Australia’s Parliament approves gun buyback and stricter checks following deadly Bondi Beach shooting
Published on: 2026-01-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Australia passes guncontrol bill after Bondi Hanukkah attack
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Australia’s legislative response to the Bondi Beach attack, involving a national gun buyback program and stricter firearm regulations, aims to enhance national security and social cohesion. The move is likely to face political resistance but reflects a strategic shift towards more stringent gun control. The overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the ongoing legislative process and potential for political opposition.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The gun control legislation will significantly reduce the likelihood of future mass shootings in Australia. This is supported by the historical effectiveness of similar measures in reducing gun violence. However, uncertainties remain regarding the enforcement of new regulations and potential loopholes.
- Hypothesis B: The legislation will have limited impact on preventing mass shootings due to potential non-compliance and the existence of illegal firearms. This is supported by the possibility of resistance from conservative groups and individuals who may circumvent the new laws.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to historical precedents of successful gun control in Australia. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the level of compliance with the buyback program and the effectiveness of background checks.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The government will effectively implement and enforce the new gun control measures; public support for the legislation will remain strong; intelligence agencies will improve coordination to prevent future attacks.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the current distribution of illegal firearms; insights into potential non-compliance rates; effectiveness of intelligence sharing between agencies.
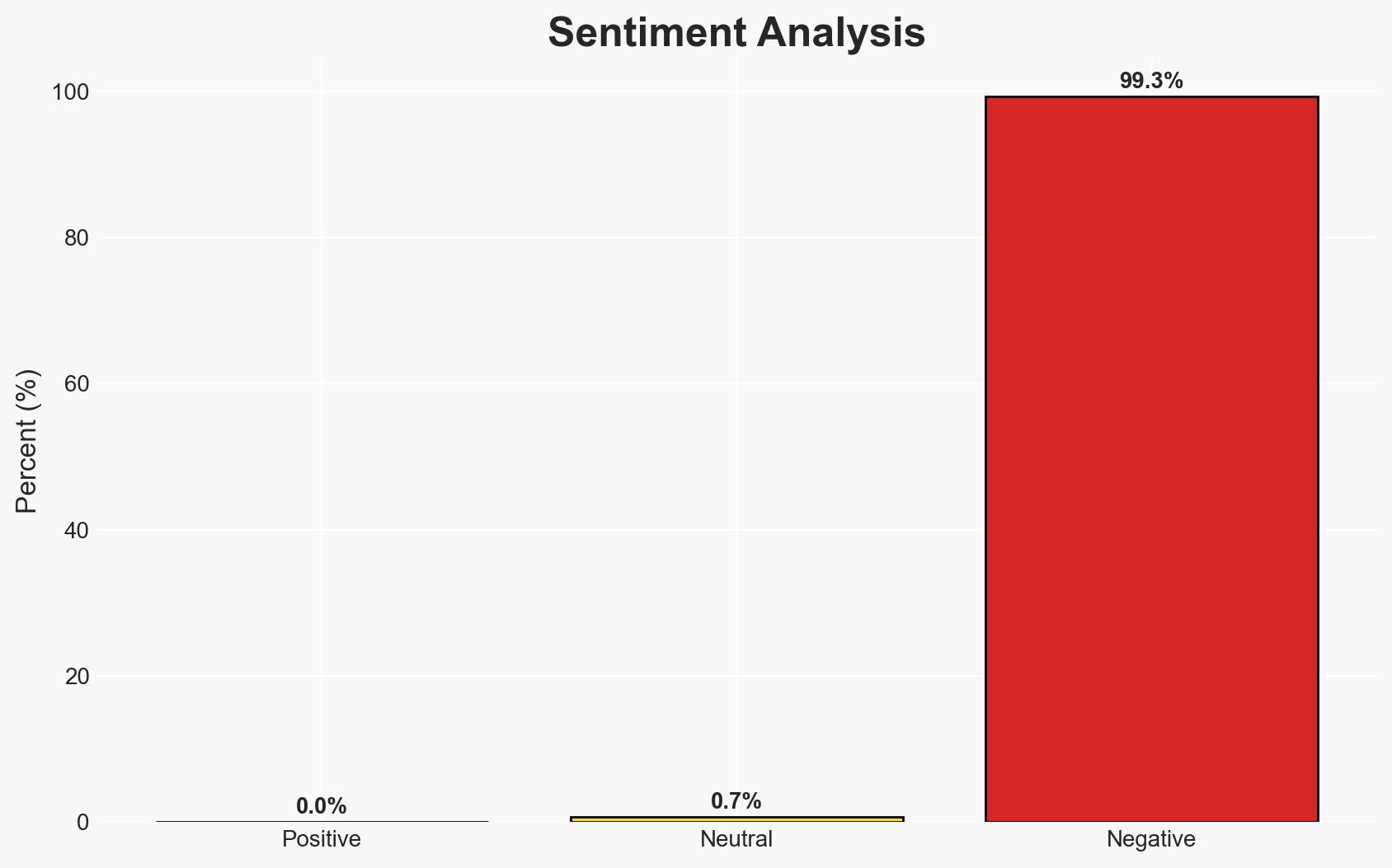
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from political sources; risk of underestimating the adaptability of individuals seeking to circumvent new laws; possible manipulation of public opinion by interest groups.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The legislative measures could lead to significant shifts in Australia’s domestic security landscape and influence broader policy discussions on gun control.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased political polarization and debate over civil liberties versus security.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced focus on preventing radicalization and improving intelligence operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in online discourse and propaganda from both pro- and anti-gun control factions.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on firearms industry; social cohesion may improve if measures are perceived as effective.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor the legislative process and public response; engage with stakeholders to ensure compliance and support.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with community organizations to promote gun safety; enhance intelligence-sharing frameworks.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful implementation and reduction in gun violence; Worst: Significant non-compliance and political backlash; Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security with ongoing political debate.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Anthony Albanese, Prime Minister
- Tony Burke, Home Affairs Minister
- Sajid Akram, Deceased Attacker
- Naveed Akram, Suspected Attacker
- Australian Security Intelligence Organization
7. Thematic Tags
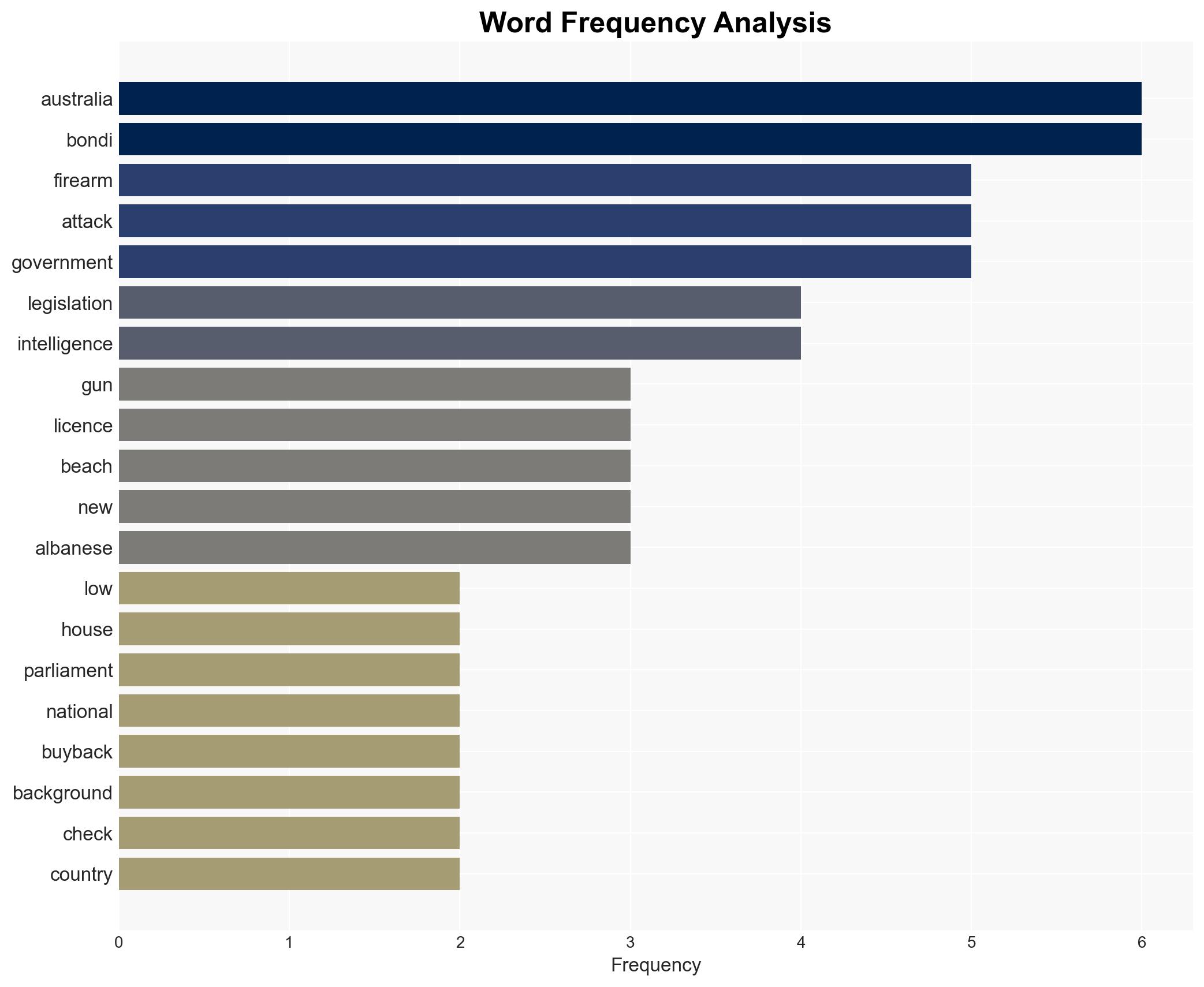
national security threats, gun control, counter-terrorism, legislative process, national security, intelligence coordination, social cohesion, political resistance
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us