The Gambia initiates genocide case against Myanmar at ICJ for Rohingya persecution
Published on: 2026-01-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Why The Gambia wants Myanmar punished for Rohingya genocide
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
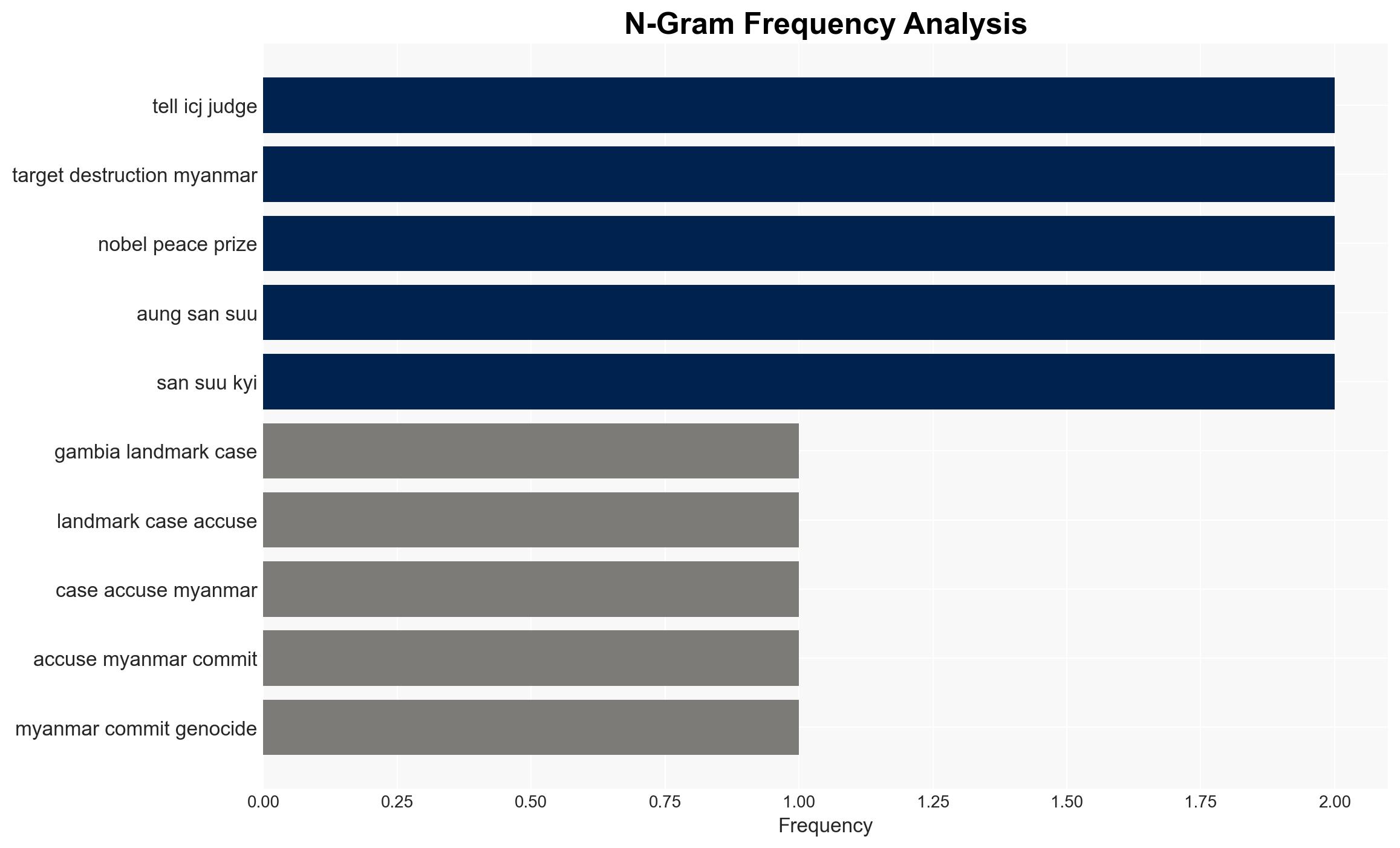
The Gambia has initiated a landmark case against Myanmar at the International Court of Justice (ICJ) for alleged genocide against the Rohingya minority. This action is primarily motivated by The Gambia’s membership in the Organisation for Islamic Cooperation and aims to hold Myanmar accountable under the 1948 Genocide Convention. The case has garnered international support and could influence similar cases globally. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the legal complexities and geopolitical implications.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Gambia’s actions are driven by genuine humanitarian concerns and its commitment to international law, supported by its role in the Organisation for Islamic Cooperation. Evidence includes The Gambia’s historical advocacy for human rights and the involvement of multiple countries supporting the case. However, the timing and geopolitical context remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The Gambia’s case is primarily a strategic move to enhance its international standing and influence within the Organisation for Islamic Cooperation. This is supported by the high-profile nature of the case and the involvement of former Attorney General Abubacarr Tambadou, now in a significant UN position. Contradicting evidence includes the genuine humanitarian crisis faced by the Rohingya.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to The Gambia’s consistent advocacy for human rights and the broad international support for the case. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in The Gambia’s diplomatic posture or new evidence of strategic motivations.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The ICJ will proceed impartially; international support for The Gambia’s case will remain consistent; Myanmar’s government will continue to deny allegations.
- Information Gaps: Details on the timing of the ICJ’s final ruling and the potential reactions from Myanmar and other regional actors.
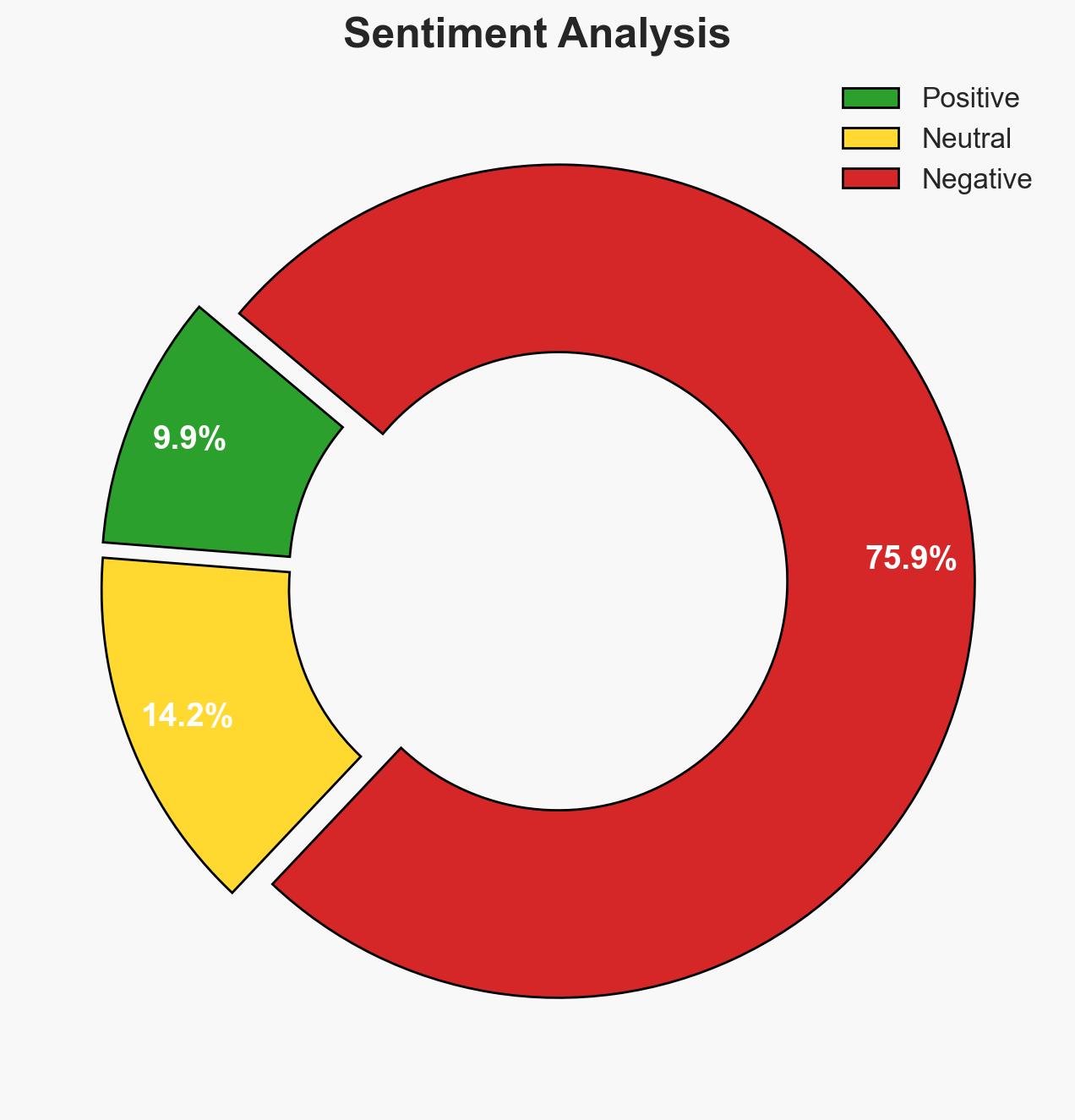
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in international media coverage; risk of Myanmar’s government engaging in information manipulation to counter the allegations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could set a precedent for international legal actions against states accused of genocide, influencing global human rights advocacy and international law enforcement.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential strain on Myanmar’s diplomatic relations and increased scrutiny of its human rights record.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Possible escalation of tensions within Myanmar and increased risk of regional instability.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting entities involved in the case, including misinformation campaigns.
- Economic / Social: Economic sanctions against Myanmar could impact regional trade and economic stability, affecting social cohesion.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor ICJ proceedings and international reactions; engage with key stakeholders to assess potential geopolitical shifts.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential economic impacts; strengthen partnerships with international human rights organizations.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: ICJ ruling leads to accountability and improved conditions for the Rohingya, fostering regional stability.
- Worst: Myanmar rejects ICJ ruling, leading to increased regional tensions and humanitarian crises.
- Most-Likely: Prolonged legal proceedings with incremental diplomatic and economic pressures on Myanmar.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Dawda A Jallow – The Gambia’s Attorney General and Justice Minister
- Abubacarr Tambadou – Former Attorney General of The Gambia, now at the UN
- Organisation for Islamic Cooperation – Supporting entity
- International Court of Justice – Adjudicating body
7. Thematic Tags
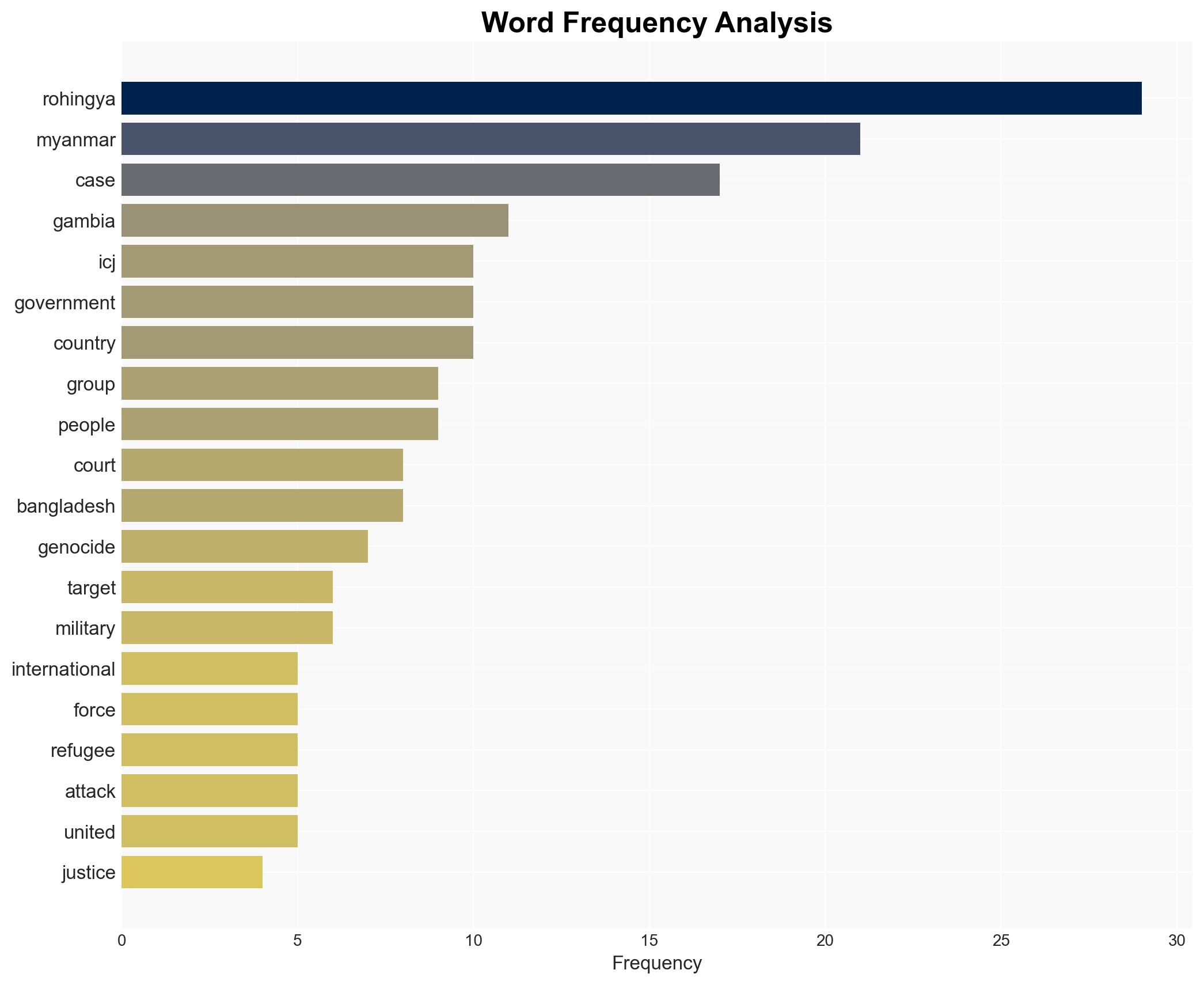
regional conflicts, genocide, international law, human rights, geopolitical strategy, Rohingya crisis, Organisation for Islamic Cooperation, Myanmar
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us