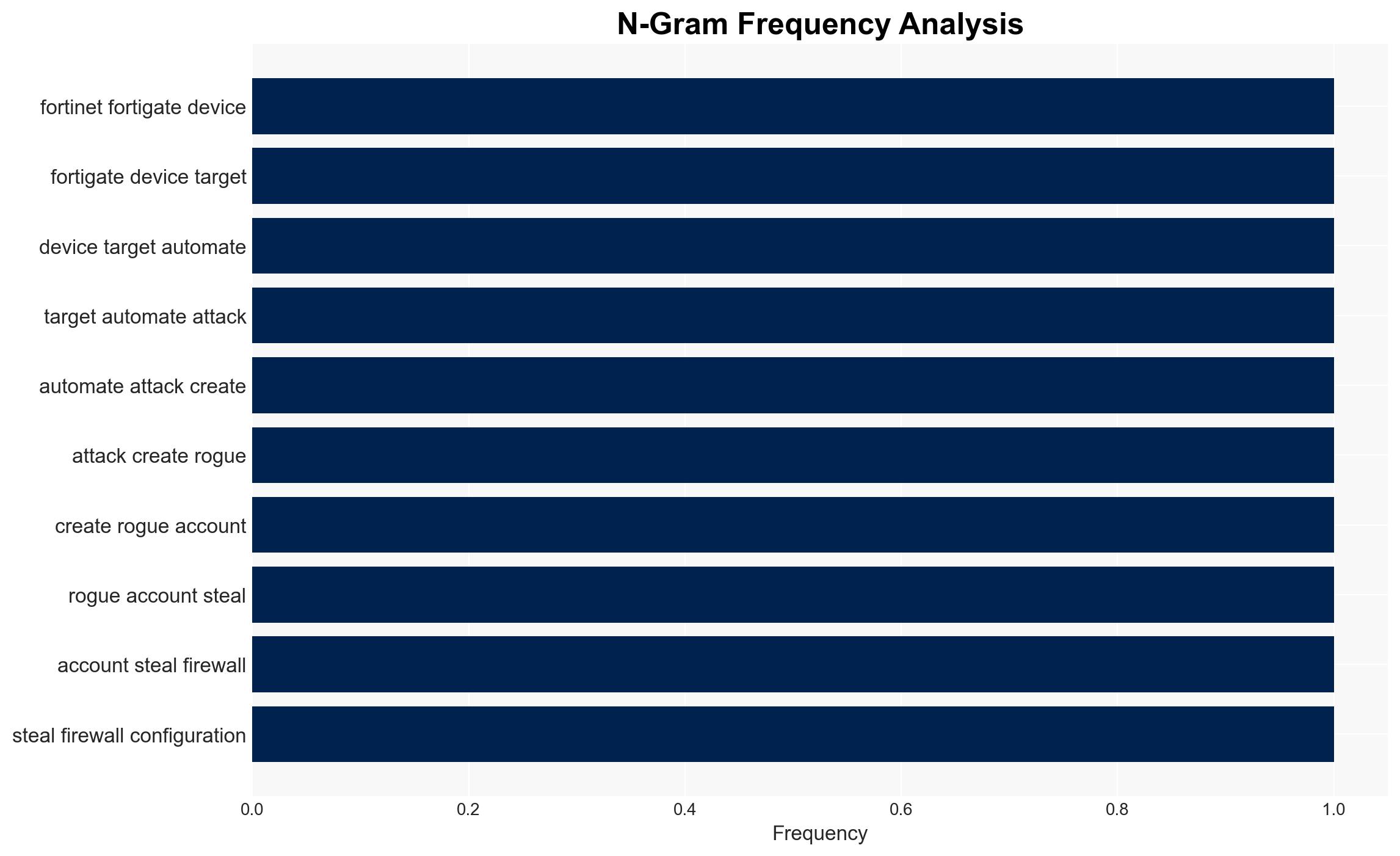
Automated Attacks Target Fortinet FortiGate Devices, Compromising Firewall Configurations
Published on: 2026-01-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Hackers breach Fortinet FortiGate devices steal firewall configs
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
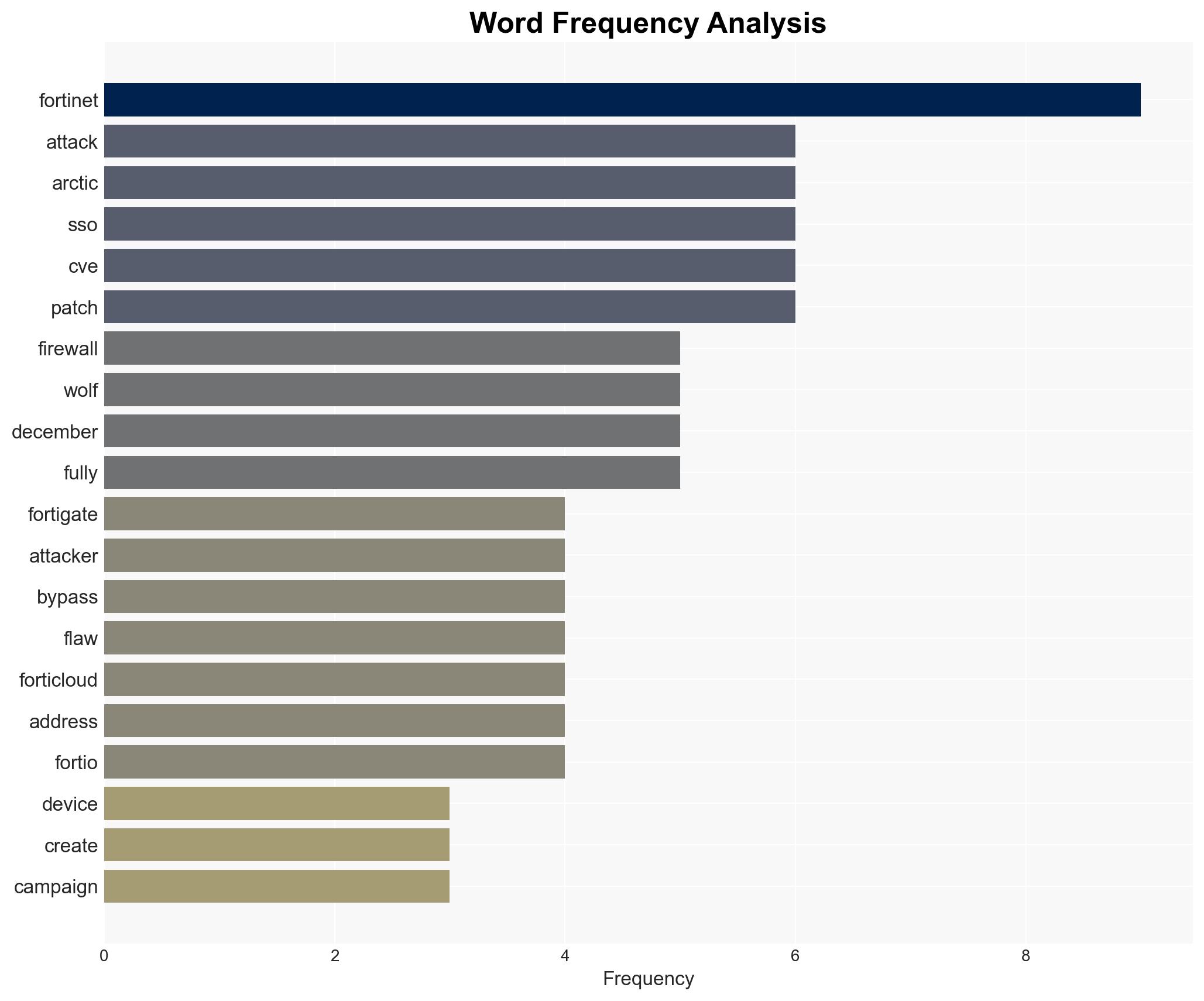
Recent cyberattacks have targeted Fortinet FortiGate devices, exploiting a vulnerability in the single sign-on (SSO) feature to create rogue accounts and steal firewall configurations. The attacks appear to be automated and are similar to previous incidents linked to a known vulnerability (CVE-2025-59718). This situation affects organizations using Fortinet products, with moderate confidence in the assessment due to ongoing patch development and incomplete vulnerability mitigation.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The current attacks are leveraging a new, undisclosed vulnerability in Fortinet FortiGate devices. Supporting evidence includes the similarity to past incidents and the partial ineffectiveness of existing patches. However, the exact mechanism of exploitation remains unclear.
- Hypothesis B: The attacks are exploiting a bypass of the existing patch for CVE-2025-59718. This is supported by reports of continued breaches despite patching efforts, and the similarity to previous exploitation methods. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of comprehensive patch effectiveness data.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the pattern of attacks aligning with known vulnerabilities and the partial success of existing patches. Indicators that could shift this judgment include the discovery of a new vulnerability or a comprehensive patch that halts the attacks.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability is not fully patched; attackers have advanced knowledge of Fortinet systems; affected organizations have not fully disabled vulnerable features.
- Information Gaps: Exact technical details of the vulnerability exploitation; full scope of affected devices and organizations; effectiveness of upcoming patches.
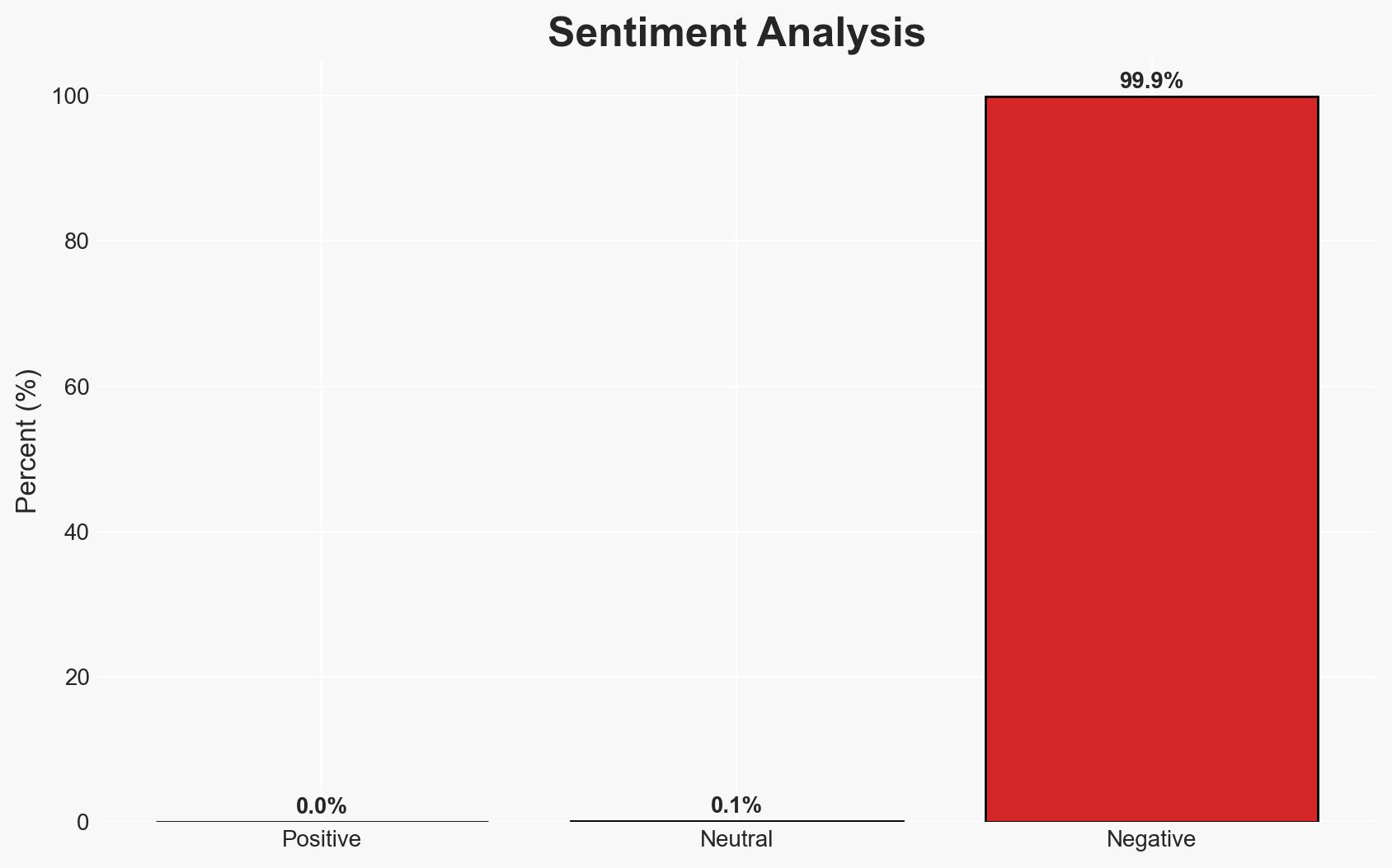
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on Arctic Wolf’s analysis; confirmation bias towards known vulnerabilities; possible misinformation from attackers to obfuscate methods.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing exploitation of Fortinet vulnerabilities could lead to significant security breaches, affecting critical infrastructure and sensitive data. The situation may evolve with broader implications if not swiftly addressed.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state actors are involved or if critical national infrastructure is compromised.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cyber-attacks on critical infrastructure, requiring heightened security measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for widespread data breaches and information manipulation, impacting trust in cybersecurity solutions.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses for affected companies and potential disruptions to services reliant on Fortinet devices.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgently disable vulnerable SSO features, apply available patches, and monitor for indicators of compromise.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, enhance cybersecurity partnerships, and invest in capability development for threat detection and response.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Effective patching halts attacks; Worst: New vulnerabilities emerge, leading to widespread breaches; Most-Likely: Continued exploitation until comprehensive patching is achieved.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Fortinet
- Arctic Wolf
- Shadowserver
- CISA
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability exploitation, Fortinet, network security, cyber defense, information security, patch management
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us