Active Exploitation of SmarterMail Authentication Bypass Vulnerability Identified, No CVE Assigned
Published on: 2026-01-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Critical SmarterMail vulnerability under attack no CVE yet
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
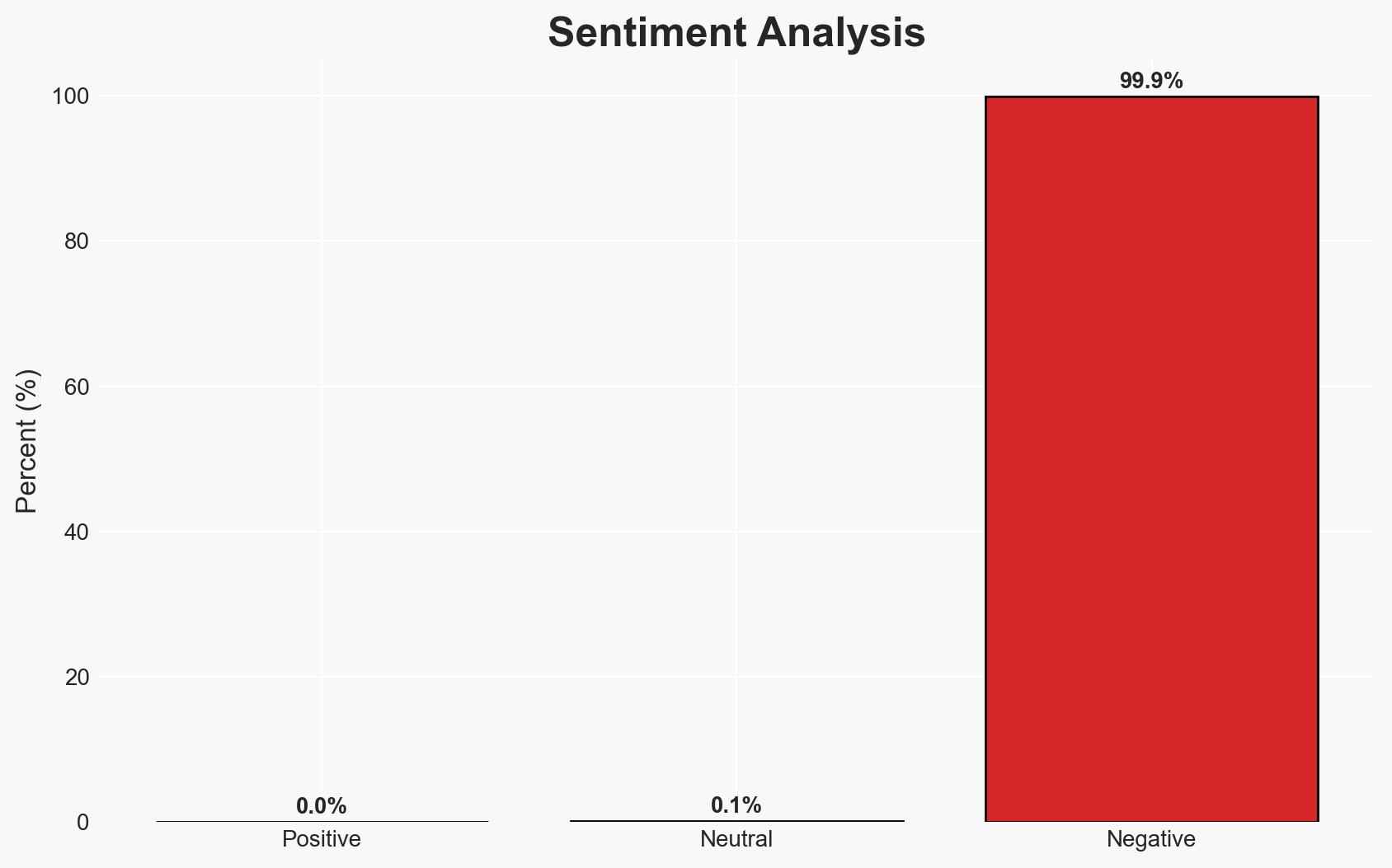
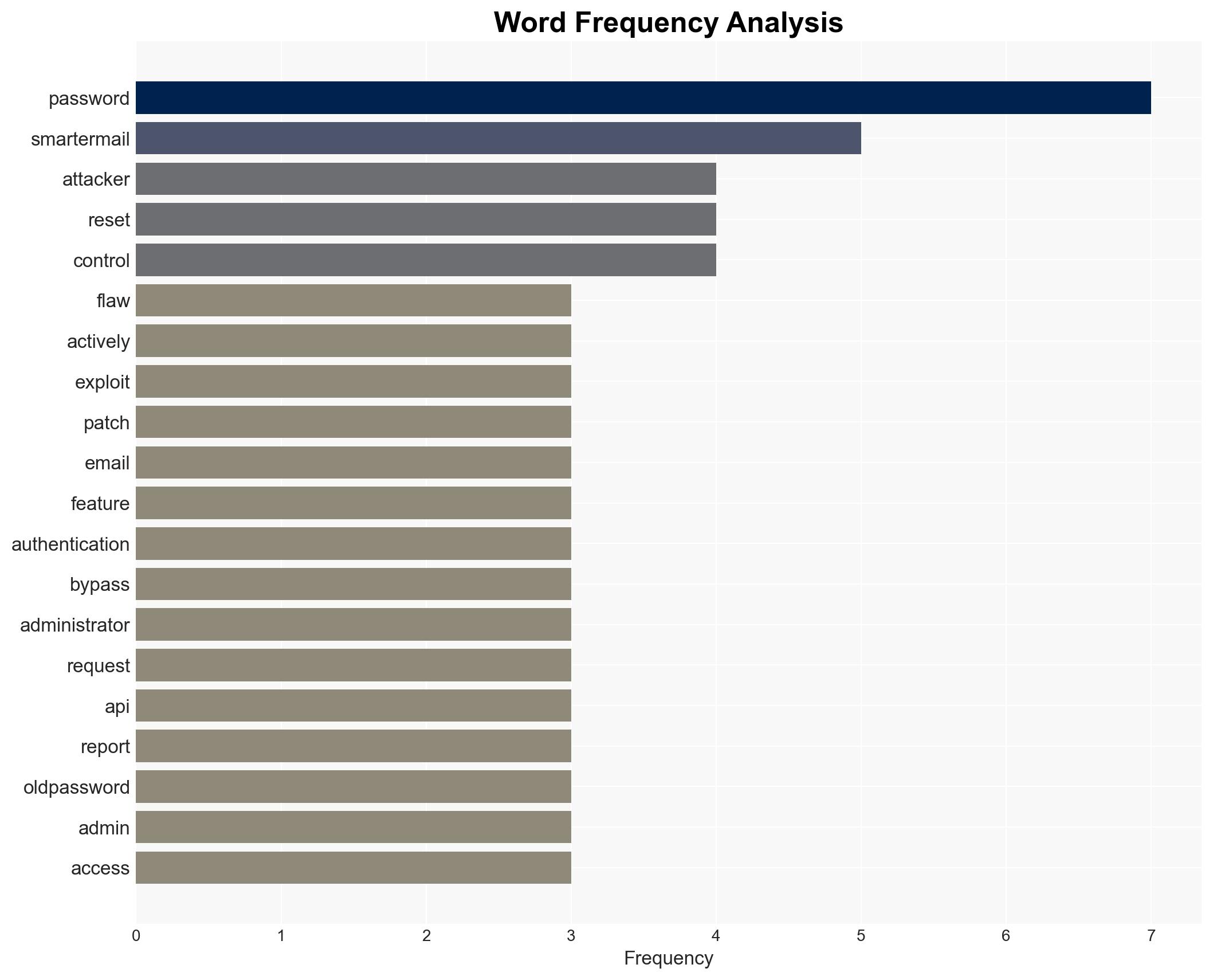
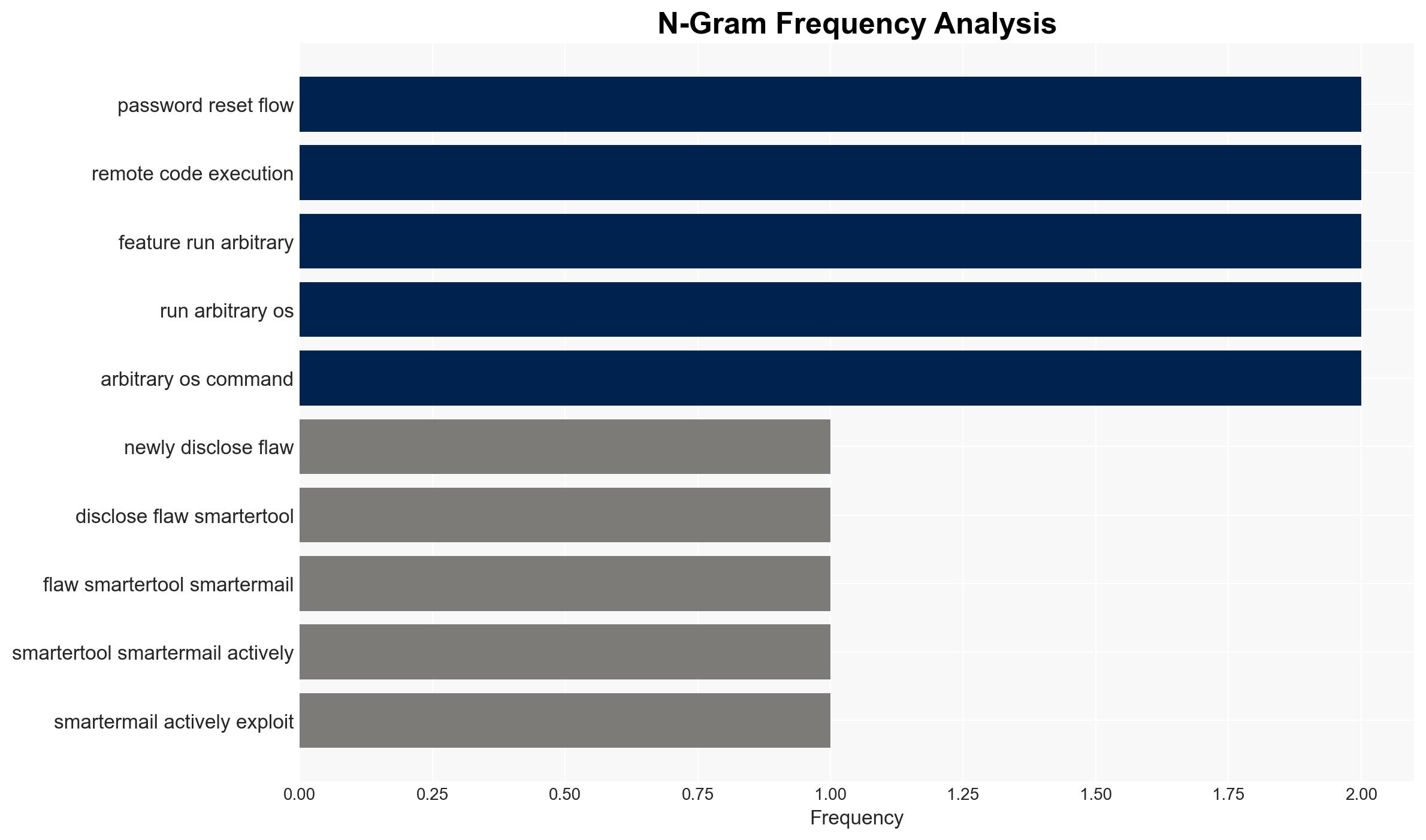
A critical vulnerability in SmarterTools SmarterMail, identified as WT-2026-0001, is actively exploited, allowing attackers to gain SYSTEM-level access. The vulnerability, patched on January 15, 2026, lacks a CVE, complicating tracking and mitigation efforts. Organizations using SmarterMail are at risk, with moderate confidence that exploitation will continue until widespread patching occurs.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability is being exploited primarily by opportunistic cybercriminals seeking to gain unauthorized access to systems for financial gain. Supporting evidence includes the rapid exploitation post-disclosure and the lack of sophisticated attack vectors. Key uncertainties include the identity and motivations of the attackers.
- Hypothesis B: The exploitation is part of a coordinated campaign by a state-sponsored actor aiming to compromise critical infrastructure or gather intelligence. This is less supported due to the absence of complex tactics typically associated with state actors. However, the potential for state involvement cannot be entirely dismissed.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported given the nature of the exploitation and the typical profile of cybercriminals targeting commercial software vulnerabilities. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of targeted attacks on specific high-value targets or geopolitical entities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The patch effectively mitigates the vulnerability; attackers lack advanced persistence mechanisms; organizations will prioritize patching.
- Information Gaps: Details on the identity of the attackers; the extent of exploitation across different sectors; the timeline for CVE assignment.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing attacks to cybercriminals without sufficient evidence; risk of underestimating state actor involvement.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This vulnerability’s exploitation could lead to significant disruptions in organizations relying on SmarterMail, with potential cascading effects if not addressed promptly.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation could occur if state actors are involved, potentially leading to diplomatic tensions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Cyber / Information Space: Highlights the importance of timely patching and vulnerability management; potential for increased cyber insurance claims.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses for affected organizations; potential reputational damage impacting customer trust.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgently apply the patch to SmarterMail systems; monitor for signs of exploitation; enhance logging and alerting mechanisms.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for threat intelligence sharing; invest in cybersecurity training and awareness programs.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patch adoption mitigates the threat with minimal impact.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant data breaches and operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued exploitation in unpatched systems with gradual decline as patches are applied.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- WatchTowr Labs (responsible disclosure entity)
- SmarterTools (vendor of SmarterMail)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet (attackers)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability management, patching, cybercrime, enterprise software, information security, threat intelligence
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us