Myanmar Launches Defense Against Genocide Allegations at International Court of Justice
Published on: 2026-01-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Myanmar begins defence in landmark genocide case at UN court
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
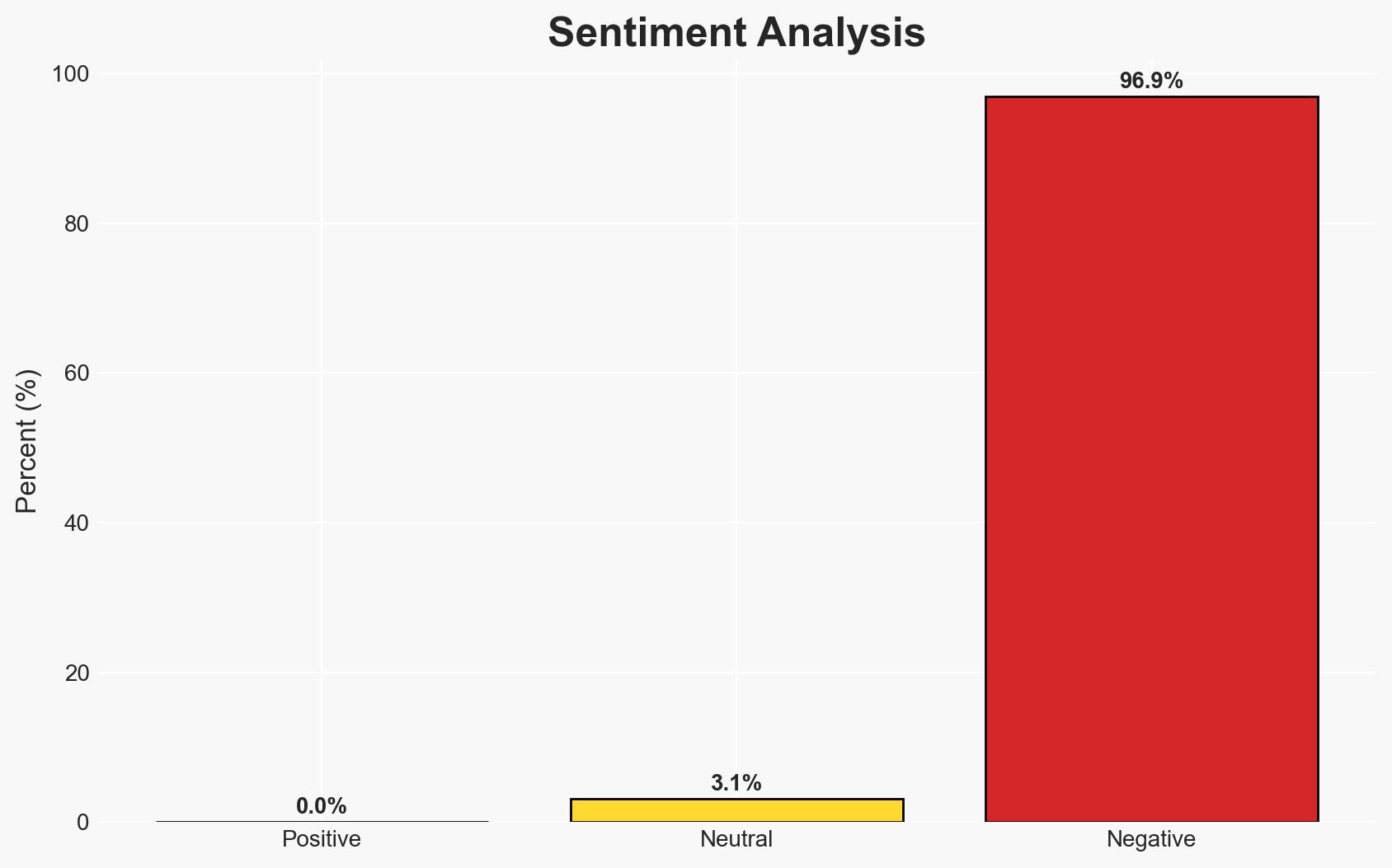
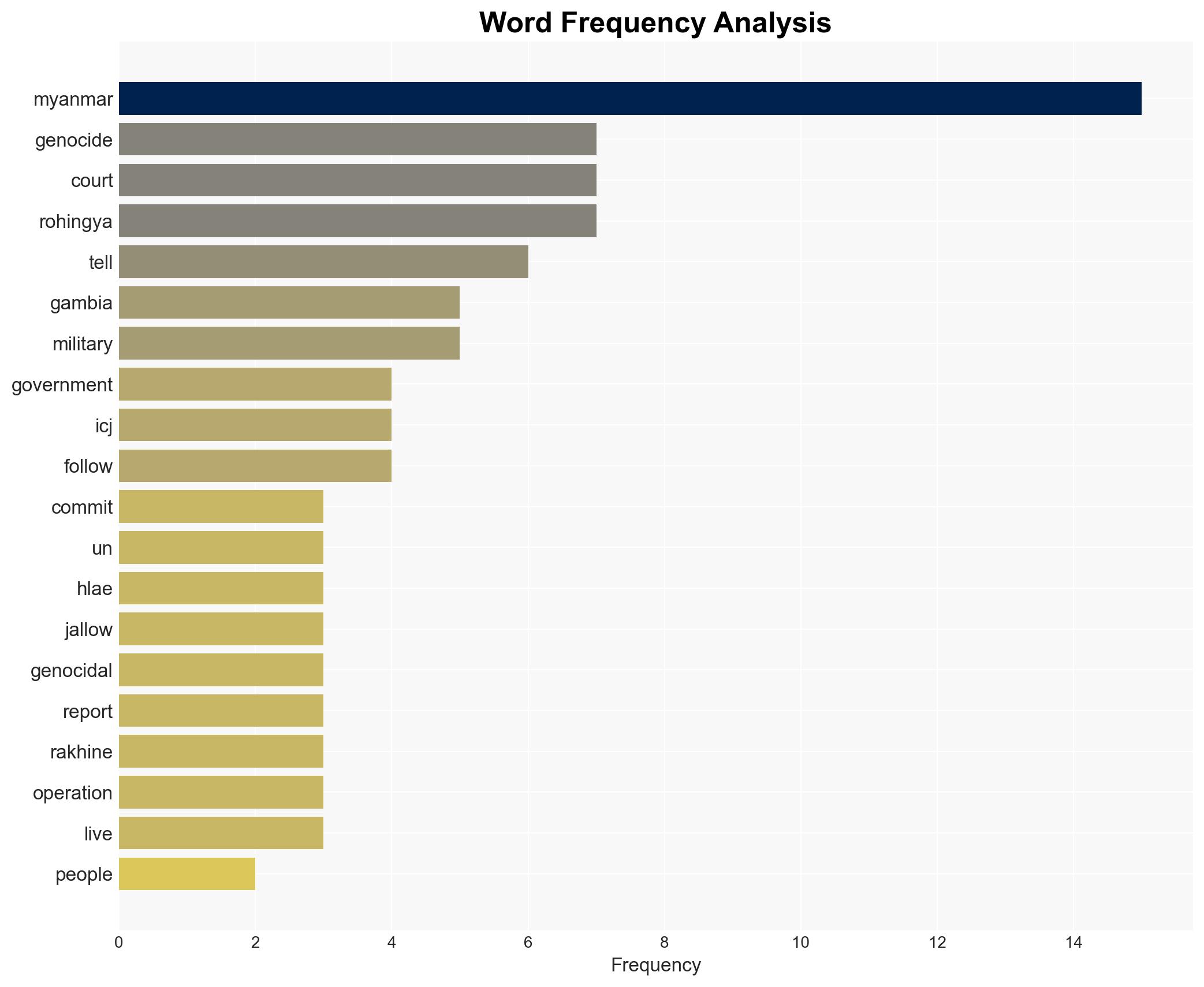
Myanmar is defending itself against genocide allegations at the International Court of Justice (ICJ), primarily arguing that its military actions were counter-terrorism measures. The Gambia, supported by the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, claims these actions were genocidal. The case’s outcome could significantly impact Myanmar’s international standing and the Rohingya’s future. Overall confidence in the current assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Myanmar’s military operations in Rakhine State were legitimate counter-terrorism efforts. This is supported by Myanmar’s consistent narrative of targeting insurgent threats. However, this hypothesis is contradicted by reports of widespread human rights abuses and the scale of displacement.
- Hypothesis B: Myanmar’s actions were genocidal, aimed at eradicating the Rohingya population. This is supported by The Gambia’s arguments and UN reports citing genocidal intent. Contradictions arise from Myanmar’s denial and lack of direct evidence of intent.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to international reports and the scale of the humanitarian crisis. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence from the ICJ proceedings or changes in Myanmar’s internal policies.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The ICJ will base its decision on available evidence without bias; Myanmar’s military actions were primarily in response to security threats; The Gambia’s motivations are purely humanitarian.
- Information Gaps: Detailed evidence of Myanmar’s internal decision-making processes; comprehensive data on the current conditions of Rohingya in Myanmar and Bangladesh.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in international reporting; Myanmar’s narrative may be influenced by state-controlled media; The Gambia’s position may be influenced by political alliances.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ICJ’s decision could affect Myanmar’s international relations and the Rohingya’s future. The case may influence global perceptions of Myanmar’s government and military.
- Political / Geopolitical: Possible international sanctions or diplomatic isolation of Myanmar; increased support for Rohingya from Muslim-majority countries.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Potential escalation of insurgency in Rakhine State; increased regional instability.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened propaganda and misinformation campaigns from both sides; potential cyber operations targeting involved parties.
- Economic / Social: Economic sanctions could impact Myanmar’s economy; continued displacement may strain resources in Bangladesh.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor ICJ proceedings closely; engage with regional partners to assess potential impacts; prepare for humanitarian response in Bangladesh.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential sanctions; strengthen diplomatic channels with ASEAN members; support capacity-building for Rohingya communities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: ICJ ruling leads to peaceful resolution and repatriation efforts, reducing regional tensions.
- Worst: Escalation of violence in Rakhine; increased international isolation of Myanmar.
- Most-Likely: Prolonged legal proceedings with incremental diplomatic and economic impacts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
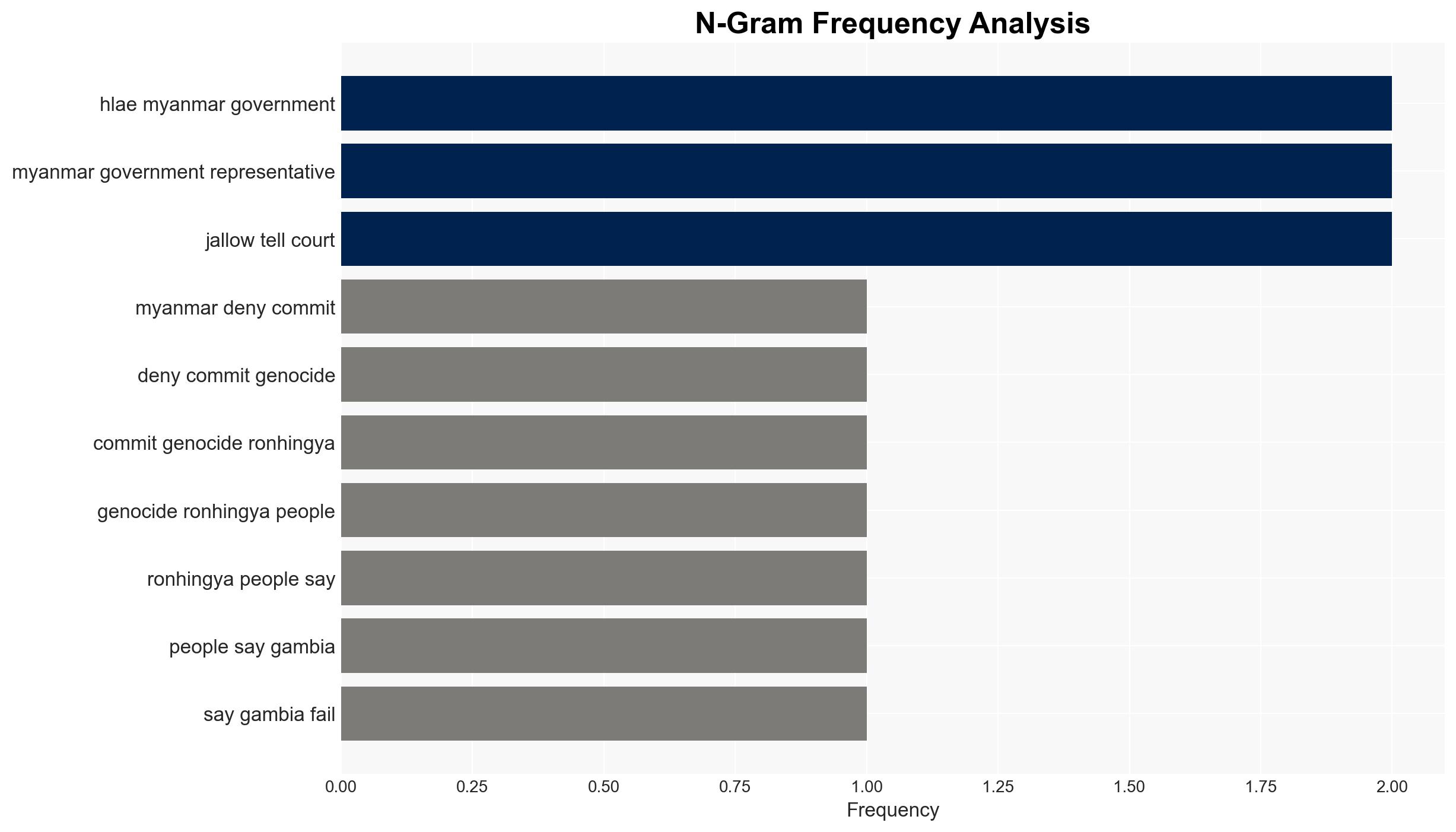
- Ko Ko Hlaing – Myanmar government representative
- Dawda Jallow – The Gambia’s Foreign Minister
- Philippe Sands – Legal representative for The Gambia
- Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, genocide, international law, Rohingya crisis, Myanmar military, human rights, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us