80% of small businesses experienced cyberattacks last year, with nearly half involving AI technology.
Published on: 2026-01-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: 4 in 5 small businesses had cyberattacks last year and almost half of those were AI powered
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The prevalence of cyberattacks on small businesses, with a significant portion being AI-powered, indicates a shift towards more automated and scalable threats. This trend affects small businesses across multiple industries, increasing their operational costs and cybersecurity challenges. Moderate confidence in this assessment is based on reported data from a comprehensive survey.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The rise in AI-powered cyberattacks is primarily due to increased accessibility and affordability of AI tools for cybercriminals. Supporting evidence includes the report’s findings on the scalability and automation of threats. Key uncertainties involve the specific technological advancements enabling this trend.
- Hypothesis B: The increase in AI-powered attacks is a result of targeted campaigns by sophisticated threat actors focusing on small businesses as easy targets. While the report suggests opportunistic attacks, the lack of detailed attribution data limits this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the broad and opportunistic nature of the attacks reported, indicating a shift towards automated tools rather than targeted campaigns. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of coordinated campaigns or significant technological breakthroughs in AI.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Small businesses have inadequate cybersecurity measures; AI tools are increasingly accessible to cybercriminals; the survey sample is representative of broader trends.
- Information Gaps: Specific AI technologies used in attacks; detailed attribution of cyber actors; longitudinal data on attack trends.
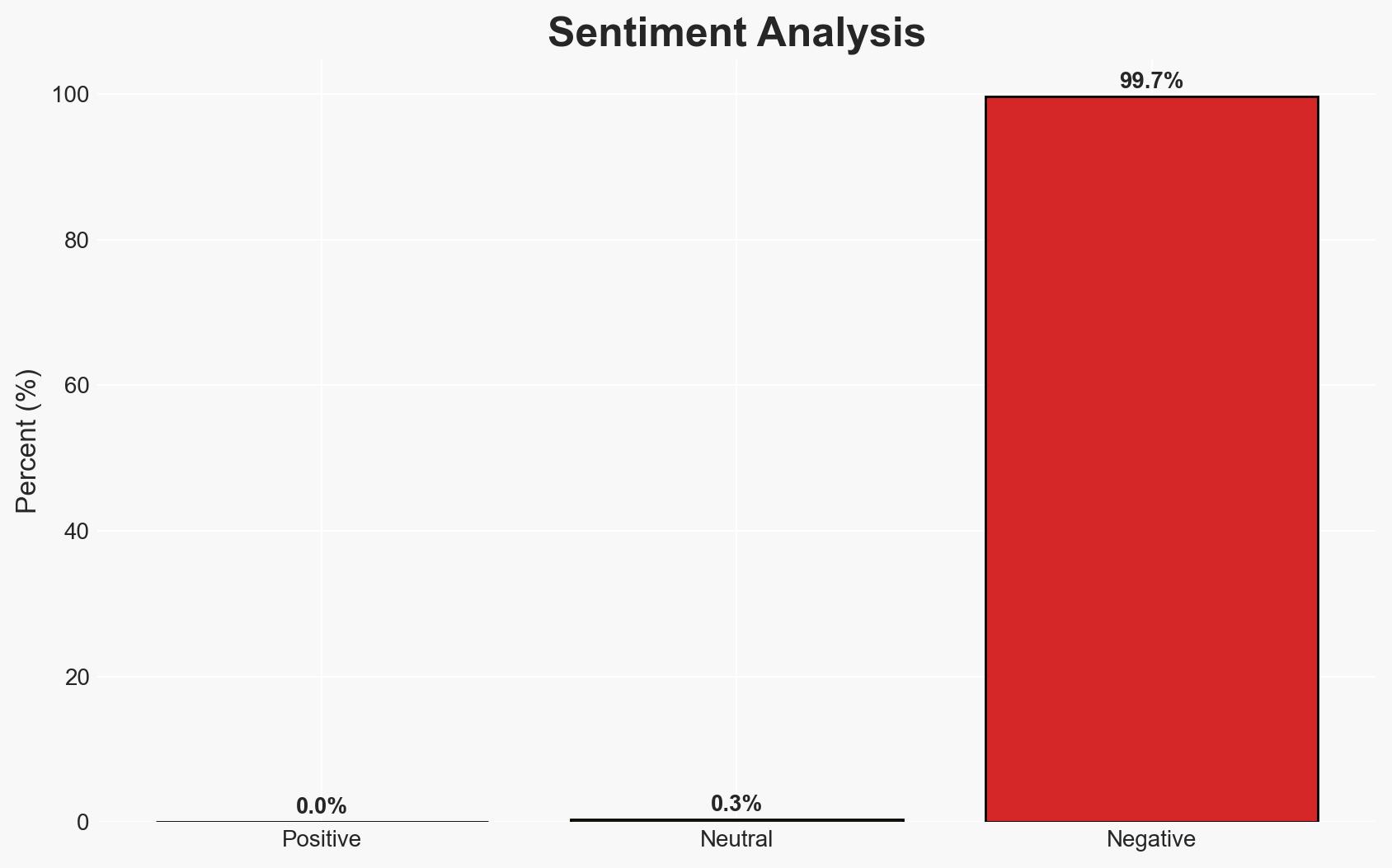
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in survey responses due to self-reporting; nonprofit’s financial motivations might influence report emphasis.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of AI-powered cyberattacks on small businesses could lead to increased financial strain and potential market instability. This development may also influence broader cybersecurity policies and practices.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny and international cooperation on cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Small businesses may become vectors for larger cyber threats if not adequately protected.
- Cyber / Information Space: Rise in AI-driven attacks could lead to more sophisticated cyber defense strategies and technologies.
- Economic / Social: Increased costs for small businesses may lead to higher consumer prices and reduced competitiveness.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage small businesses to conduct cybersecurity audits and enhance employee training on cyber hygiene.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships between small businesses and cybersecurity firms to improve defenses; advocate for policy incentives for cybersecurity investments.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Improved defenses reduce attack success rates; Worst: Continued rise in attacks overwhelms small business resources; Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in defenses with ongoing attack pressures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Eva Velasquez, CEO of the Identity Theft Resource Center
- Identity Theft Resource Center
- Small businesses across various industries
7. Thematic Tags
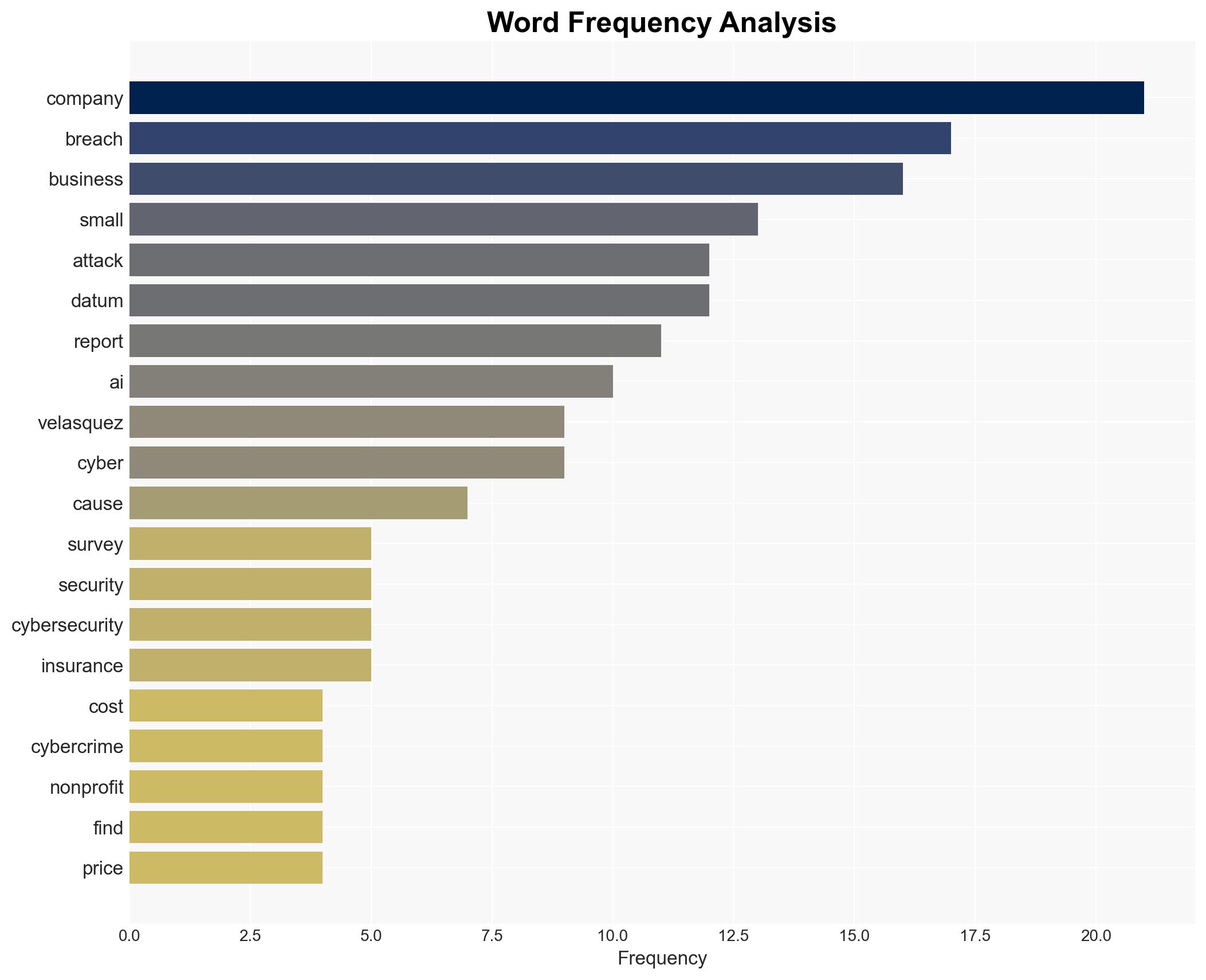
cybersecurity, AI-powered attacks, small business vulnerability, cybercrime trends, economic impact, cybersecurity policy, automated threats
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us