US Military Action in Venezuela Signals Erosion of International Law and Global Security Norms
Published on: 2026-01-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The US attack on Venezuela and the collapse of international law
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
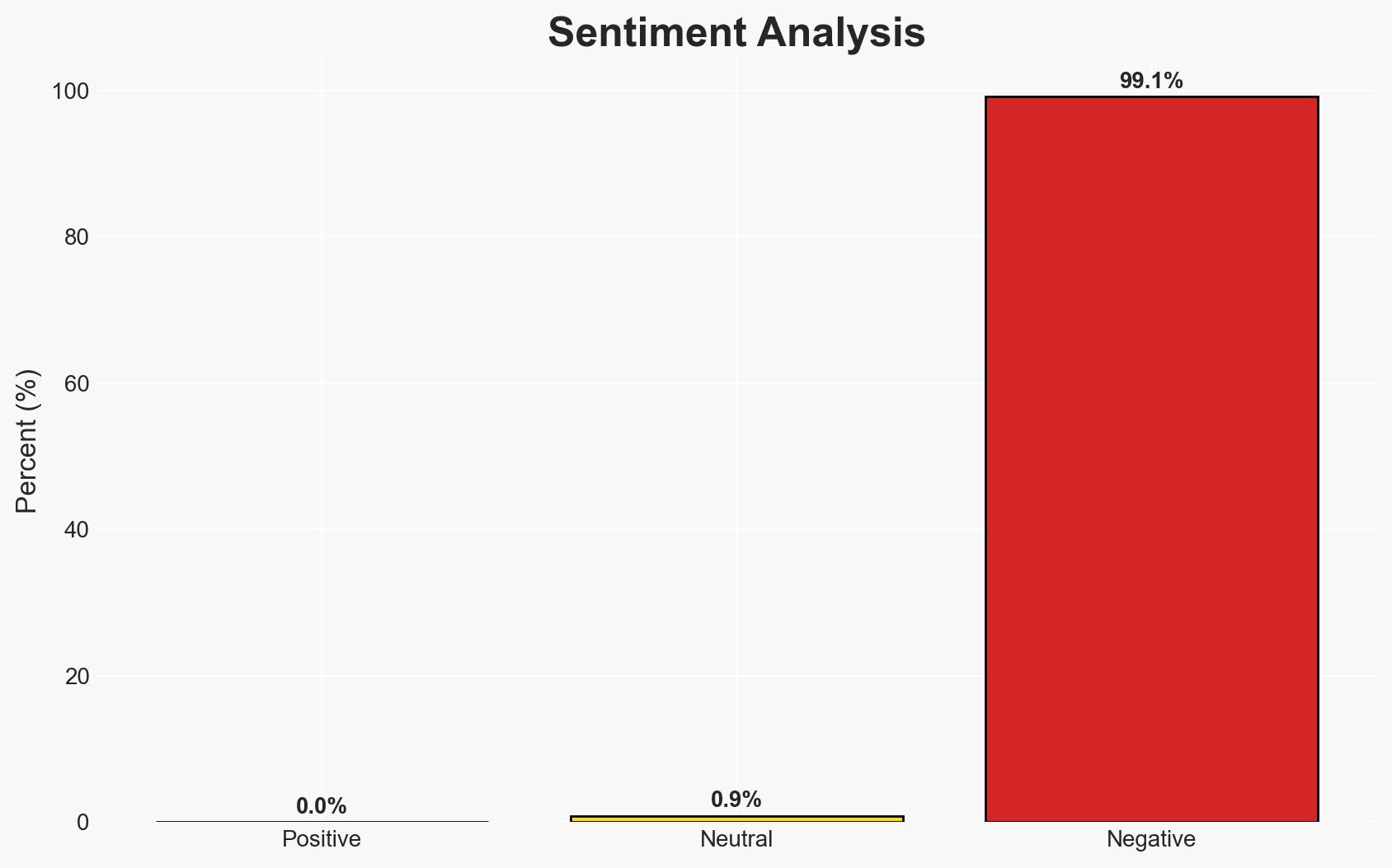
The US intervention in Venezuela represents a significant departure from established international norms, posing risks to global stability and the integrity of international law. The most likely hypothesis is that this action is part of a broader US strategy to assert control over Venezuelan resources and influence regional geopolitics. This development affects Venezuela’s sovereignty, regional stability, and the credibility of international legal frameworks. Overall, there is moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The US intervention is primarily driven by strategic interests in controlling Venezuelan oil resources and influencing regional geopolitics. Supporting evidence includes the capture of Venezuelan leaders and the stated intention to direct Venezuelan policymaking. Contradicting evidence is limited but could include potential diplomatic efforts not visible in the snippet.
- Hypothesis B: The US action is a response to perceived threats from Venezuela, such as narco-terrorism or regional instability. Supporting evidence includes the charges of “narco-terrorism” against Venezuelan leaders. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of a clear, imminent threat to justify such an intervention under international law.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the overt economic and political objectives stated by US leadership. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of imminent threats from Venezuela or substantial international support for the US actions.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The US has strategic interests in Venezuelan oil; International law is being selectively applied; Venezuela lacks the capacity to effectively counter US actions.
- Information Gaps: Details on international reactions and support for US actions; Evidence of any imminent threats from Venezuela; Internal Venezuelan political dynamics post-intervention.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential US bias in framing the intervention as a security measure; Risk of Venezuelan propaganda to delegitimize US actions; Possible manipulation of international narratives by both parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased geopolitical tensions, undermine international legal norms, and destabilize the region. The erosion of trust in international institutions may embolden other states to act unilaterally.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for regional alliances to shift; increased anti-US sentiment in Latin America.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of asymmetric responses from Venezuela or allied non-state actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting US interests; information warfare to shape international perceptions.
- Economic / Social: Disruption in oil markets; potential humanitarian crises due to political instability in Venezuela.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence collection on regional reactions; engage diplomatically with key international stakeholders to manage fallout.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential cyber threats; strengthen regional partnerships to mitigate geopolitical risks.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Stabilization and diplomatic resolution; Worst: Escalation into broader conflict; Most-Likely: Prolonged instability with sporadic diplomatic engagements. Triggers include changes in US domestic policy, regional alliances, or significant international interventions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Nicolas Maduro, Cilia Flores, US Special Forces, President Trump, Chevron, Exxon Mobil, ConocoPhillips
7. Thematic Tags
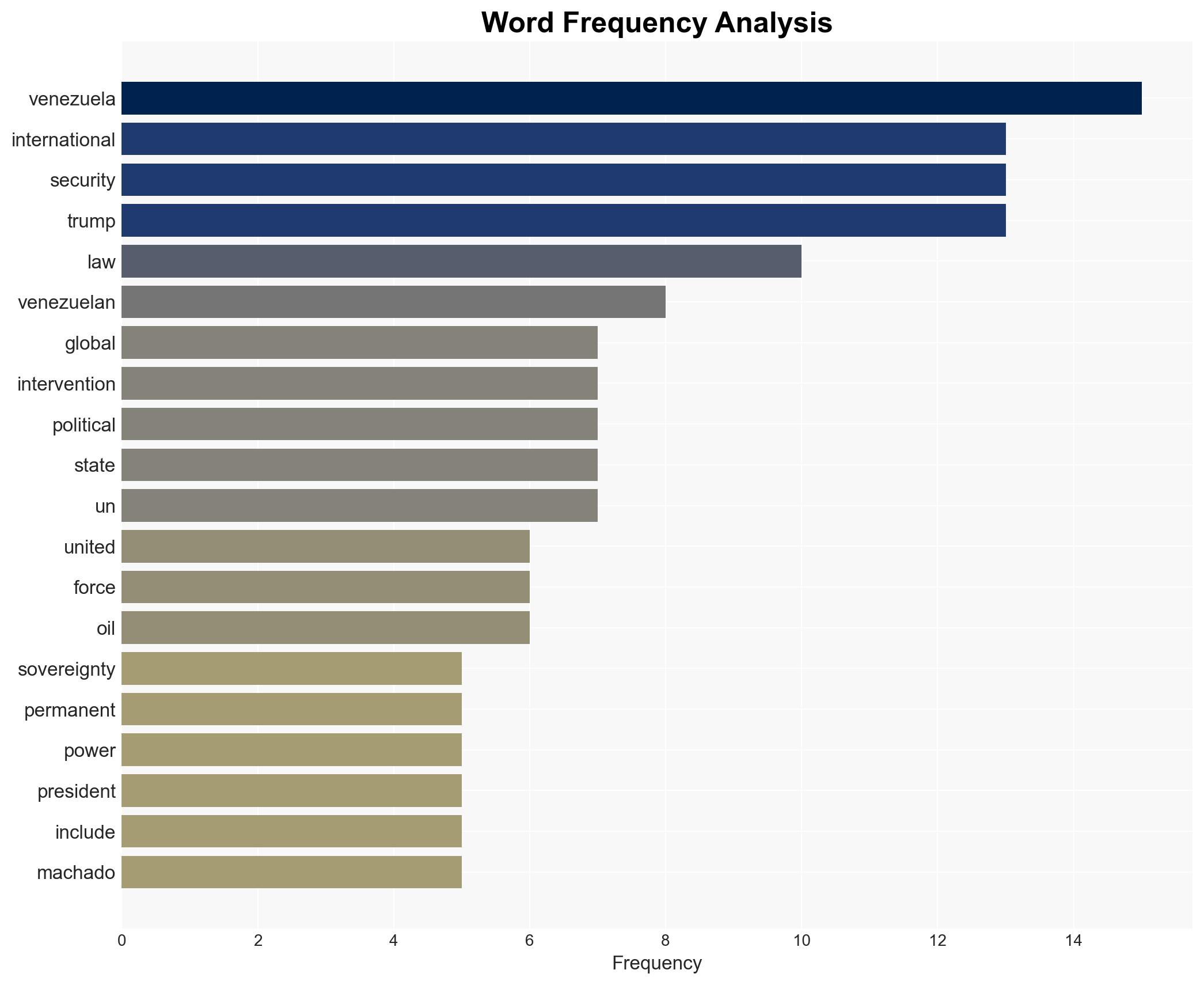
national security threats, international law, US foreign policy, Venezuela, geopolitical strategy, oil resources, sovereignty, regional stability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Empirical → systemic → worldview → myth layers.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us