Rockwell Automation CompactLogix 5370
Published on: 2026-01-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Rockwell Automation CompactLogix 5370
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
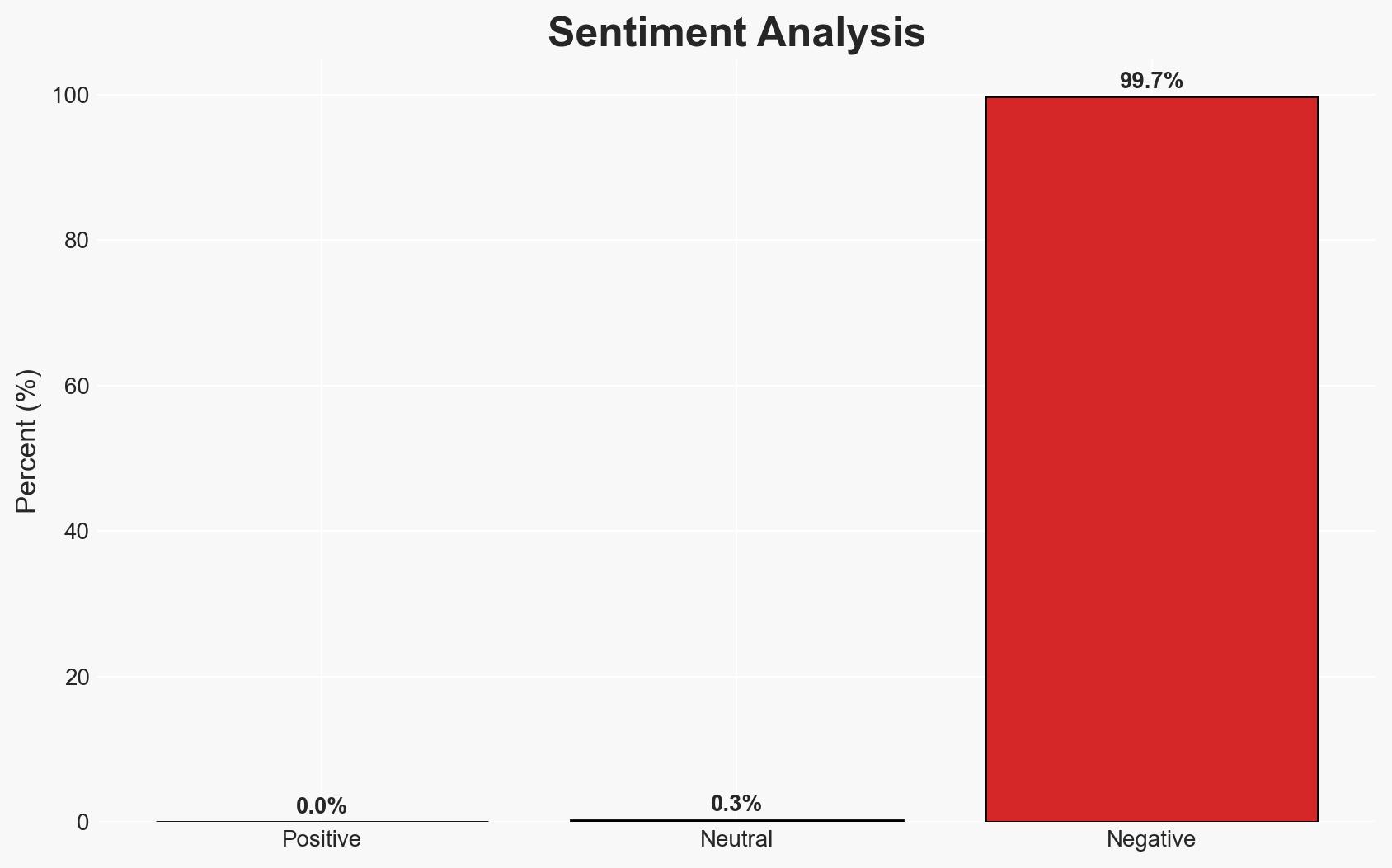
The Rockwell Automation CompactLogix 5370 series is vulnerable to a denial-of-service (DoS) attack due to a flaw in handling malformed CIP messages. This vulnerability affects critical infrastructure sectors worldwide, with no current evidence of public exploitation. The overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the lack of reported exploitation and the availability of remediation measures.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability will remain unexploited in the short term due to the lack of remote exploitability and the availability of patches. Supporting evidence includes the absence of reported public exploitation and the non-remote nature of the vulnerability. Key uncertainties involve potential undisclosed exploitation attempts.
- Hypothesis B: Malicious actors will exploit the vulnerability, targeting unpatched systems in critical infrastructure sectors. This is supported by the widespread deployment of the affected systems and the potential impact on critical operations. Contradicting evidence includes the current lack of public exploitation reports.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the absence of known exploitation and the availability of mitigations. Indicators that could shift this judgment include reports of new exploitation attempts or significant delays in patch deployment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations will apply available patches promptly; the vulnerability is not currently being exploited; Rockwell Automation’s remediation measures are effective.
- Information Gaps: The extent of patch deployment across affected systems; potential undisclosed exploitation incidents.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underreporting of exploitation due to reputational concerns; reliance on vendor-provided information without independent verification.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This vulnerability could impact the operational integrity of critical infrastructure if exploited, potentially leading to significant disruptions. The situation requires ongoing monitoring and proactive mitigation to prevent escalation.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased scrutiny on cybersecurity practices in critical infrastructure sectors.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Elevated risk of cyber-attacks targeting critical systems, necessitating enhanced defensive measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing industrial control systems and potential for information warfare tactics.
- Economic / Social: Disruptions could lead to economic impacts and public concern over infrastructure security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Ensure all affected systems are patched to the latest versions; enhance monitoring for signs of exploitation attempts; report any incidents to CISA.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop and implement comprehensive cybersecurity training and awareness programs; strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity agencies and industry peers.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Rapid patch deployment prevents exploitation, maintaining operational stability.
- Worst Case: Exploitation leads to significant disruptions in critical infrastructure, prompting regulatory action.
- Most Likely: Sporadic exploitation attempts occur but are mitigated by effective patching and defensive measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Rockwell Automation (Vendor)
- CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for specific individuals.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, critical infrastructure, industrial control systems, vulnerability management, denial-of-service, Rockwell Automation, CISA
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us