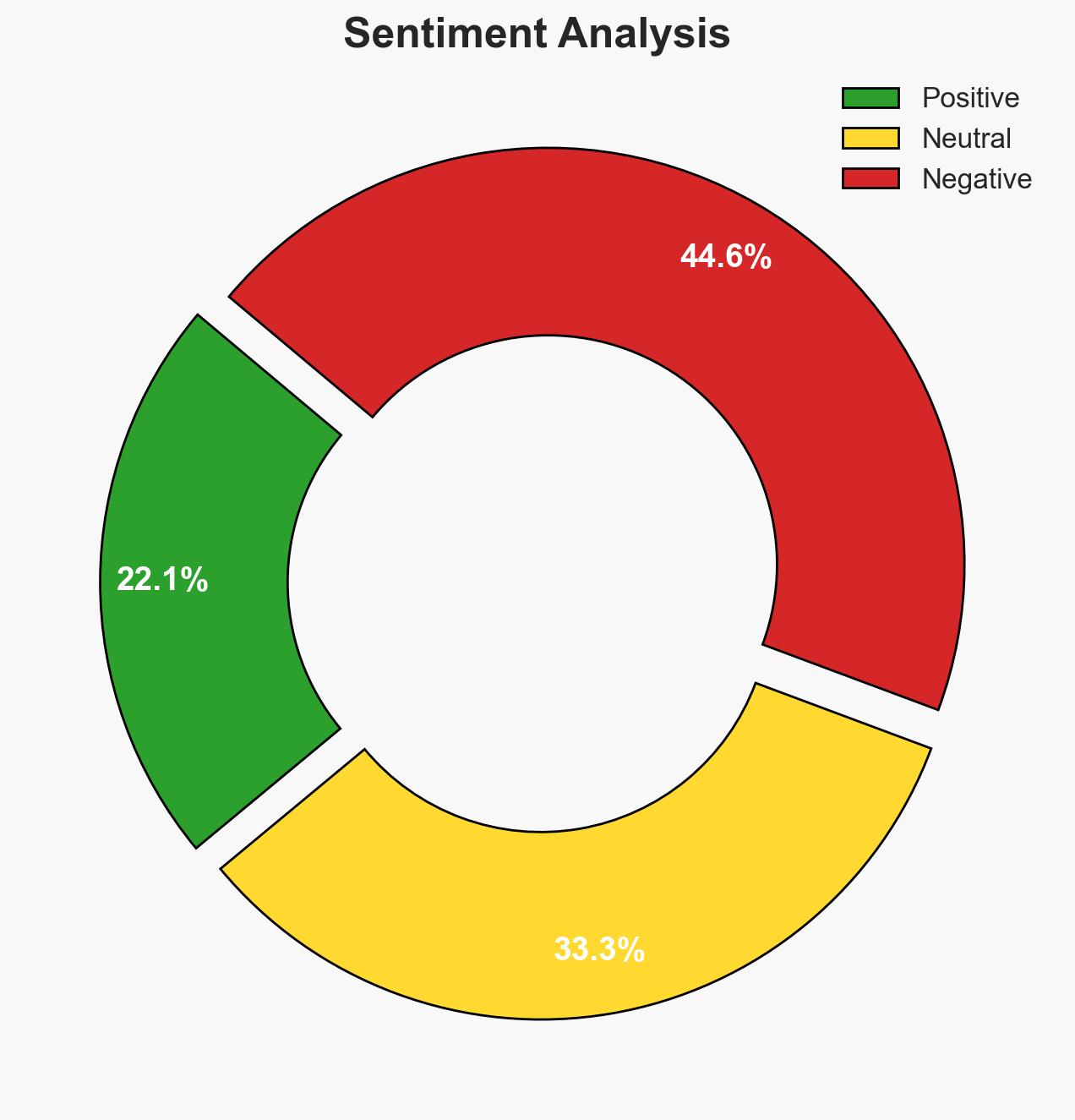
The ransomware attack on Kyowon Group has significantly disrupted its operations and potentially exposed sensitive customer data, affecting millions of accounts. The attack exploited vulnerabilities in Kyowon’s network infrastructure, impacting numerous subsidiaries. The absence of a claim of responsibility complicates attribution. Overall confidence in the assessment is moderate, given the ongoing investigation and lack of conclusive evidence regarding the perpetrators.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attack was orchestrated by a financially motivated cybercriminal group exploiting known vulnerabilities in Kyowon’s network. Supporting evidence includes the use of ransomware and extortion attempts. Contradicting evidence is the lack of a claim of responsibility, which is atypical for financially motivated groups seeking notoriety.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was conducted by a state-sponsored actor aiming to disrupt South Korean economic activities and gather intelligence. This hypothesis is supported by the scale of the attack and the strategic importance of Kyowon in South Korea’s corporate landscape. However, the use of ransomware and extortion attempts is less typical of state-sponsored activities.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the nature of the attack and the financial extortion attempts, which align with typical cybercriminal activities. Indicators that could shift this judgment include the emergence of a claim of responsibility or evidence of state-sponsored tactics.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Kyowon’s network vulnerabilities were known and exploitable; the attackers had financial motives; the attack was not an isolated incident but part of a broader campaign.
- Information Gaps: The identity of the attackers, the specific vulnerabilities exploited, and the full extent of data compromised remain unknown.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing the attack to cybercriminals due to the use of ransomware; risk of deception if attackers are using false flags to mislead attribution efforts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The Kyowon ransomware attack could have significant implications for South Korea’s cybersecurity posture and corporate sector resilience. If not addressed, similar attacks could proliferate, targeting other key industries.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential strain on South Korea’s international relations if state-sponsored involvement is suspected, leading to diplomatic tensions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased focus on securing critical infrastructure and corporate networks to prevent future attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness and investment in cybersecurity measures; potential for increased cyber defense collaboration with international partners.
- Economic / Social: Economic impact due to operational disruptions and potential loss of consumer trust; possible regulatory changes to enhance data protection.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of Kyowon’s network for further threats, collaborate with cybersecurity experts to patch vulnerabilities, and communicate transparently with affected customers.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop and implement comprehensive cybersecurity strategies, including regular audits and employee training; strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity firms and government agencies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Rapid recovery and improved cybersecurity posture prevent future incidents.
- Worst Case: Further attacks occur, leading to severe economic and reputational damage.
- Most Likely: Gradual recovery with ongoing cybersecurity enhancements and regulatory adjustments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Kyowon Group
- Korea Internet & Security Agency (KISA)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, ransomware, South Korea, corporate security, data breach, cybercrime, network vulnerability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us