Foreign Interference in Iran’s Protests: Analyzing External Influences on Domestic Unrest
Published on: 2026-01-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Iranian unrest The role of foreign interference
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
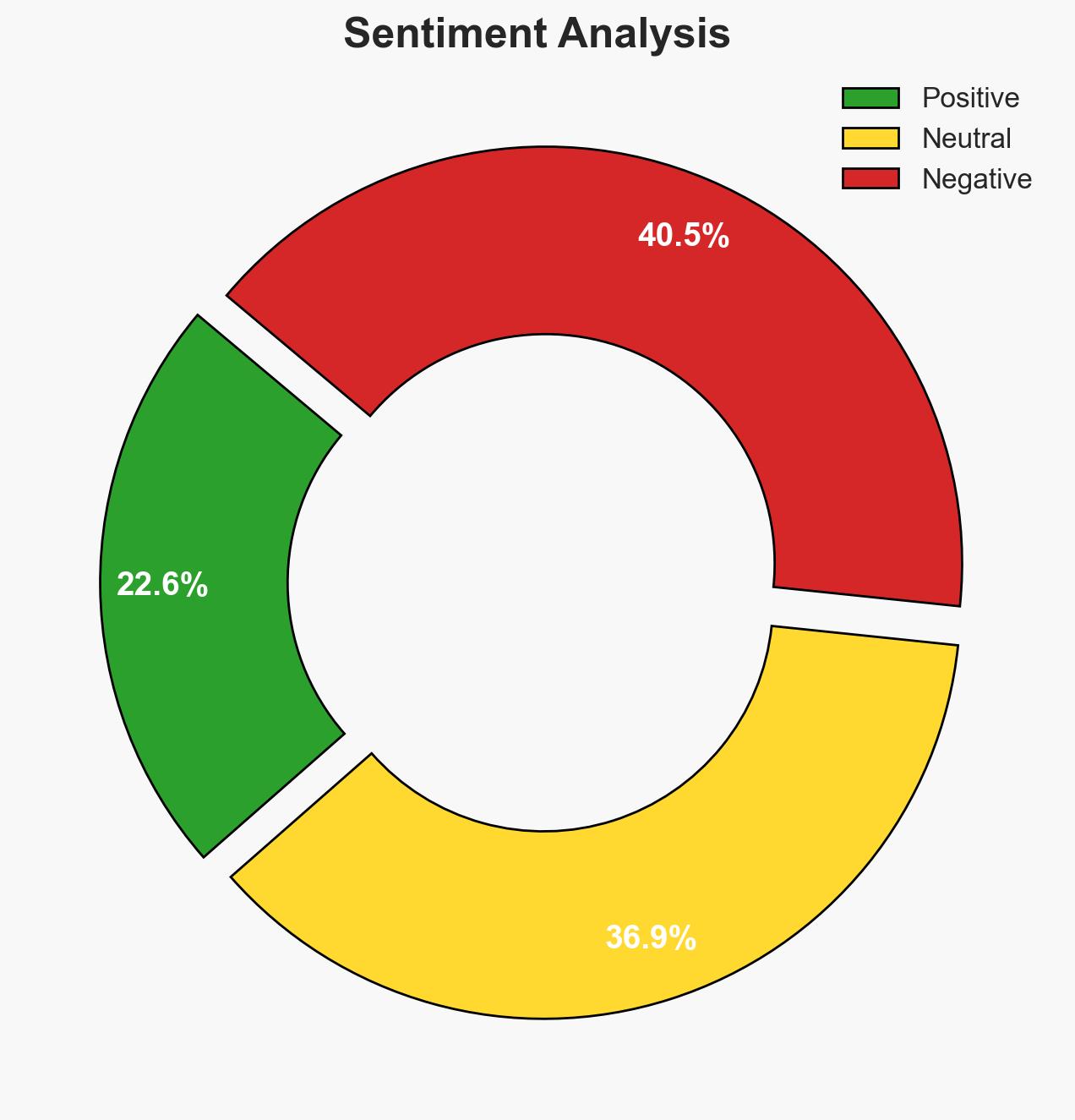
Recent unrest in Iran, initially driven by economic grievances, has reportedly been exacerbated by foreign interference, leading to increased violence and instability. The most likely hypothesis is that external actors are leveraging domestic discontent to destabilize the Iranian regime. This assessment is made with moderate confidence, acknowledging significant information gaps regarding the extent and nature of foreign involvement.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The unrest in Iran is primarily a result of domestic economic issues and public dissatisfaction, with limited or no significant foreign interference. Supporting evidence includes the initial economic grievances and public dissatisfaction. Contradicting evidence includes reports of foreign-backed groups exacerbating the unrest. Key uncertainties involve the scale of foreign involvement.
- Hypothesis B: Foreign actors are actively exploiting domestic unrest to destabilize Iran, coordinating with local groups to escalate violence. Supporting evidence includes reports of organized foreign-backed activities and increased insecurity. Contradicting evidence is the lack of direct attribution to specific foreign entities. Key uncertainties include the identity and objectives of these foreign actors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to reports of organized foreign-backed activities and increased violence. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include concrete evidence of foreign coordination or lack thereof.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Iranian government’s claims of foreign interference are based on credible intelligence; domestic unrest is primarily driven by economic factors; foreign actors have the capability and intent to destabilize Iran.
- Information Gaps: Specific identities and objectives of foreign actors; concrete evidence of foreign coordination; the scale of domestic support for unrest.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Iranian government reports to externalize blame; risk of deception by foreign actors to obscure their involvement; cognitive bias towards attributing unrest to external factors.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing unrest could lead to increased regional instability and further strain Iran’s relations with neighboring countries and global powers. If foreign interference is confirmed, it may provoke retaliatory actions by Iran, escalating tensions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic conflicts and increased regional tensions, particularly with countries perceived as hostile by Iran.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat of internal violence and potential for cross-border terrorist activities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased likelihood of cyber operations and information warfare targeting Iranian infrastructure and public opinion.
- Economic / Social: Further economic destabilization and erosion of social cohesion, potentially leading to prolonged unrest.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence gathering on foreign actors involved; increase diplomatic engagement to de-escalate tensions; monitor social media for signs of coordinated disinformation campaigns.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional alliances and partnerships to counter foreign interference; invest in cybersecurity measures to protect critical infrastructure; promote economic reforms to address root causes of unrest.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful diplomatic resolution and economic stabilization reduce unrest.
- Worst: Escalation into broader regional conflict with significant foreign involvement.
- Most-Likely: Continued unrest with intermittent foreign interference, leading to prolonged instability.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, foreign interference, economic unrest, regional stability, cyber operations, information warfare, counter-terrorism, international law
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us