Survivor recounts harrowing escape from church abduction in northern Nigeria amid ongoing crisis
Published on: 2026-01-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: ‘Blood was all over’ – victim of Nigeria church abduction describes escape
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
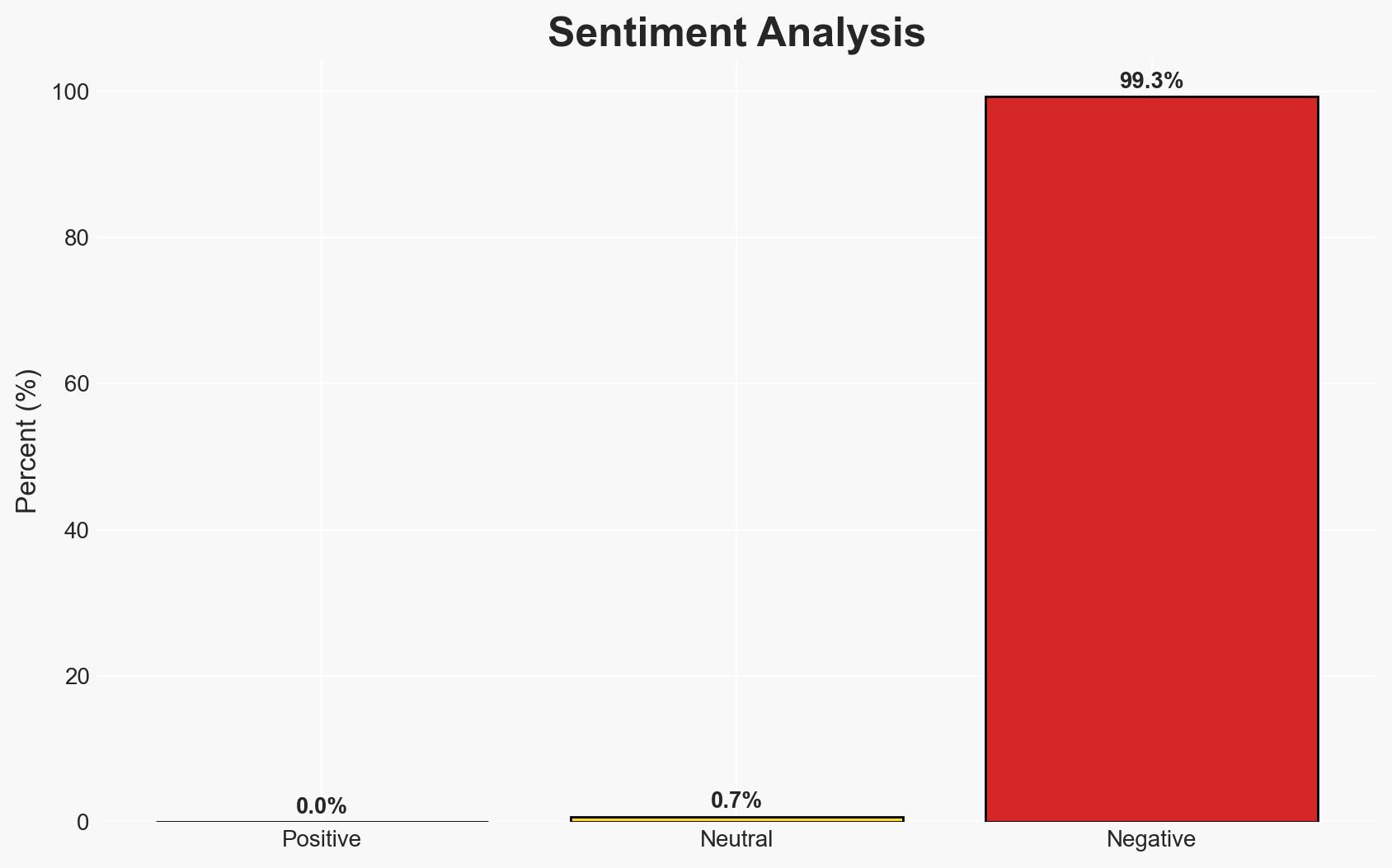
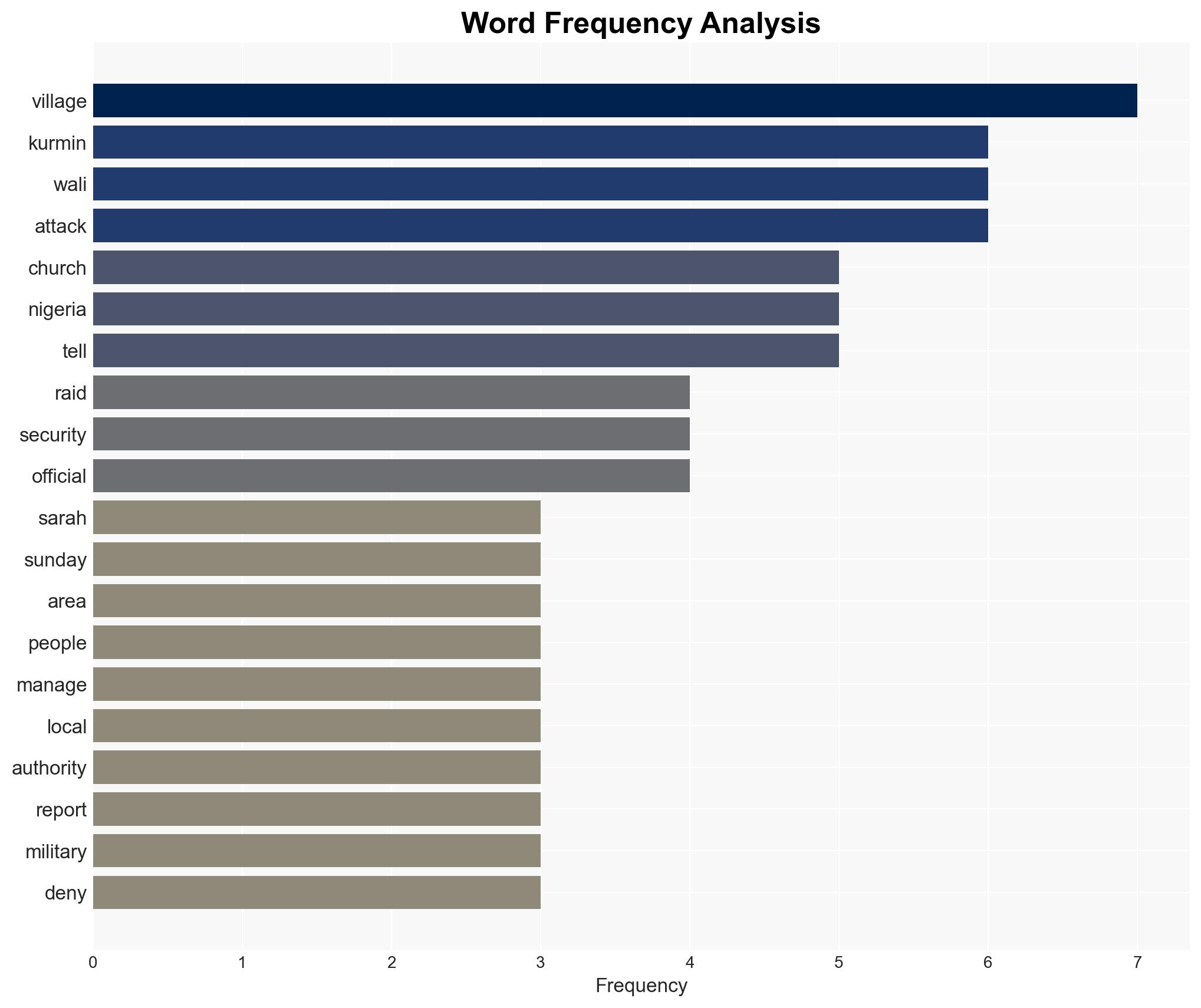
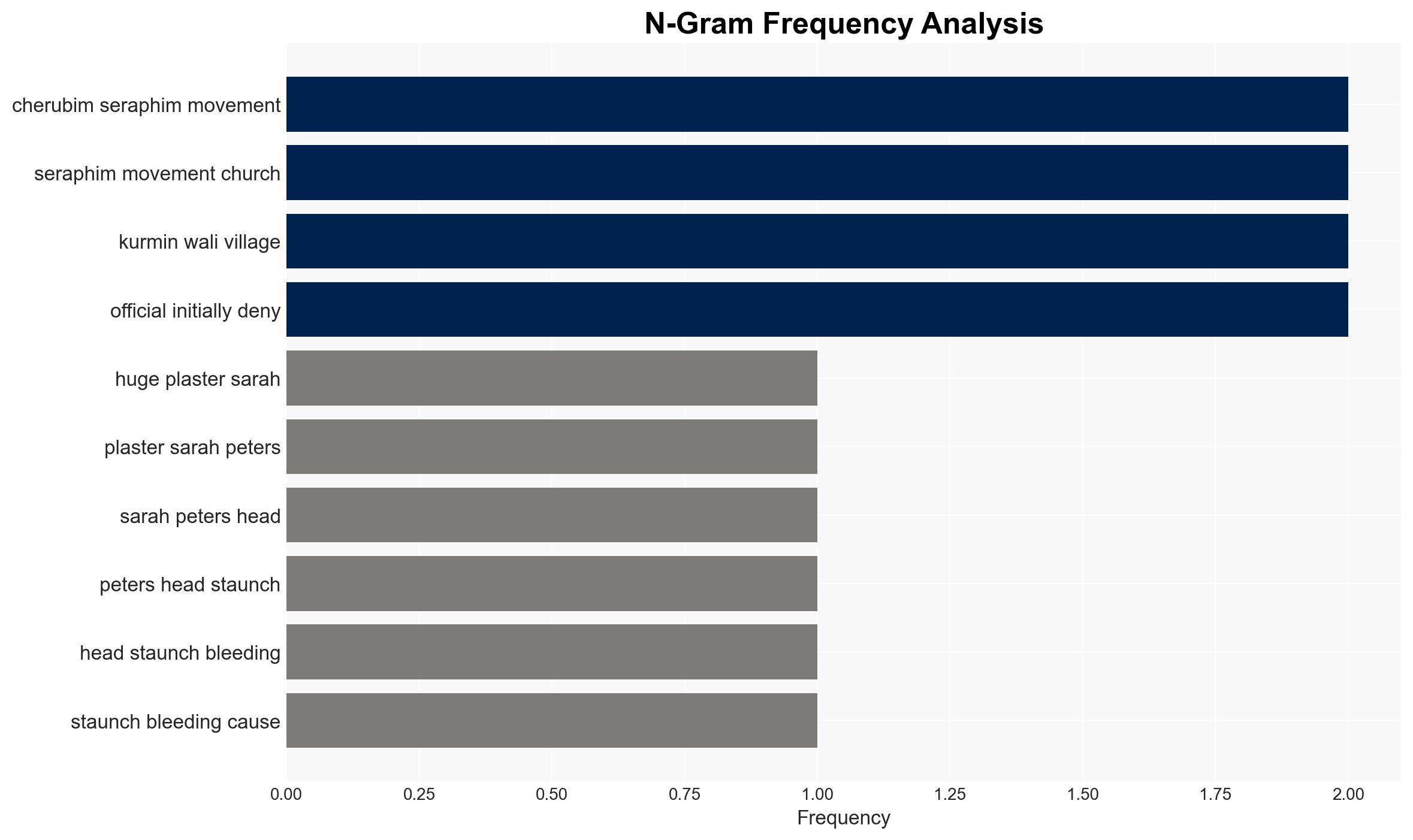
The recent abduction of over 160 individuals from churches in northern Nigeria highlights the ongoing security crisis in the region, characterized by rampant kidnapping for ransom. The lack of immediate ransom demands and the absence of a claiming group suggest a complex threat landscape. This incident underscores the vulnerability of religious communities and the potential for further destabilization. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The abductions were conducted by local bandit groups primarily for ransom purposes. This is supported by the region’s history of similar incidents and the proximity to known bandit hideouts. However, the absence of a ransom demand introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was orchestrated by a larger, possibly ideologically motivated group aiming to destabilize the region or target religious communities. This is less supported due to the lack of claims of responsibility and the mixed religious impact reported by officials.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the historical context of banditry in the area and the modus operandi of the attackers. Indicators such as a delayed ransom demand or a claim of responsibility could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attackers are motivated by financial gain; the local security forces are under-resourced; the community’s fear is based on past incidents.
- Information Gaps: Specific identities and motivations of the attackers; details on any negotiations or communications post-abduction.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underreporting or misinformation by local authorities; cognitive bias towards viewing all kidnappings as financially motivated.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate regional instability and strain local resources, potentially leading to increased international attention and intervention. The ongoing insecurity may also deter investment and development efforts.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international scrutiny and pressure on the Nigerian government to enhance security measures.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment with possible escalation in attacks if not addressed.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for misinformation campaigns or propaganda to exploit the situation.
- Economic / Social: Disruption to local economies and social cohesion, with potential migration of populations seeking safety.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence gathering on local bandit groups; enhance community security measures; engage with local leaders to restore confidence.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop regional security partnerships; invest in community resilience programs; improve rapid response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful negotiation and release of hostages without further incidents.
- Worst: Escalation of violence and further abductions leading to regional destabilization.
- Most-Likely: Continued sporadic abductions with slow improvements in security response.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, kidnapping, banditry, Nigeria security, religious communities, ransom, regional instability, counter-terrorism
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us