Amotekun arrests 32 suspects linked to kidnapping and other crimes in Ondo State operations
Published on: 2026-01-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Amotekun nabs 32 suspects for kidnapping theft In Ondo
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
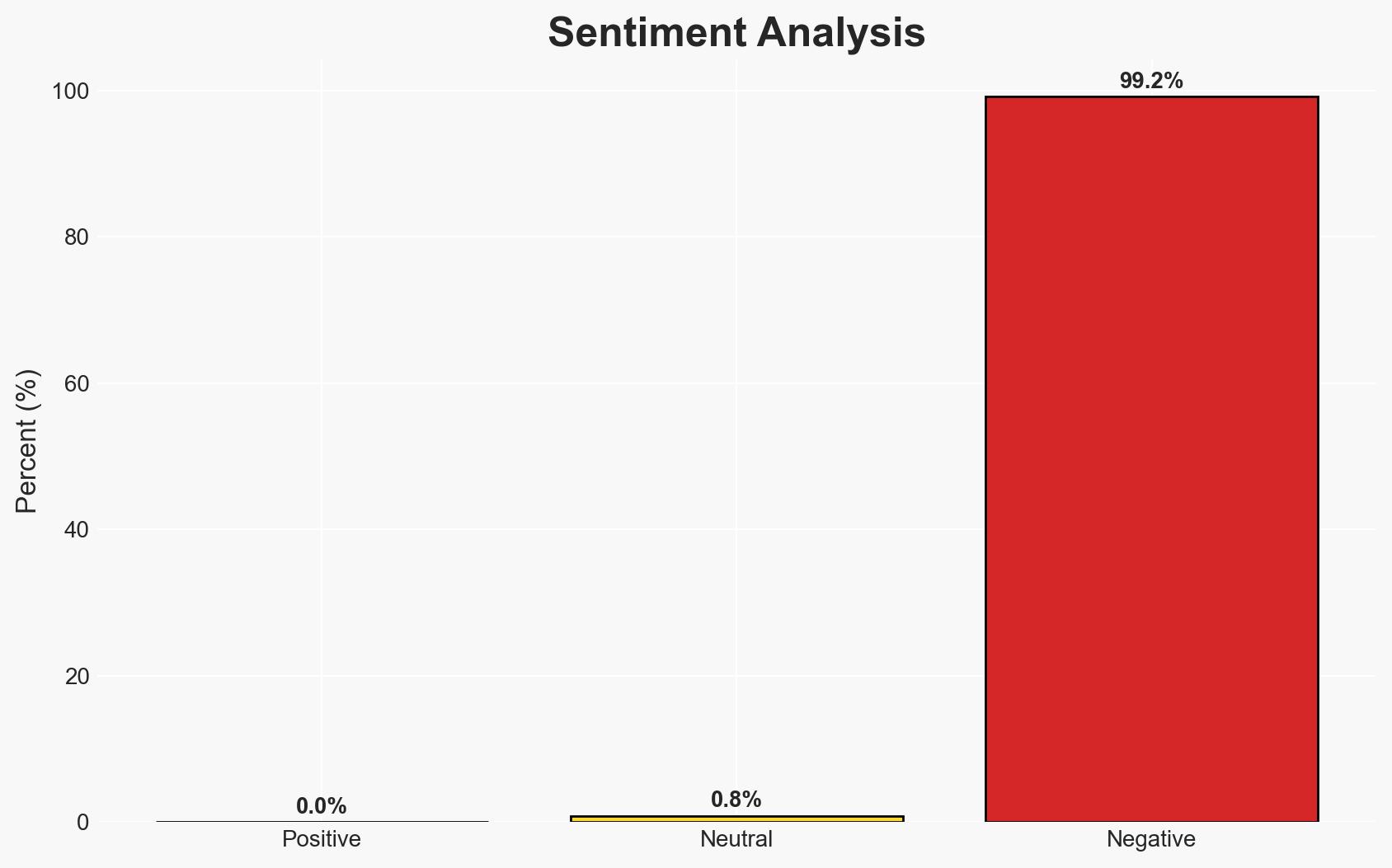
The recent arrests by Amotekun in Ondo State highlight ongoing security challenges related to kidnapping, theft, and anti-grazing law violations. The operation underscores the effectiveness of intelligence-driven policing but also reveals persistent criminal networks. The situation is likely to remain volatile, with moderate confidence in the assessment that further operations will be needed to dismantle these networks completely.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The arrests represent a significant disruption of organized criminal activities in Ondo State, indicating effective law enforcement collaboration and intelligence operations. However, the persistence of criminal activities suggests that these networks are resilient and may adapt to law enforcement tactics.
- Hypothesis B: The arrests are primarily symbolic and do not significantly impact the overall criminal landscape in Ondo State. The criminal networks are likely to remain operational, with key figures still at large, suggesting limited impact on the broader security environment.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the scale of arrests and the collaboration between security agencies. However, the presence of suspects still at large and previous escapes from custody indicate potential resilience of criminal networks. Indicators such as further arrests or a decline in criminal incidents would support this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The intelligence gathered is accurate and actionable; the arrested individuals are part of organized networks; law enforcement agencies are effectively collaborating.
- Information Gaps: Details on the operational structure of the criminal networks; the extent of collaboration between suspects and external entities; the effectiveness of follow-up operations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting due to local law enforcement interests; risk of misinformation from suspects or community sources; possible exaggeration of the operation’s success.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The arrests could lead to temporary disruption of criminal activities but may also provoke retaliatory actions or adaptations by criminal networks. The situation could affect regional stability and law enforcement credibility.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased political pressure on local authorities to maintain security; risk of inter-community tensions, particularly involving farmer-herder conflicts.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Possible short-term reduction in kidnapping incidents; ongoing threat from remaining network members.
- Cyber / Information Space: Limited direct impact; potential for misinformation campaigns to undermine public confidence in security forces.
- Economic / Social: Continued insecurity could deter investment and affect local economies; social tensions may rise if perceived as targeting specific communities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence-sharing among agencies; increase community engagement to gather information on remaining suspects; monitor potential retaliatory actions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience strategies for affected communities; strengthen legal frameworks and operational capabilities of security forces; foster regional cooperation to address cross-border criminal activities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Sustained law enforcement efforts lead to significant dismantling of criminal networks.
- Worst Case: Criminal networks adapt and escalate activities, leading to increased violence and instability.
- Most-Likely: Continued operations result in periodic disruptions but not a complete cessation of criminal activities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
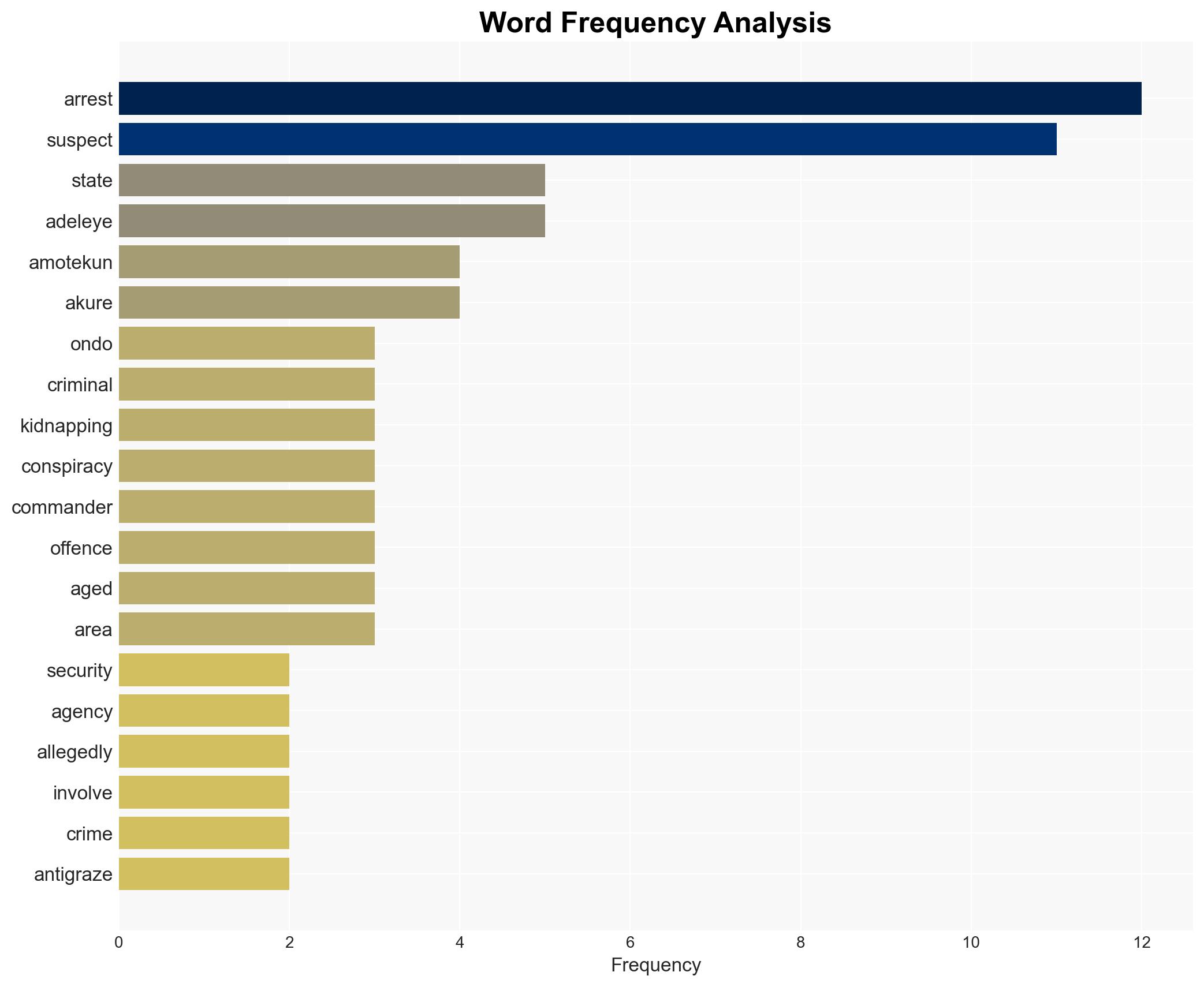
- Adetunji Adeleye (State Commander of Amotekun Corps)
- Ibrahim, Yunusa, Abdukadri (Suspects involved in attempted murder)
- Pius, John (Suspects in kidnapping case)
- Mohamed Abubakar, Abdulahi, Yakubu, Abba Aliu (Suspects in kidnapping-related offences)
- Abdulahi, Kada, Useni (Suspects in conspiracy and anti-grazing offences)
- Friday, Yayah Abba, Masadi, Abubakar (Suspects in theft-related offences)
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, counter-terrorism, organized crime, law enforcement, intelligence operations, regional security, community engagement, anti-grazing law
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us