Iran’s Crypto Market Reaches $7.78 Billion Amid Protests and Economic Instability
Published on: 2026-01-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
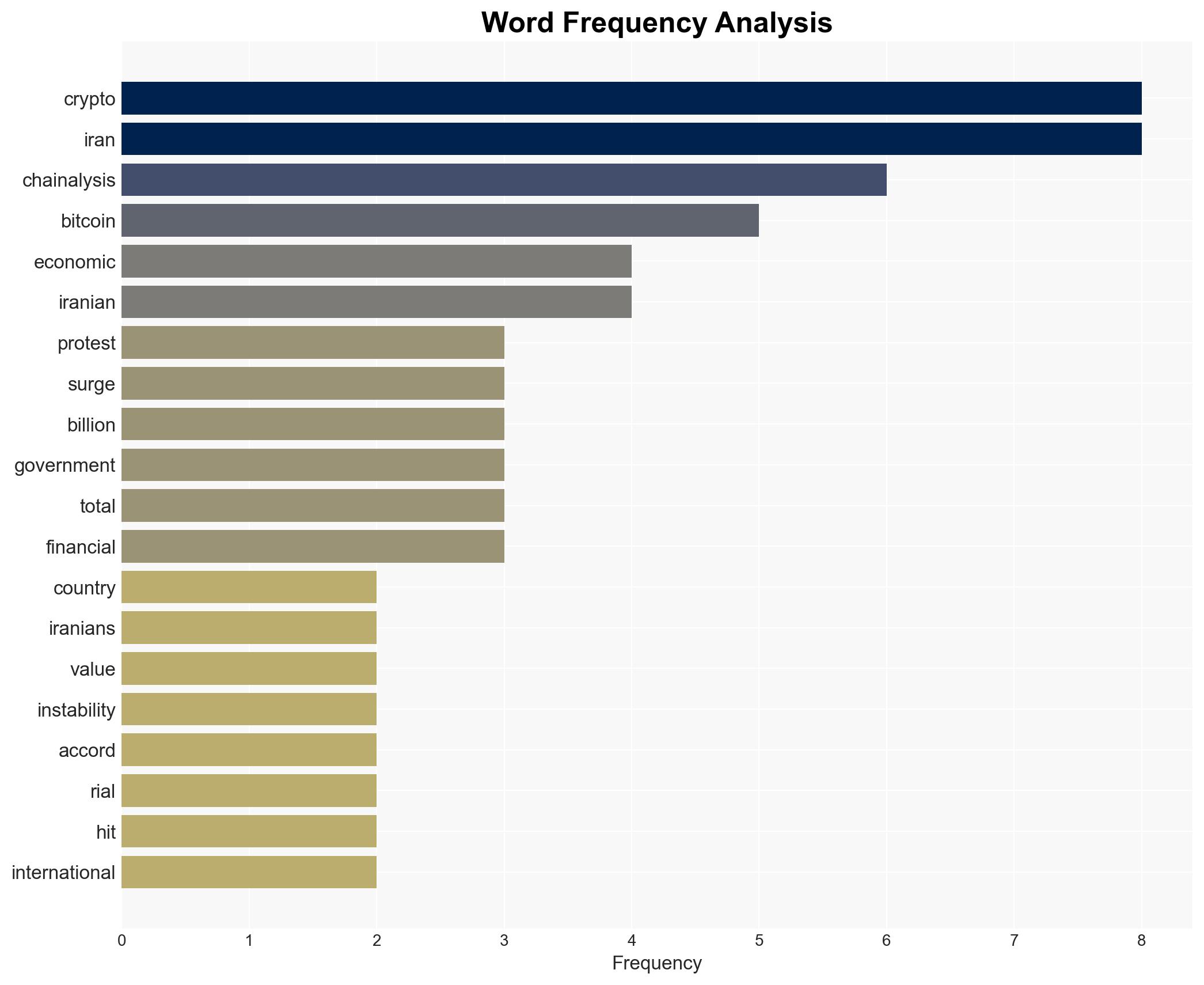
Intelligence Report: Irans crypto ecosystem spikes to 78B amid mass protests Chainalysis
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
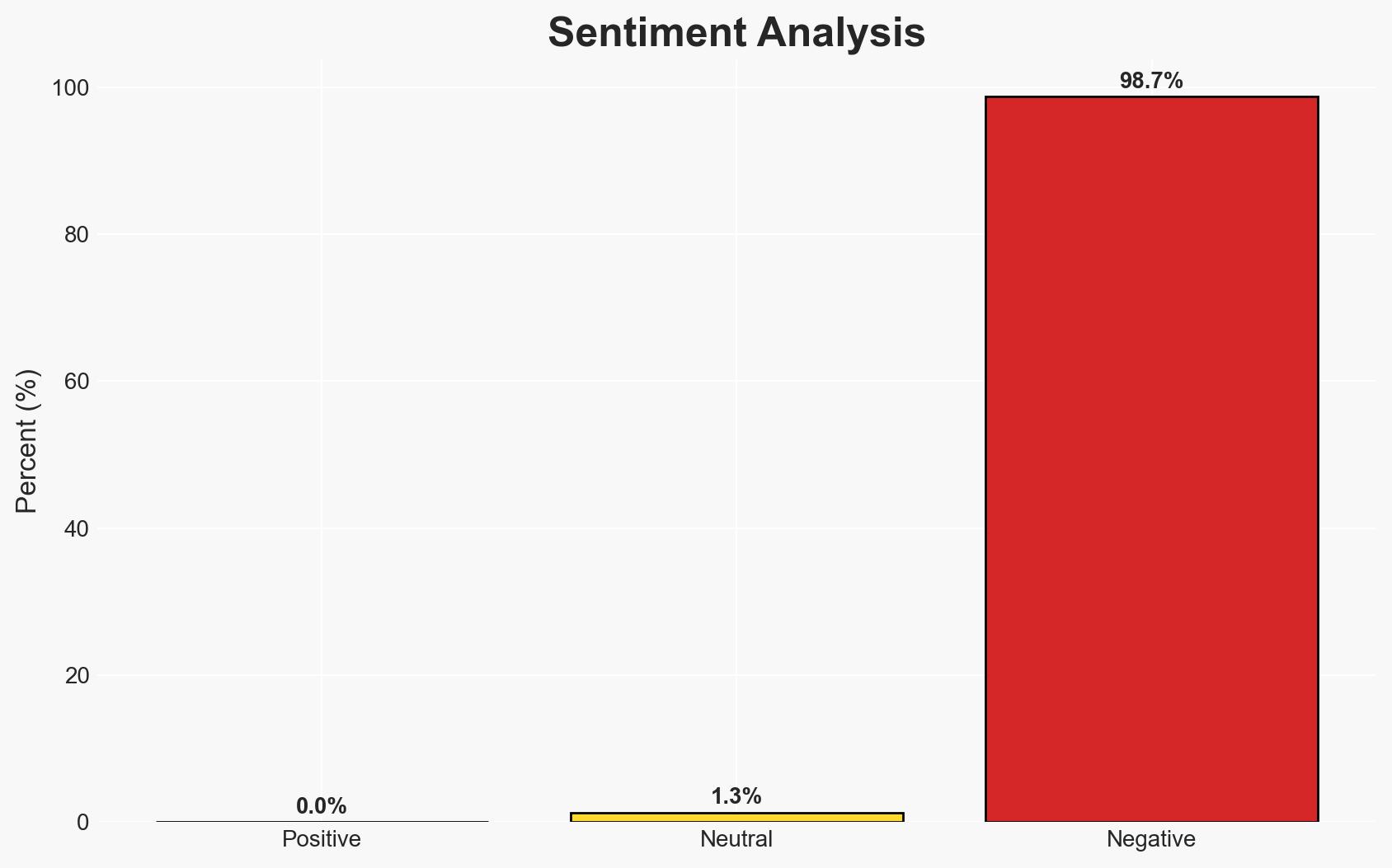
The surge in Iran’s cryptocurrency activity, particularly in Bitcoin, is a response to economic instability and government repression amid mass protests. This trend reflects both a means of financial preservation and a form of resistance against state control. The involvement of the IRGC in crypto activities suggests potential state-level strategic use. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The increase in crypto usage is primarily driven by individual Iranians seeking to preserve wealth and maintain financial autonomy amid economic collapse and state repression. Supporting evidence includes the surge in Bitcoin withdrawals and the collapse of the Iranian rial. Key uncertainties include the exact scale of individual versus state-driven crypto activities.
- Hypothesis B: The rise in crypto activity is significantly influenced by state actors, particularly the IRGC, using cryptocurrencies to circumvent international sanctions and fund operations. Supporting evidence includes the substantial crypto flows associated with IRGC addresses. Contradicting evidence is the broader population’s involvement in crypto activities.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the widespread individual adoption of cryptocurrencies as a response to economic instability and government repression. Indicators that could shift this judgment include further evidence of state-level strategic crypto use or changes in international sanctions enforcement.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Iranian public has sufficient access to cryptocurrency platforms; the IRGC’s crypto activities are primarily for sanction evasion; economic conditions will remain volatile.
- Information Gaps: Detailed breakdown of crypto transactions by individual versus state actors; the extent of government control over crypto exchanges.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in data interpretation from Chainalysis; risk of IRGC using deceptive practices to obscure crypto flows.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The increased use of cryptocurrencies in Iran could lead to further economic destabilization and complicate international sanction efforts. It may also embolden other state and non-state actors to adopt similar strategies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions with countries enforcing sanctions; risk of Iran leveraging crypto for geopolitical maneuvering.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced capabilities for the IRGC and other groups to fund operations discreetly.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber activity related to crypto transactions; potential for misinformation campaigns around economic conditions.
- Economic / Social: Further erosion of trust in national currency; increased social unrest as economic conditions worsen.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of crypto transactions linked to Iranian entities; engage with international partners to address crypto-related sanction evasion.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop capabilities to track and analyze crypto flows; strengthen partnerships with crypto platforms for compliance enforcement.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: International cooperation leads to effective sanction enforcement, reducing IRGC crypto activities.
- Worst: Crypto becomes a primary tool for state and non-state actors in Iran, undermining sanctions and increasing regional instability.
- Most-Likely: Continued individual and state-level crypto usage with periodic international efforts to curb illicit activities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC)
- Chainalysis
- TRM Labs
- Statista
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, cryptocurrency, economic instability, sanctions, Iran protests, IRGC, financial sovereignty, cyber operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us