Vulnerable training applications are actively targeted in cloud security breaches, exposing critical risks.
Published on: 2026-01-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Exposed training apps are showing up in active cloud attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
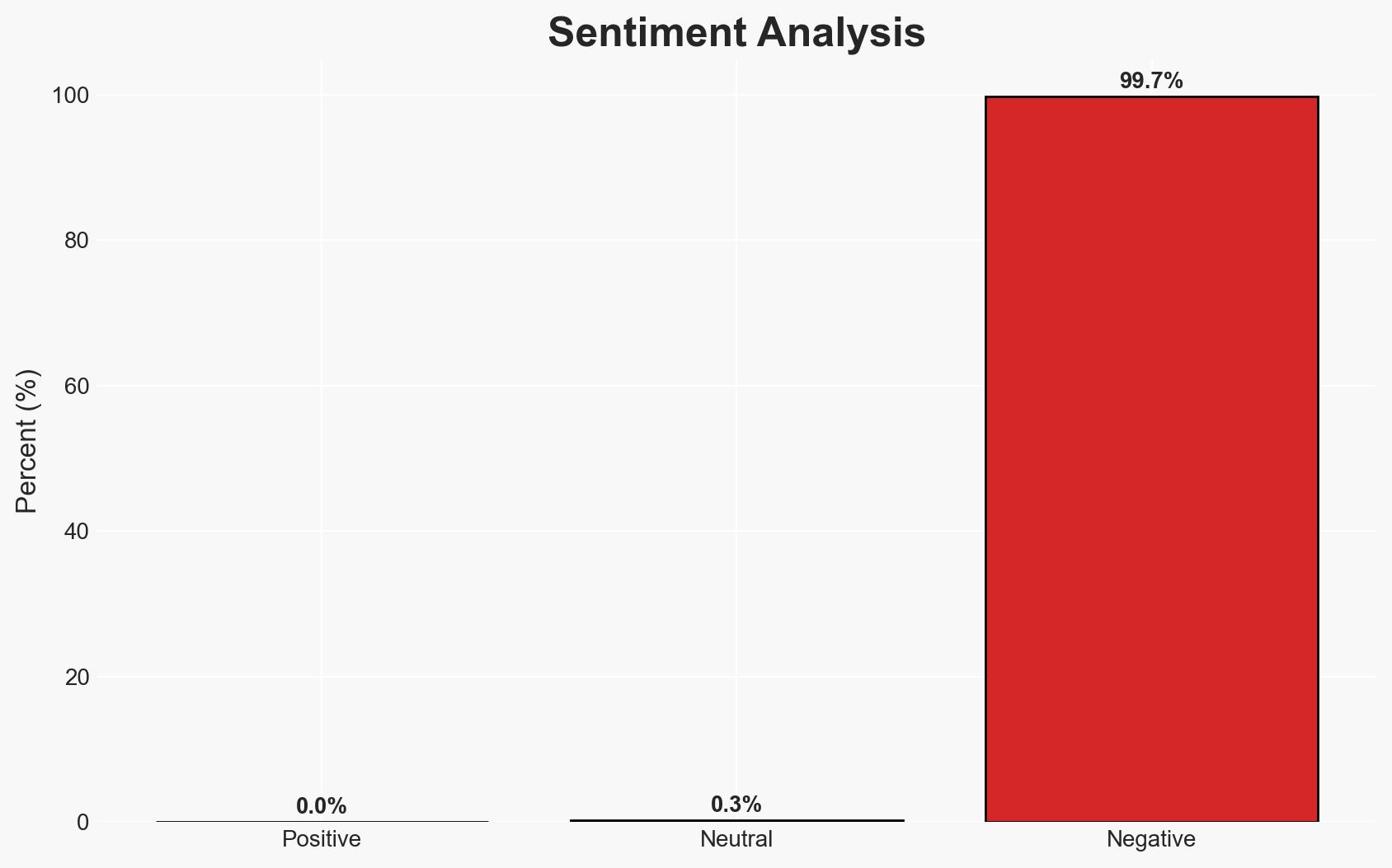
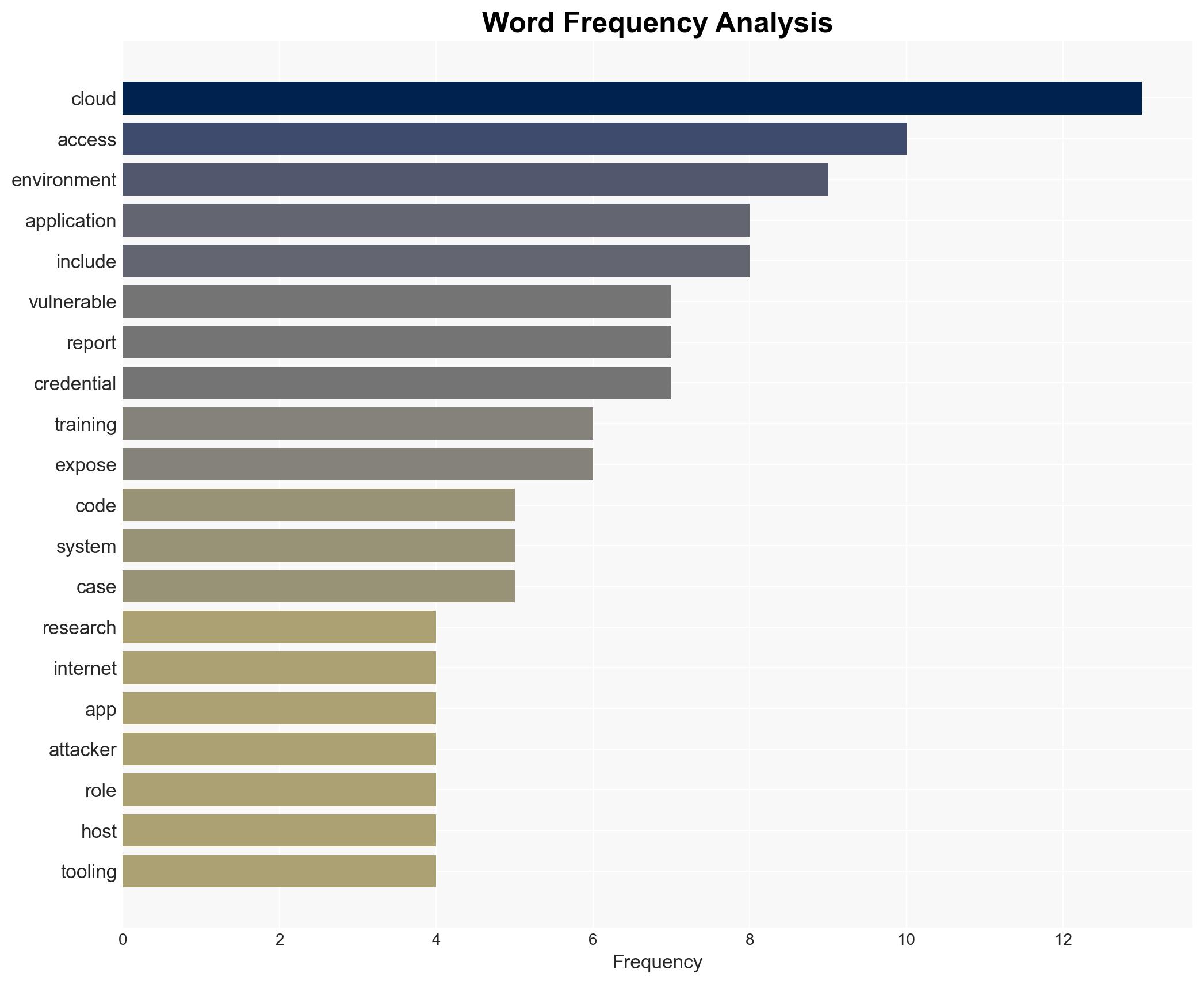
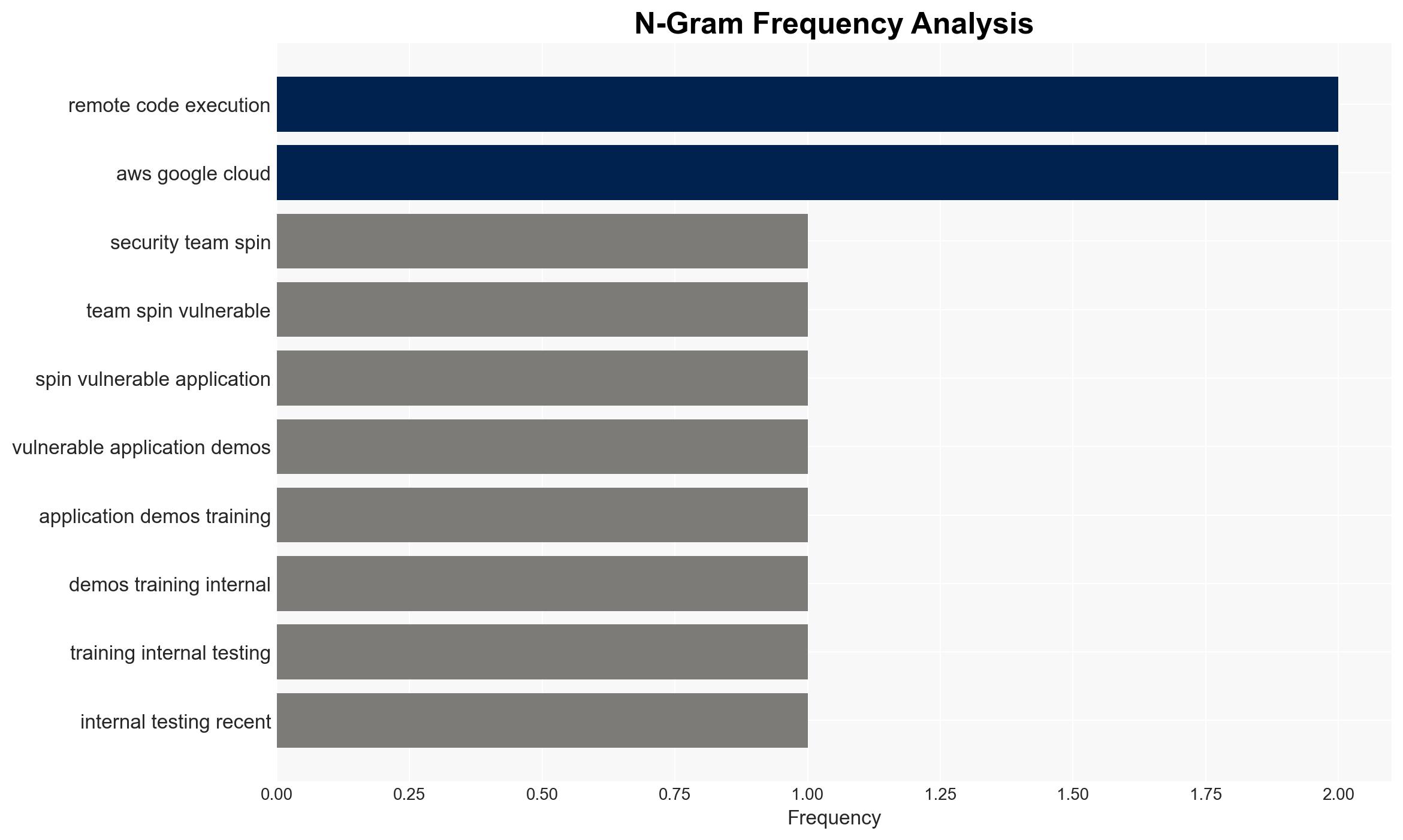
Exposed training applications on public cloud platforms are being actively exploited, leading to unauthorized access and potential data breaches. The most likely hypothesis is that these vulnerabilities are being systematically targeted by cyber actors to gain deeper access into cloud environments. This situation affects organizations using major cloud services like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the documented evidence but limited scope of the study.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The exposure of training applications is primarily due to oversight and misconfiguration by security teams, leading to opportunistic exploitation by cybercriminals. Supporting evidence includes the presence of default or misconfigured states and the use of public scanning platforms to identify targets. However, the scale of exploitation suggests a more systematic approach.
- Hypothesis B: The exploitation of these applications is part of a coordinated effort by organized cyber actors to infiltrate cloud environments. Supporting evidence includes the systematic use of automated tools to exploit known vulnerabilities and the strategic extraction of cloud credentials. Contradicting evidence is the lack of direct attribution to specific threat actors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the organized nature of the attacks and the strategic value of the compromised credentials. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include attribution to specific threat groups or evidence of widespread accidental exposures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations are not fully aware of the exposure of their training environments; cloud service providers are not actively monitoring for such misconfigurations; attackers have the capability and intent to exploit these vulnerabilities.
- Information Gaps: Specific attribution to threat actors; comprehensive data on the scale of exploitation beyond the reported cases; details on the response measures by affected organizations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in the research focusing on specific cloud platforms; risk of deception if attackers intentionally leave misleading traces to obfuscate their identity.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of cloud security practices and potentially stricter regulations on cloud service configurations. Over time, it may drive innovation in automated security solutions and influence cloud adoption strategies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for international tensions if state-sponsored actors are implicated.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information, potentially affecting national security.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened focus on cloud security and potential shifts in cyber defense strategies.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial impacts on affected organizations and erosion of trust in cloud services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct audits of cloud environments to identify and secure exposed applications; enhance monitoring for unusual access patterns.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cloud providers for improved security practices; invest in automated security tools to detect and remediate vulnerabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid remediation of vulnerabilities and improved cloud security practices prevent further exploitation.
- Worst: Continued exploitation leads to significant data breaches and regulatory penalties.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security practices reduce but do not eliminate exposure risks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cloud security, cyber exploitation, vulnerability management, data breaches, cloud platforms, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us