NHS Calls for Enhanced Cybersecurity Collaboration with Suppliers Amid Rising Ransomware Threats
Published on: 2026-01-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: NHS Issues Open Letter Demanding Improved Cybersecurity Standards from Suppliers
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
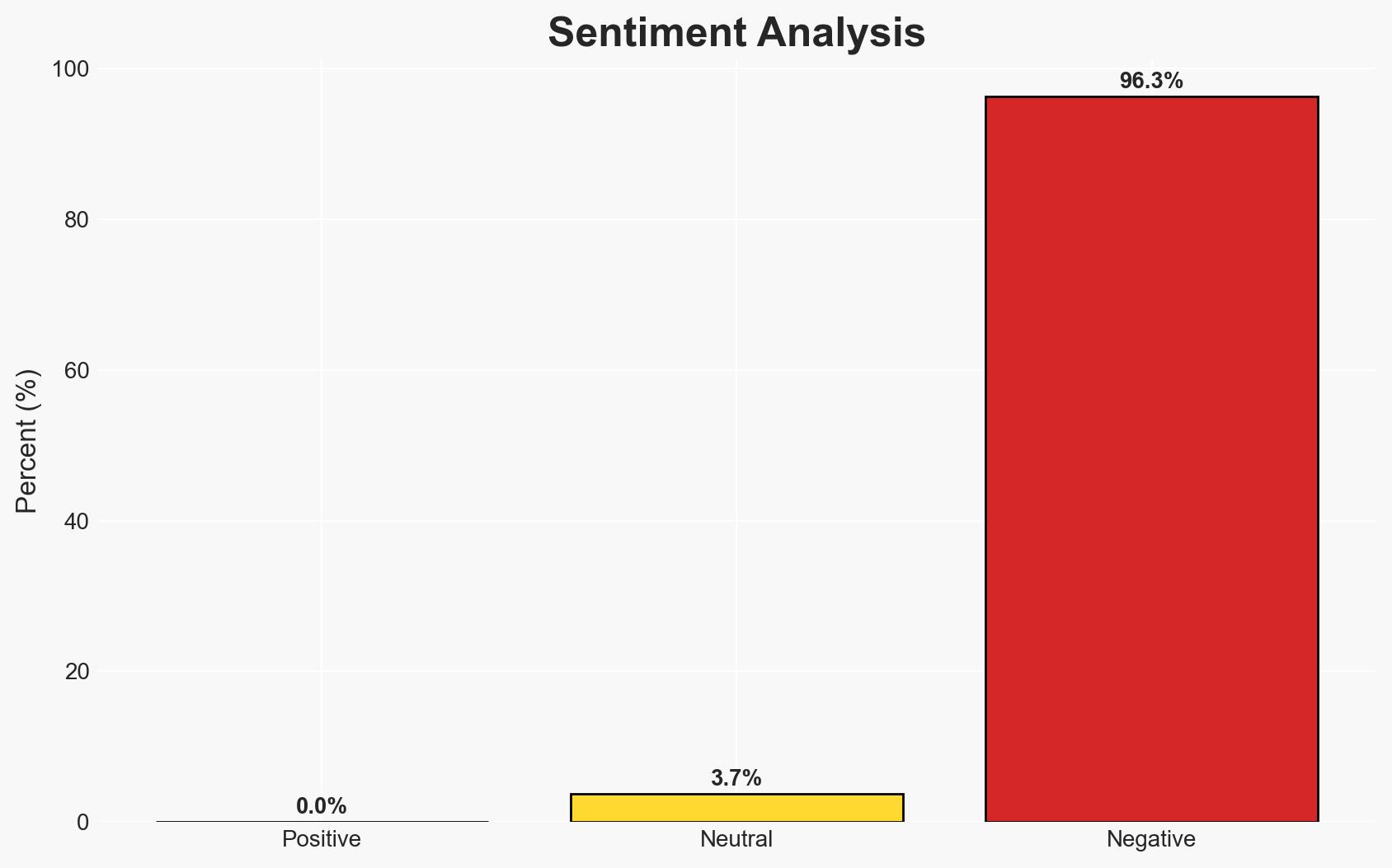
The NHS has issued an open letter to suppliers emphasizing the need for enhanced cybersecurity measures to combat ransomware threats, indicating a shift towards more direct engagement with suppliers. This initiative is likely to impact the healthcare supply chain and operational continuity. Overall, this assessment is made with moderate confidence due to existing information gaps regarding supplier compliance and potential resistance.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The NHS’s initiative will lead to significant improvements in cybersecurity resilience across the healthcare sector. This is supported by the proactive measures outlined in the open letter and the backing of recent legislative efforts. However, uncertainties remain about supplier willingness and capacity to comply.
- Hypothesis B: The initiative will face substantial resistance from suppliers, resulting in limited improvements in cybersecurity resilience. This could be due to potential costs and operational disruptions associated with implementing the required measures. The lack of an audit mechanism may also undermine enforcement.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the structured approach and government backing, but key indicators such as supplier feedback and compliance rates could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Suppliers have the technical and financial capacity to implement the recommended cybersecurity measures; the NHS will provide adequate support and resources; the threat of ransomware remains a significant motivator for compliance.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on supplier compliance rates and the effectiveness of the proposed measures are lacking; there is limited data on the potential cost implications for suppliers.
- Bias & Deception Risks: There may be cognitive bias towards overestimating supplier compliance; source bias could exist if the NHS’s communication is overly optimistic about supplier engagement.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a more secure healthcare system but may also strain supplier relationships and resources. The initiative’s success will depend on effective collaboration and resource allocation.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strengthened cybersecurity could enhance national resilience, but failure could expose vulnerabilities to adversaries.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Improved cybersecurity may reduce the risk of ransomware attacks, enhancing operational security.
- Cyber / Information Space: The initiative may set a precedent for other sectors, influencing broader cybersecurity policies.
- Economic / Social: Potential increased costs for suppliers could impact service delivery and pricing, affecting economic stability in the sector.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Establish a monitoring framework to assess supplier compliance and identify early challenges; engage with suppliers to address concerns and provide support.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance supplier capabilities; invest in training and resources to support compliance efforts.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: High compliance leads to reduced cyber threats. Worst: Supplier resistance causes minimal improvement. Most-Likely: Gradual improvement with some resistance, contingent on ongoing support and engagement.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Phil Huggins, National CISO for health and care at the DHSC
- Mike Fell, Executive Director of National Cyber Operations for NHS England
- NHS England
- Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC)
7. Thematic Tags
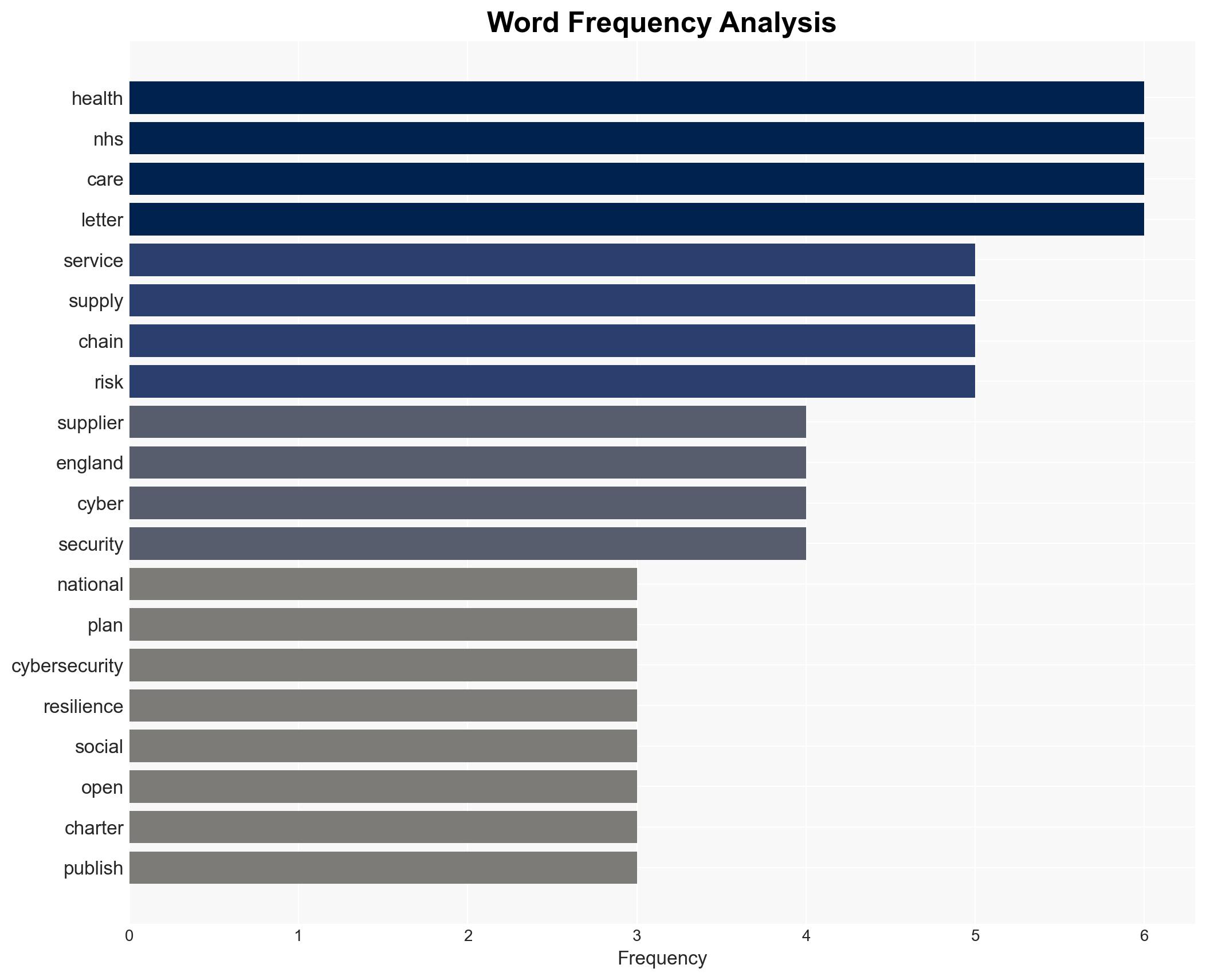
cybersecurity, healthcare, ransomware, supply chain, NHS, policy implementation, risk management
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us