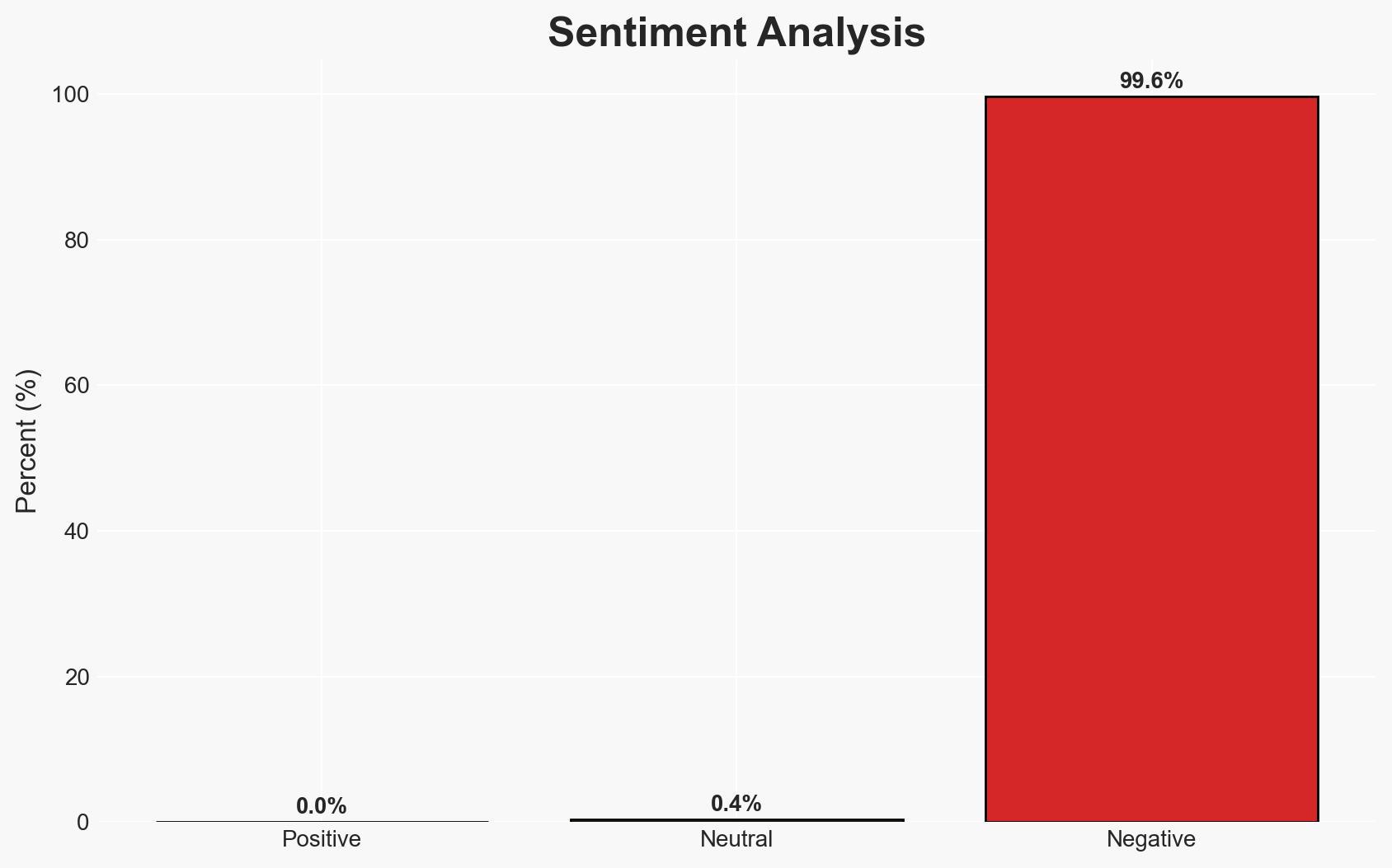
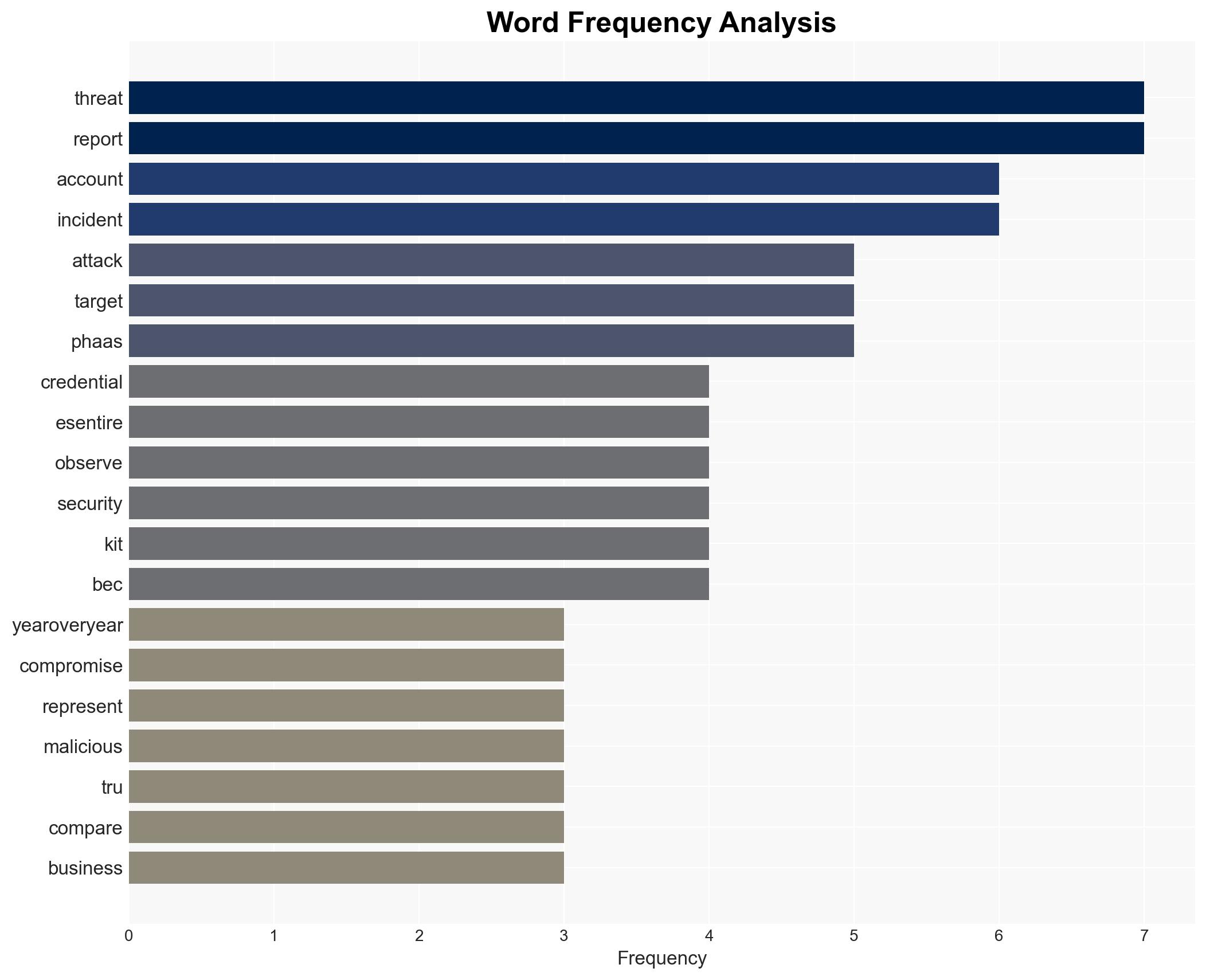
eSentire Reports 389% Increase in Account Compromises in 2025, Dominating Cyber Attack Landscape
Published on: 2026-01-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Account Compromise Surged 389 in 2025 Says eSentire
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The eSentire report indicates a significant surge in account compromises, primarily driven by credential theft and phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) operations. This trend poses a substantial threat to sectors such as finance, real estate, and retail. The most likely hypothesis is that the proliferation of sophisticated PhaaS kits is the primary driver of this increase, with moderate confidence due to existing information gaps and potential biases in reporting.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The surge in account compromises is primarily due to the increased sophistication and availability of PhaaS kits, which are designed to bypass security measures like MFA. This is supported by the reported widespread use of PhaaS kits and their role in facilitating account takeovers.
- Hypothesis B: The increase in account compromises is largely due to a general rise in cybercriminal activity and not specifically linked to PhaaS kits. The decline in BEC incidents and malware threats could indicate a shift in tactics rather than an increase in capability.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the specific mention of PhaaS kits’ role in the majority of account compromises. However, further data on the overall cyber threat landscape could shift this assessment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: PhaaS kits are the primary enabler of the observed increase in account compromises; Microsoft 365 accounts remain a prime target; the reported data accurately reflects broader trends.
- Information Gaps: Detailed breakdown of attack vectors across different sectors; comparative data on non-PhaaS related account compromises.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in eSentire’s reporting due to its business interests; risk of overemphasizing PhaaS kits’ role without corroborating data from other sources.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The surge in account compromises could lead to increased operational costs for businesses as they enhance cybersecurity measures. The trend may also drive regulatory changes and impact international relations if state-sponsored actors are implicated.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state actors are found to be involved in PhaaS operations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Elevated threat environment requiring enhanced vigilance and response capabilities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater emphasis on developing advanced cybersecurity solutions and information-sharing initiatives.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact due to increased cybersecurity spending and loss of consumer trust in digital services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of PhaaS kit developments; enhance MFA and other security protocols; initiate sector-specific threat assessments.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for intelligence sharing; invest in cybersecurity training and awareness programs; consider regulatory updates to address emerging threats.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Successful mitigation of PhaaS threats through improved security measures.
- Worst Case: Continued rise in account compromises leading to significant economic and reputational damage.
- Most-Likely: Gradual adaptation to the threat landscape with periodic spikes in activity as new PhaaS kits emerge.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Spence Hutchinson, senior manager of TRU and lead investigator for the report
- eSentire
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for other individuals/entities.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, credential theft, phishing-as-a-service, business email compromise, threat landscape
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us