Haiti Faces Severe Security Crisis Amid Gang Violence and Political Instability
Published on: 2026-01-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How safe is Haiti right now
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
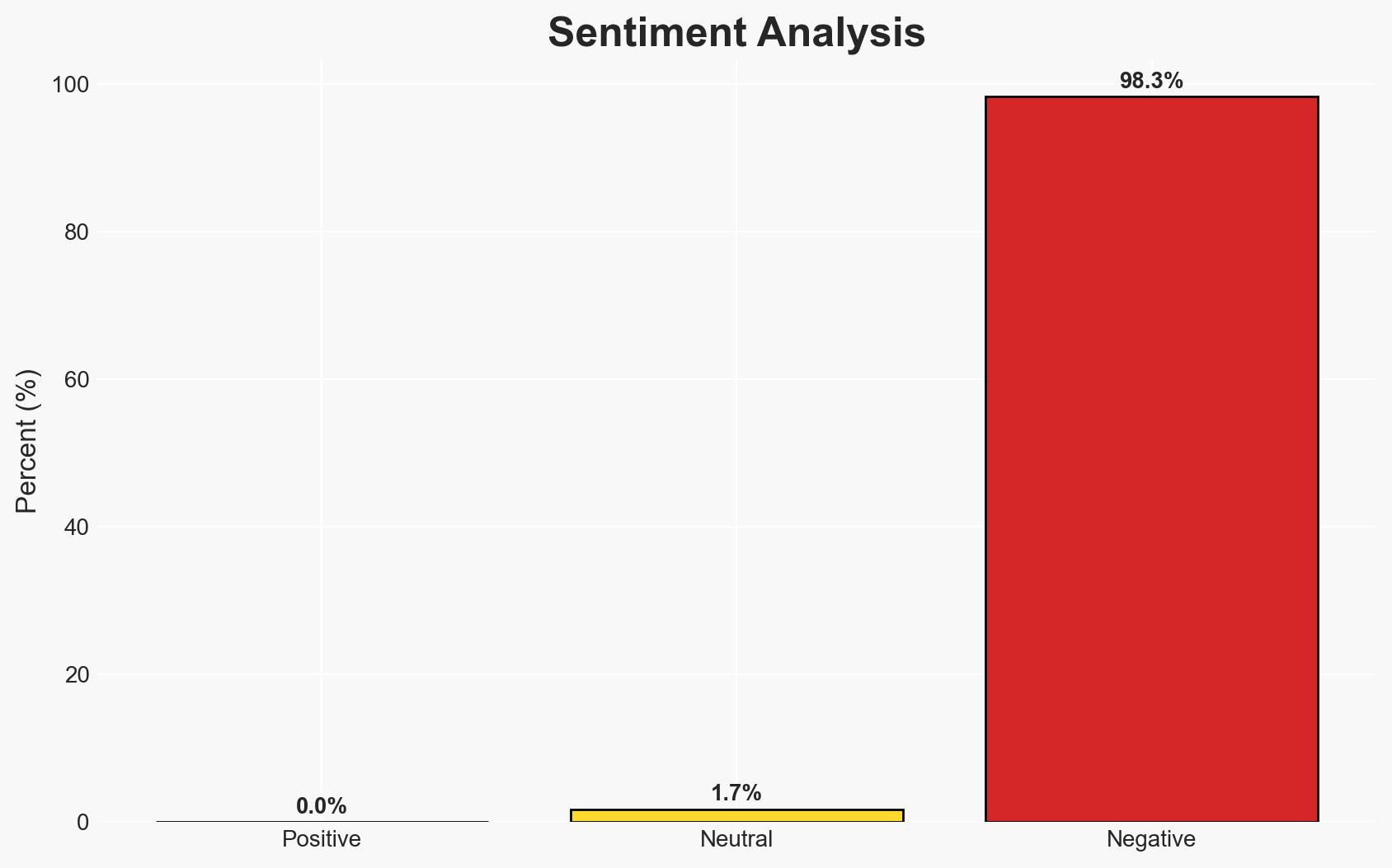
The security situation in Haiti is critically unstable, marked by rampant gang violence and political instability, exacerbated by a humanitarian crisis. The most likely hypothesis is that gangs will continue to exploit the power vacuum, further deteriorating safety conditions. This affects residents, international aid workers, and foreign nationals. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to significant information gaps and potential biases in available data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
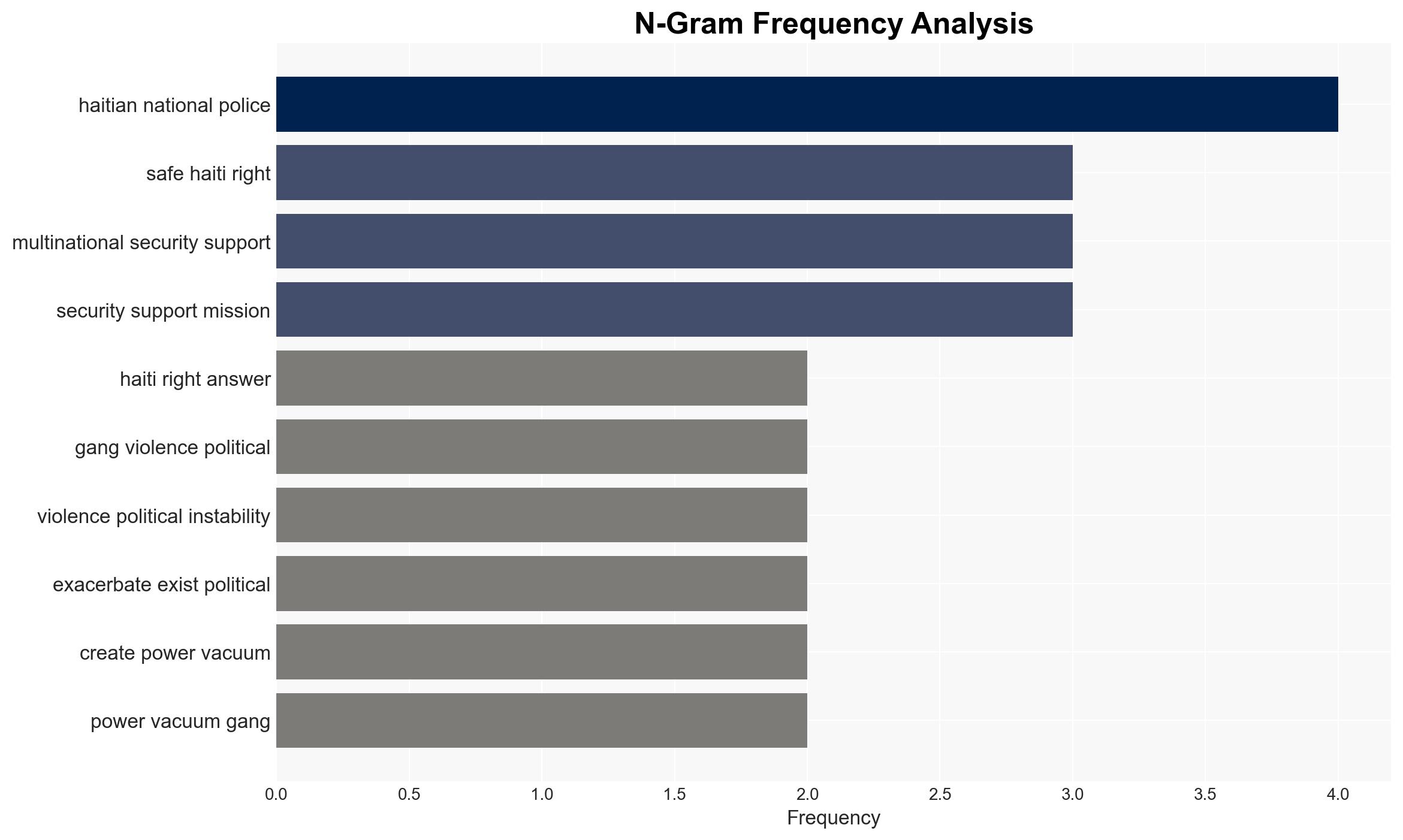
- Hypothesis A: The security situation will continue to deteriorate as gangs expand their control due to the power vacuum and ineffective policing. This is supported by current gang activities and the Haitian National Police’s limited capacity. Key uncertainties include potential international intervention and internal political shifts.
- Hypothesis B: The situation may stabilize if international aid and intervention bolster the Haitian National Police and government institutions. This is less supported due to current logistical challenges and the entrenched nature of gang control.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the ongoing expansion of gang activities and the lack of effective countermeasures. Indicators that could shift this judgment include significant international intervention or a change in local governance dynamics.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Haitian National Police will remain under-resourced; gangs will continue to exploit the political vacuum; international aid will face logistical challenges; local governance will not stabilize in the short term.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the internal dynamics of gangs, the potential for international intervention, and the resilience of local governance structures.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting due to reliance on sources with vested interests; risk of underestimating local resilience or overestimating gang capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing instability in Haiti could lead to further regional destabilization and increased migration pressures. The humanitarian crisis may worsen, impacting regional aid efforts and international relations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international diplomatic pressure or intervention; risk of regional spillover effects.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Escalation of gang violence could lead to more severe security threats, including potential for cross-border criminal activities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Limited direct implications; however, misinformation campaigns could exacerbate tensions or hinder aid efforts.
- Economic / Social: Economic stagnation and social unrest are likely to persist, further undermining stability and development efforts.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence collection on gang activities; enhance coordination with international aid organizations; prepare contingency plans for potential evacuation of foreign nationals.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with regional actors to bolster security efforts; invest in capacity-building for local governance and law enforcement.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Stabilization through effective international intervention and local governance reform.
- Worst: Complete breakdown of order leading to widespread humanitarian disaster.
- Most-Likely: Continued instability with sporadic improvements in security and humanitarian conditions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
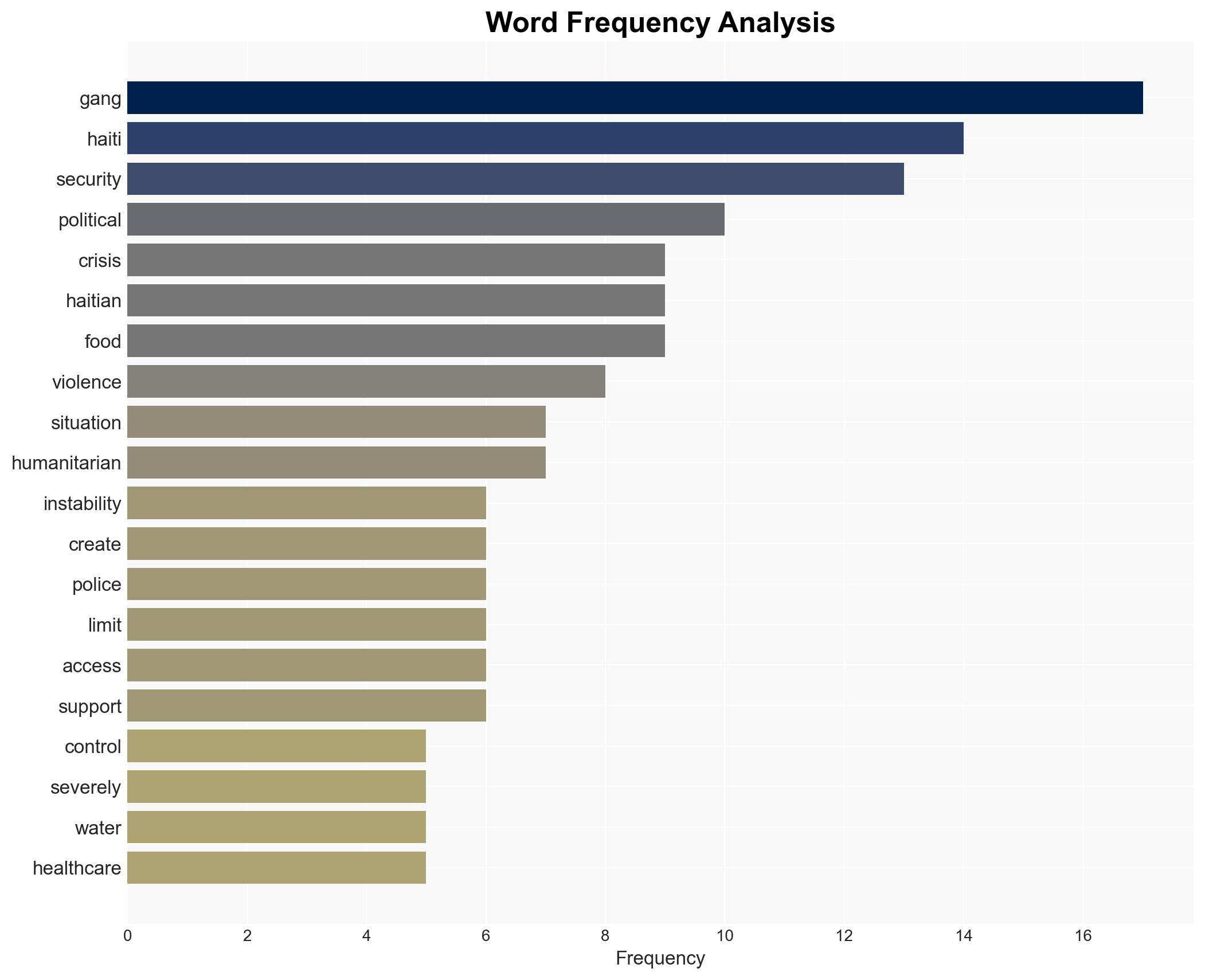
national security threats, gang violence, political instability, humanitarian crisis, international intervention, regional security, law enforcement capacity, economic impact
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us