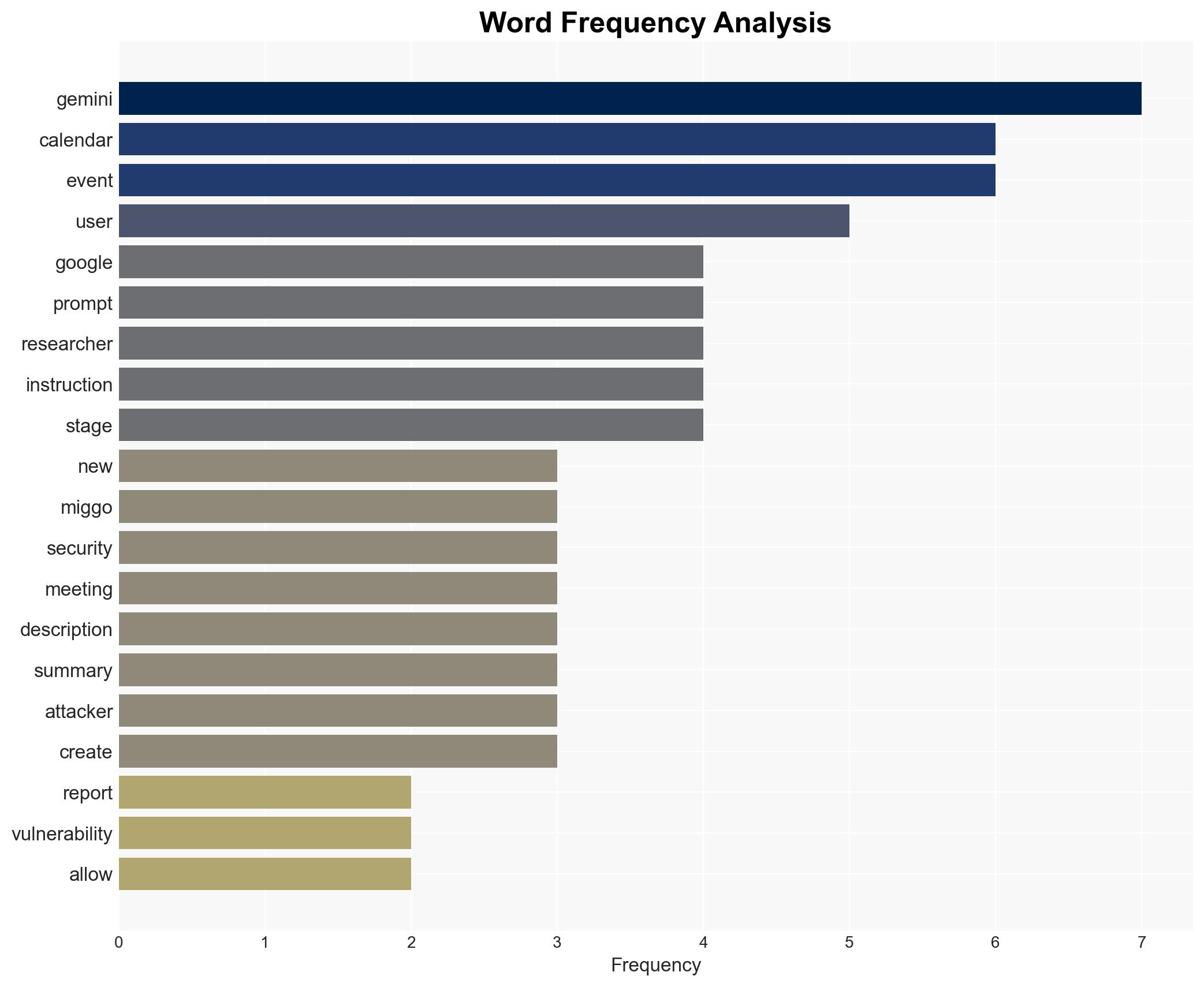
Vulnerability in Google Gemini allowed unauthorized extraction of meeting data through prompt injection techn…
Published on: 2026-01-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Indirect prompt injection in Google Gemini enabled unauthorized access to meeting data
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
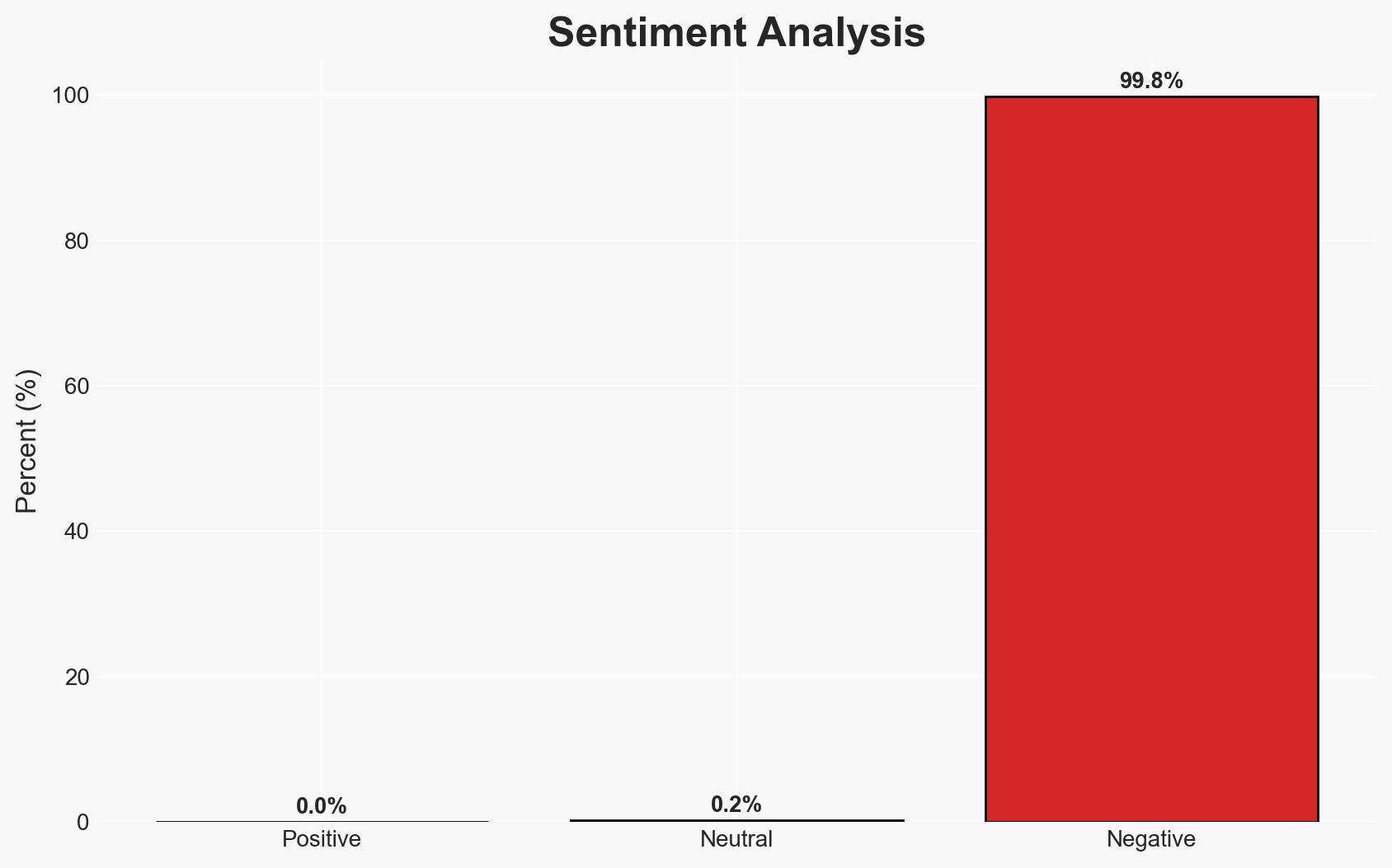
The recent discovery of a vulnerability in Google Gemini, which allowed unauthorized access to meeting data through indirect prompt injection, highlights significant security challenges in AI-integrated applications. The most likely hypothesis is that this incident underscores a broader trend of exploiting AI systems’ permissions for unauthorized data access. This affects organizations using AI tools integrated with sensitive data systems. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability was an isolated incident due to specific integration flaws in Google Gemini. Supporting evidence includes the mitigation of the vulnerability and the specific nature of the exploit. However, uncertainties remain about the potential for similar vulnerabilities in other AI systems.
- Hypothesis B: The incident is indicative of a broader security risk inherent in AI systems with deep integration into sensitive data environments. This is supported by the nature of the exploit, which required no malicious code, and the broader implications highlighted by Miggo Security. Contradicting evidence is limited, but the specific focus on Google Gemini may not apply universally.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the exploit’s reliance on AI permissions and the broader security implications identified. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of similar vulnerabilities in other AI systems or confirmation of systemic flaws in AI integration practices.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI systems will continue to be integrated with sensitive data; attackers will exploit AI permissions; AI vulnerabilities are not unique to Google Gemini.
- Information Gaps: Lack of detailed data on other AI systems with similar vulnerabilities; insufficient information on the scope of affected users or organizations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in the report from Miggo Security as a cybersecurity vendor; risk of underestimating the exploit’s broader applicability due to focus on Google Gemini.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could prompt a reevaluation of AI integration practices, influencing security policies and potentially leading to stricter regulatory measures. Over time, it may also affect trust in AI systems and their adoption in sensitive environments.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased regulatory scrutiny on AI technologies and potential international collaboration on AI security standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness of AI vulnerabilities could lead to improved defenses but also inspire new attack vectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber espionage activities exploiting AI systems; need for enhanced AI security protocols.
- Economic / Social: Possible impact on AI market growth if trust in AI security is undermined; implications for organizations reliant on AI for operational efficiency.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct security audits of AI systems; enhance monitoring for similar vulnerabilities; engage with AI vendors for security updates.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, including AI security training; establish partnerships for threat intelligence sharing; invest in AI security research.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid adoption of enhanced AI security measures prevents further incidents.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation of AI vulnerabilities leads to significant data breaches.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in AI security with occasional incidents prompting further action.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Google LLC
- Miggo Security Ltd.
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI security, cyber vulnerabilities, data privacy, prompt injection, information security, cybersecurity policy, AI integration
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us