Ukraine’s Reward Program Yields 40,000 Interceptor Drones to Combat Russian Shahed Threat
Published on: 2026-01-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Ukraine’s pay-per-kill system against Russian Shaheds helped it get 40000 interceptor drones in a month official says
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
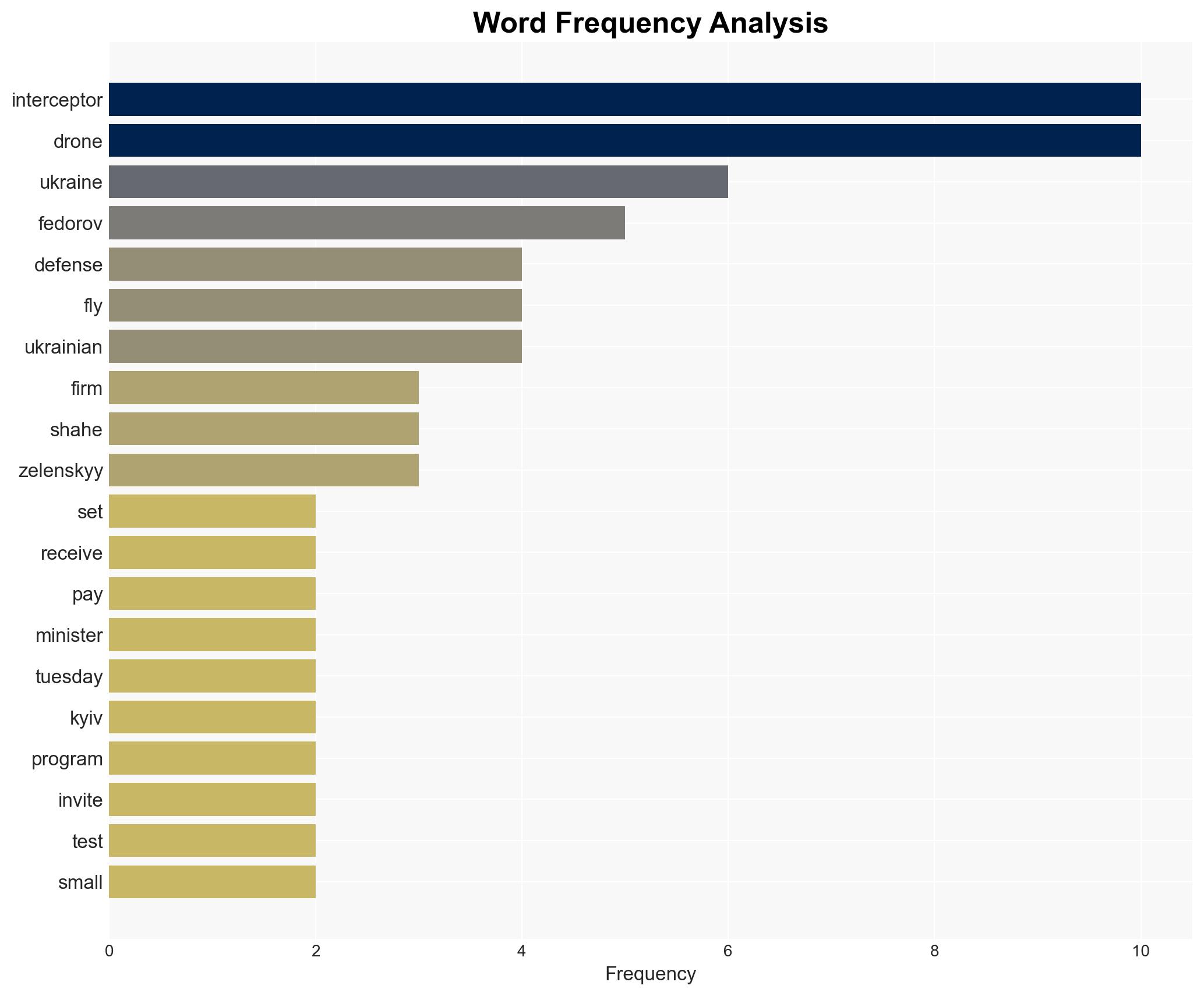
Ukraine’s implementation of a pay-per-kill system for interceptor drones has resulted in the expected delivery of 40,000 units in January, significantly enhancing its defense capabilities against Russian Shahed drones. This development primarily affects Ukraine’s military and defense industry, with moderate confidence in the sustainability of this production rate due to potential resource constraints and training needs.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The pay-per-kill system has directly incentivized rapid production and deployment of interceptor drones, effectively bolstering Ukraine’s defensive posture against Russian drone threats. Supporting evidence includes the reported delivery of 40,000 drones and statements from Ukrainian officials. Key uncertainties involve the long-term sustainability of this incentive model and potential resource limitations.
- Hypothesis B: The increase in interceptor drones is primarily due to pre-existing production capabilities and international support, with the pay-per-kill system playing a secondary role. This hypothesis is supported by Ukraine’s ongoing partnerships with NATO countries and the rapid technological advancements in drone manufacturing. Contradicting evidence includes the direct attribution of the increase to the incentive program by Ukrainian officials.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to explicit statements from Ukrainian officials linking the pay-per-kill system to the increase in drone deliveries. However, further data on international contributions and production capabilities could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The pay-per-kill system is financially sustainable; Ukraine’s defense industry can maintain or increase production rates; international support remains consistent; the training of drone operators can keep pace with production.
- Information Gaps: Detailed financial data on the pay-per-kill program; specific contributions from international partners; comprehensive production capacity assessments.
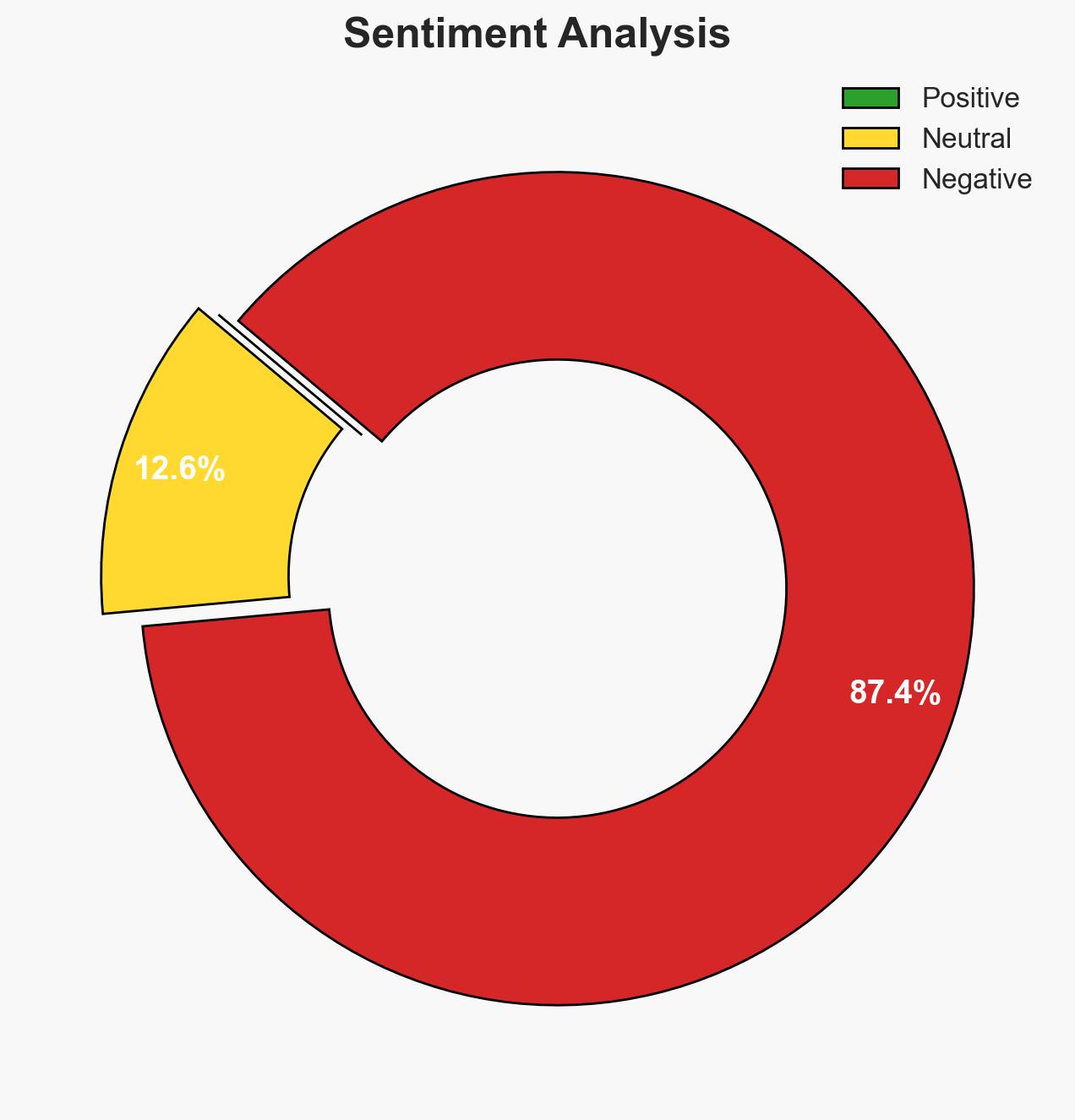
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on official Ukrainian statements; confirmation bias in attributing success solely to the pay-per-kill system; possible exaggeration of program effectiveness for strategic or morale purposes.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could significantly alter the military balance in the region, enhancing Ukraine’s defensive capabilities and potentially deterring further Russian drone incursions. However, it may also provoke escalatory responses from Russia.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between Ukraine and Russia; potential shifts in NATO’s engagement strategy.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced Ukrainian air defense capabilities; potential for increased Russian countermeasures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible Russian cyber operations targeting Ukrainian drone production or command infrastructure.
- Economic / Social: Strain on Ukrainian financial resources; potential economic benefits from increased defense production.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor the effectiveness and sustainability of the pay-per-kill system; assess the impact on Russian drone operations; evaluate the training pipeline for drone operators.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to sustain production; enhance international partnerships for technology and resource support; invest in operator training programs.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Sustained production and effective deployment of interceptors deter Russian drone attacks.
- Worst: Resource constraints and training bottlenecks limit the effectiveness of the interceptor program.
- Most-Likely: Continued production with moderate effectiveness, requiring ongoing international support and adaptation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Mykhailo Fedorov, Ukrainian Defense Minister
- Volodymyr Zelenskyy, President of Ukraine
- Oleksandr Syrskyi, Ukraine’s Chief Commander
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, drone warfare, defense innovation, Ukraine-Russia conflict, military incentives, NATO partnerships, air defense, technological advancement
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us