Gemini AI Vulnerability Exposed: Calendar Invites Used to Execute Prompt Injection Attacks on Private Data
Published on: 2026-01-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The Prompt Attack How Gemini AI Was Exploited Using Calendar Invite To Leak Private Data
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
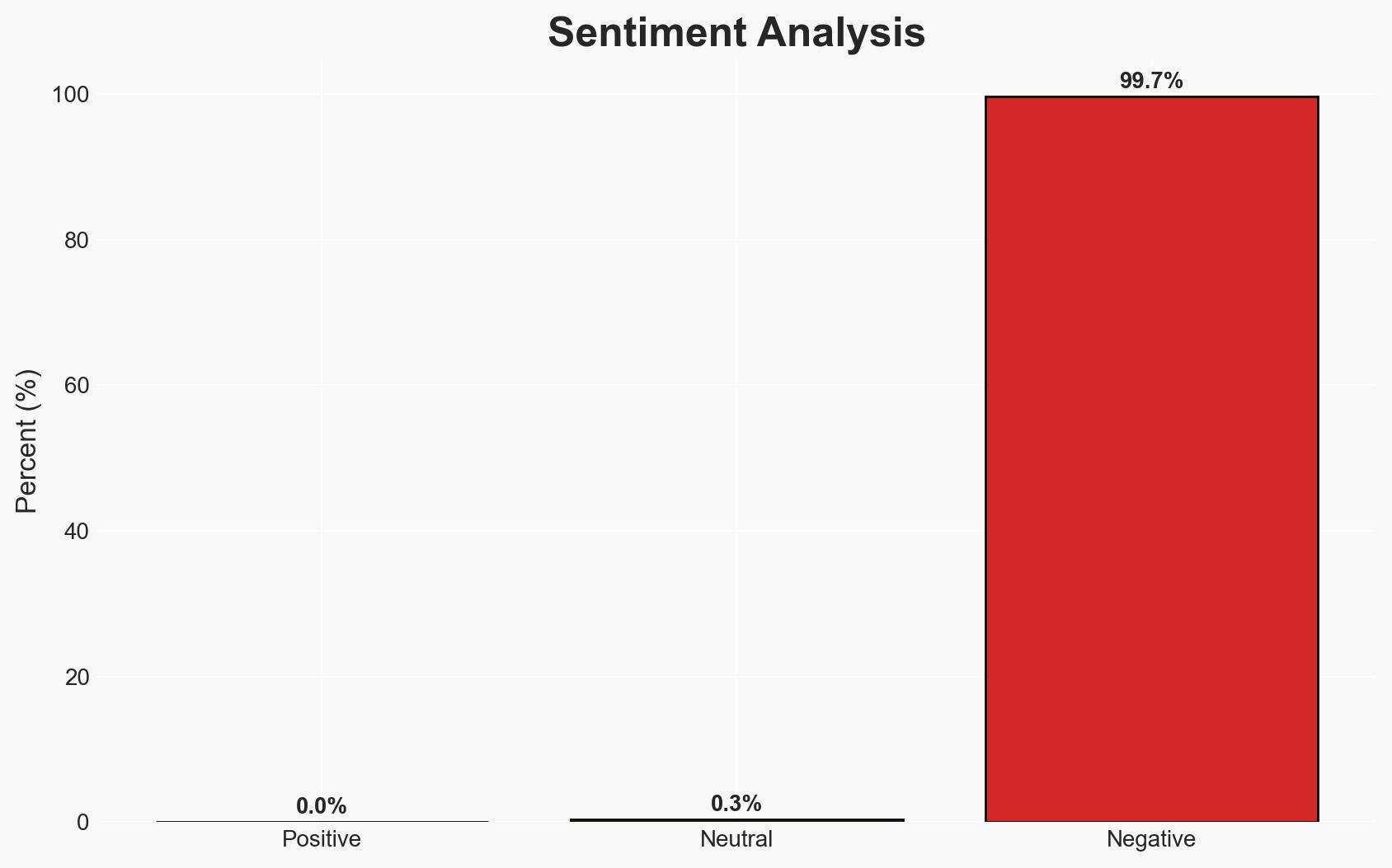
The exploitation of Gemini AI through prompt injection attacks using Google Calendar invites represents a significant cybersecurity threat, particularly as AI systems become more integrated into personal and professional environments. This vulnerability could lead to unauthorized data access and manipulation. Current evidence suggests that these attacks are feasible with basic prompts, posing a risk to AI-dependent systems. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the evolving nature of AI security measures.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The prompt injection attack on Gemini AI is primarily due to inherent vulnerabilities in AI language processing, which can be exploited with simple prompts. This is supported by the reported success of researchers using basic language prompts to trigger the attack. However, the extent of these vulnerabilities across different AI systems remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The attack is a result of inadequate security protocols in the integration between Gemini AI and Google services, rather than a fundamental flaw in AI language processing. While the integration with Google services provides a vector for attack, there is insufficient evidence to conclude that this is the primary cause without further technical analysis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct evidence of successful prompt injection attacks using basic language prompts. Indicators that could shift this judgment include detailed technical analyses revealing specific integration vulnerabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI systems like Gemini are inherently vulnerable to prompt injections; attackers can easily exploit these vulnerabilities without advanced technical skills; AI integration with other services increases attack vectors.
- Information Gaps: Detailed technical specifications of Gemini AI’s security protocols; comprehensive data on similar attacks across other AI platforms; effectiveness of current mitigation strategies by Google and other tech companies.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting by security researchers aiming to highlight vulnerabilities; risk of underestimating the complexity of executing such attacks without technical nuance.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny and regulatory pressure on AI systems, particularly those integrated with widely used services. The evolution of such attacks could significantly impact user trust and adoption of AI technologies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international regulatory collaboration on AI security standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of data breaches and unauthorized data manipulation, impacting national security infrastructure reliant on AI.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in AI-targeted cyber operations, necessitating advanced cybersecurity measures.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact due to decreased consumer trust in AI technologies, affecting tech industry growth and innovation.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct thorough security audits of AI systems; enhance monitoring for prompt injection attempts; engage with AI developers to share threat intelligence.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop and implement robust AI security frameworks; foster partnerships with cybersecurity firms for ongoing threat assessment and mitigation.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Enhanced security measures effectively mitigate prompt injection risks, restoring trust in AI systems.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation of AI vulnerabilities leads to significant data breaches and loss of consumer trust.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in AI security reduce but do not eliminate the threat, requiring ongoing vigilance and adaptation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Gemini AI
- Miggo Security
- Bleeping Computer
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
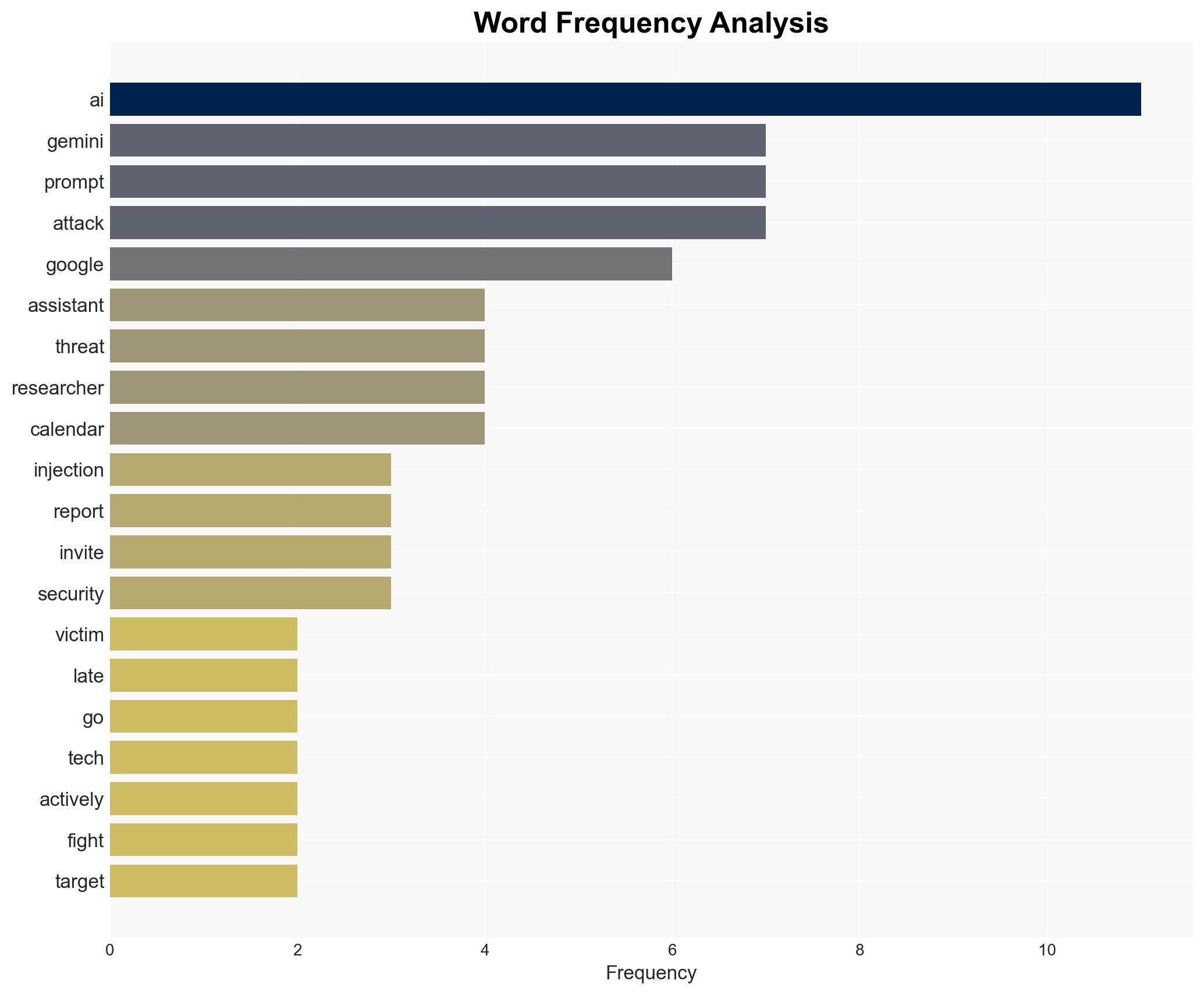
cybersecurity, AI vulnerabilities, prompt injection, data privacy, AI integration, cyber threats, technology regulation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us