Yemen Faces Escalating Conflict and Humanitarian Crisis Amidst Aid Cuts and Intensified Airstrikes in 2026
Published on: 2026-01-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Yemen on the brink War famine and the collapse of aid in 2026
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Yemen is experiencing a severe humanitarian crisis exacerbated by increased military offensives and the collapse of aid infrastructure. The most likely hypothesis is that external military interventions and internal political fragmentation will continue to destabilize the region, leading to further humanitarian degradation. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to significant information gaps and potential bias in reporting.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The escalation in violence and humanitarian crisis is primarily driven by external military interventions, particularly by Saudi Arabia and its allies, aiming to suppress separatist movements and control regional influence. This is supported by reported increases in airstrikes and blockades. However, the role of internal political dynamics remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The crisis is largely a result of internal political fragmentation and manipulation by regional actors like the UAE, exploiting separatist movements to destabilize Yemen. While there is evidence of Emirati-backed factions’ involvement, the extent of their influence compared to external military actions is less clear.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented increase in military actions by external actors and their direct impact on civilian casualties and humanitarian conditions. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include verified reports of internal political agreements or shifts in regional alliances.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: External military actions are a primary driver of the crisis; humanitarian aid reductions are due to deliberate policy choices; internal political fragmentation is exacerbated by external influences.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the internal political dynamics within Yemen; comprehensive impact assessments of aid reduction; independent verification of casualty figures and military actions.
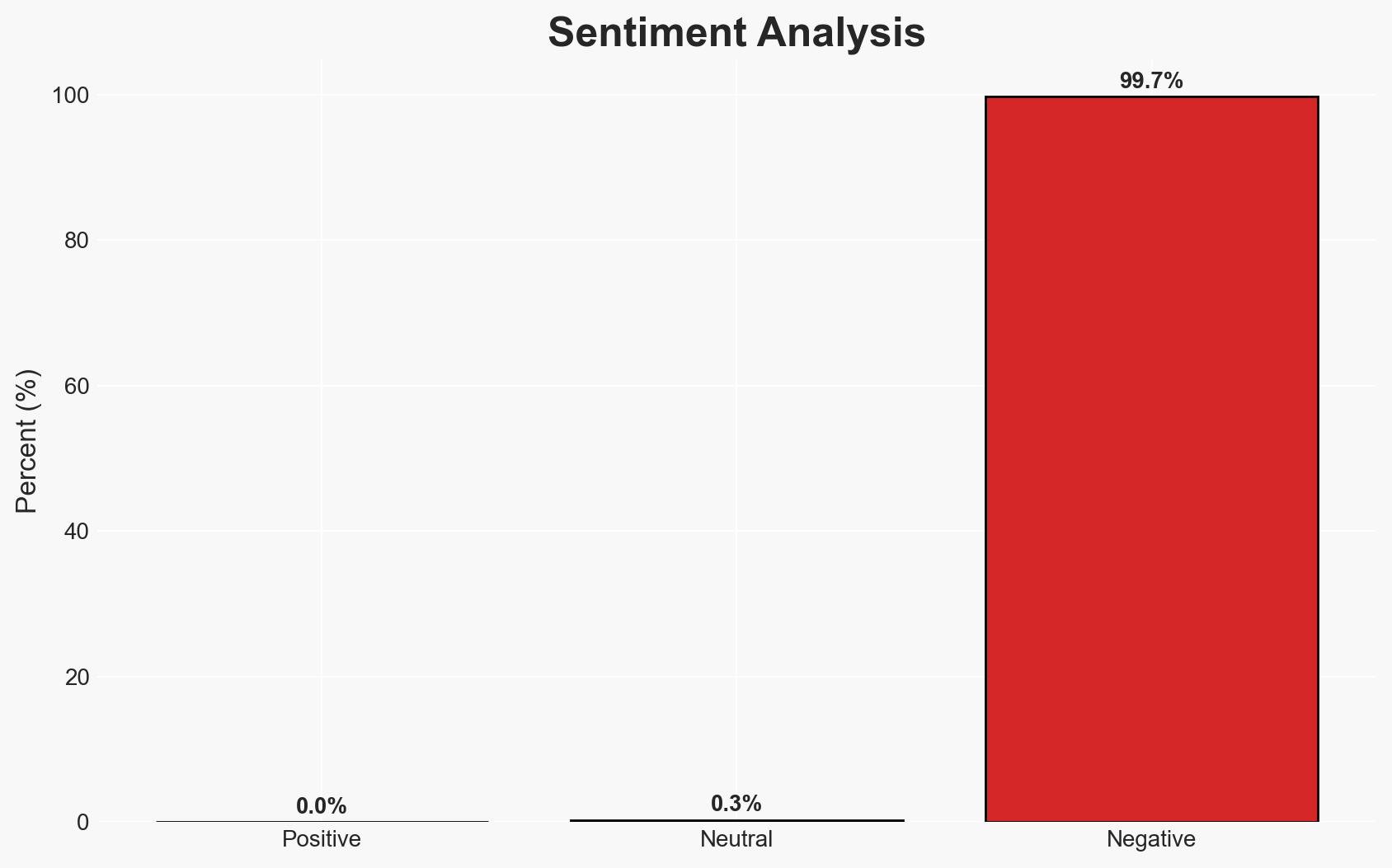
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in source reporting, particularly from parties involved in the conflict; risk of manipulation in casualty reporting and aid impact assessments; possible deception in framing of military actions as defensive.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing crisis in Yemen is likely to further destabilize the region, with significant implications for international security and humanitarian efforts. The interplay between military actions and political fragmentation could lead to prolonged conflict and increased external intervention.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation of regional tensions, particularly involving Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Iran, with broader implications for Middle Eastern stability.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of radicalization and recruitment by extremist groups exploiting the humanitarian crisis and political vacuum.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting information infrastructure to influence public perception and policy decisions.
- Economic / Social: Further deterioration of economic conditions and social cohesion, leading to increased migration and refugee flows, impacting neighboring countries and international aid systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of military and humanitarian developments; engage with regional partners to de-escalate tensions; increase support for independent media and verification mechanisms.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for humanitarian aid delivery; strengthen partnerships with regional actors to support political dialogue; enhance capabilities to counter extremist narratives.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: De-escalation of military actions and resumption of aid, leading to stabilization.
- Worst: Intensification of conflict and complete collapse of aid infrastructure, resulting in widespread famine and regional instability.
- Most-Likely: Continued conflict with intermittent aid disruptions, maintaining a high level of humanitarian need.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates (UAE)
- Southern Transitional Council (STC)
- Houthi-led government
- Israel
- United States
- United Kingdom
7. Thematic Tags
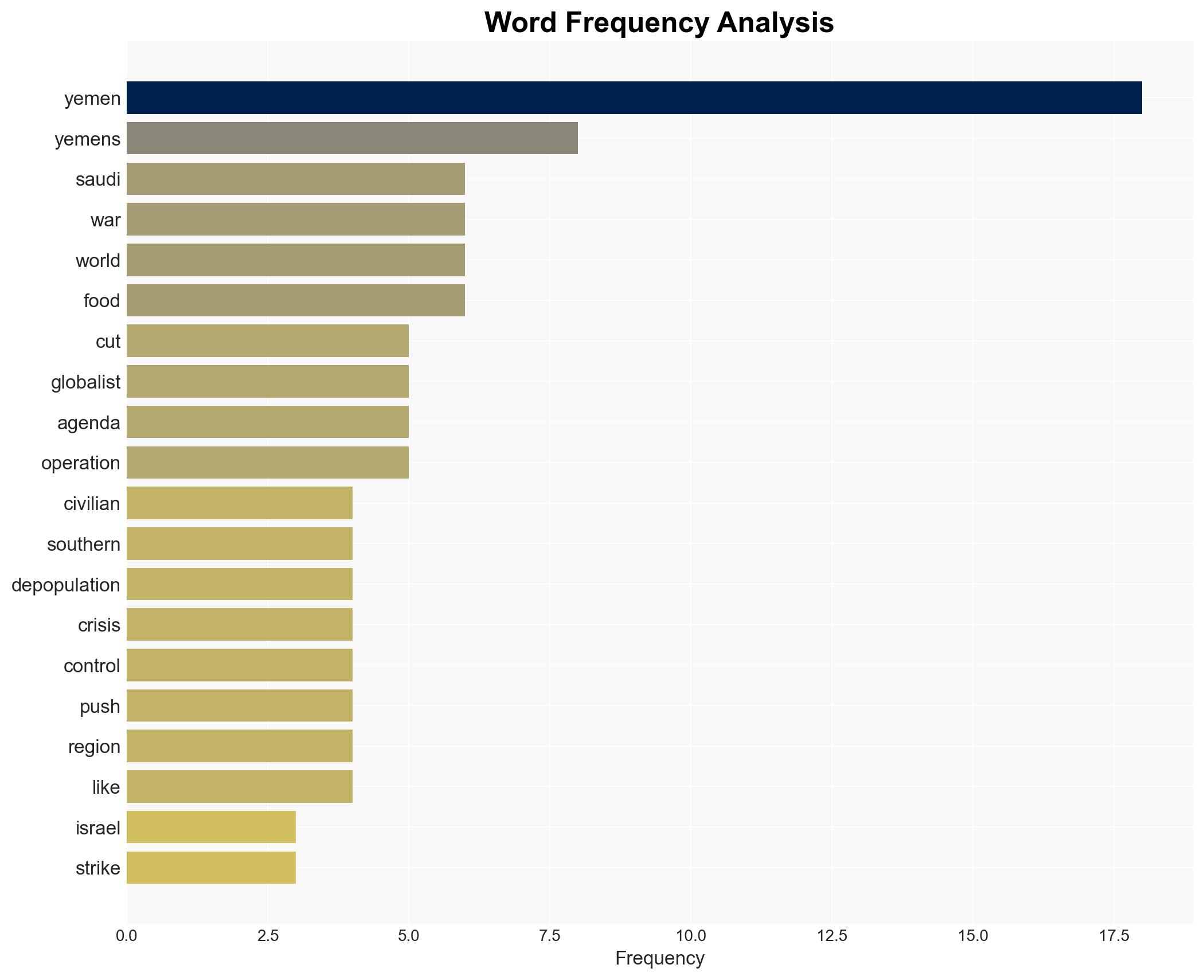
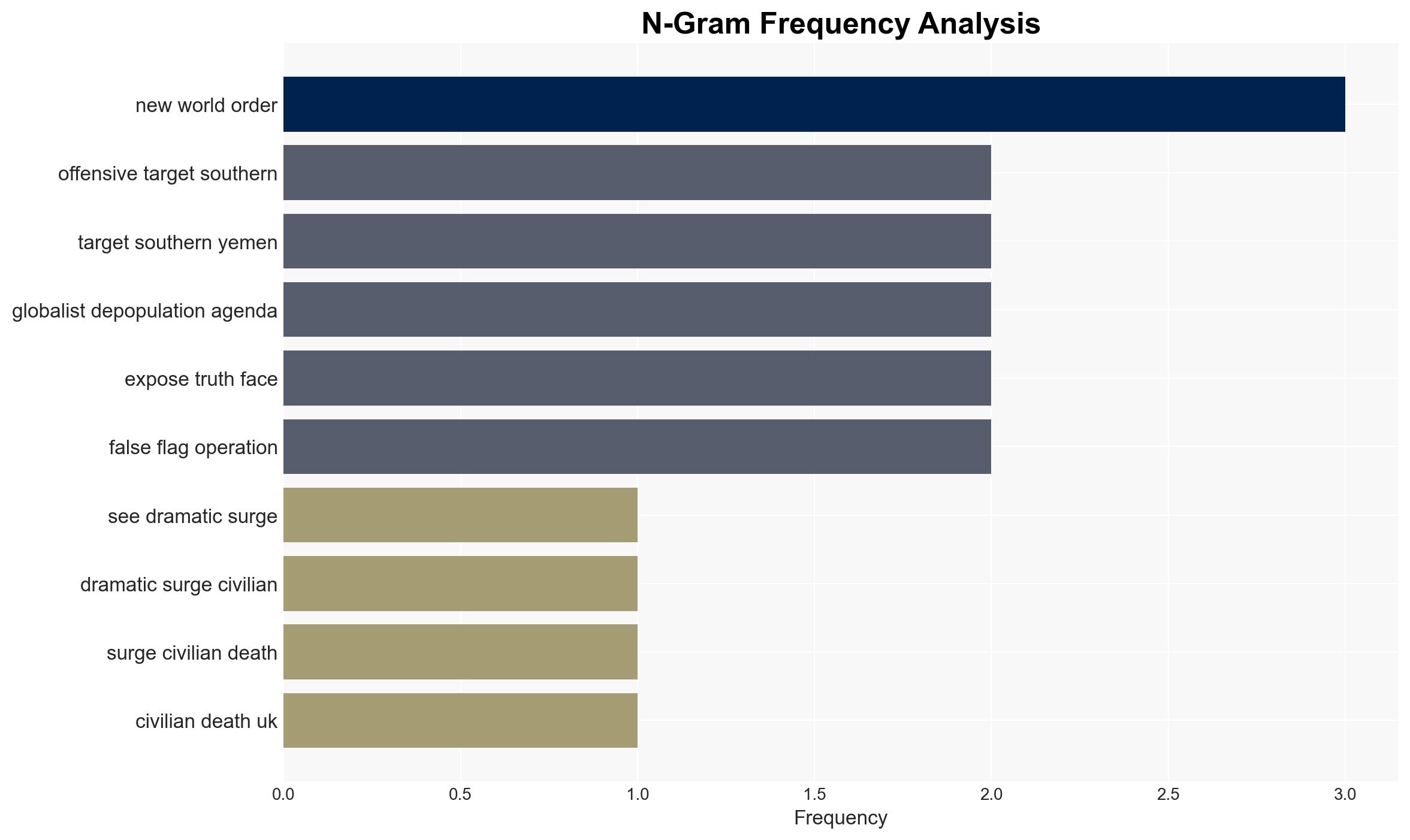
Counter-Terrorism, military intervention, humanitarian crisis, regional stability, political fragmentation, aid reduction, external influence, Middle East conflict
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us