Fortinet alerts on ongoing FortiCloud SSO bypass attacks targeting updated devices and firewall configurations
Published on: 2026-01-23
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Fortinet warns of active FortiCloud SSO bypass affecting updated devices
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
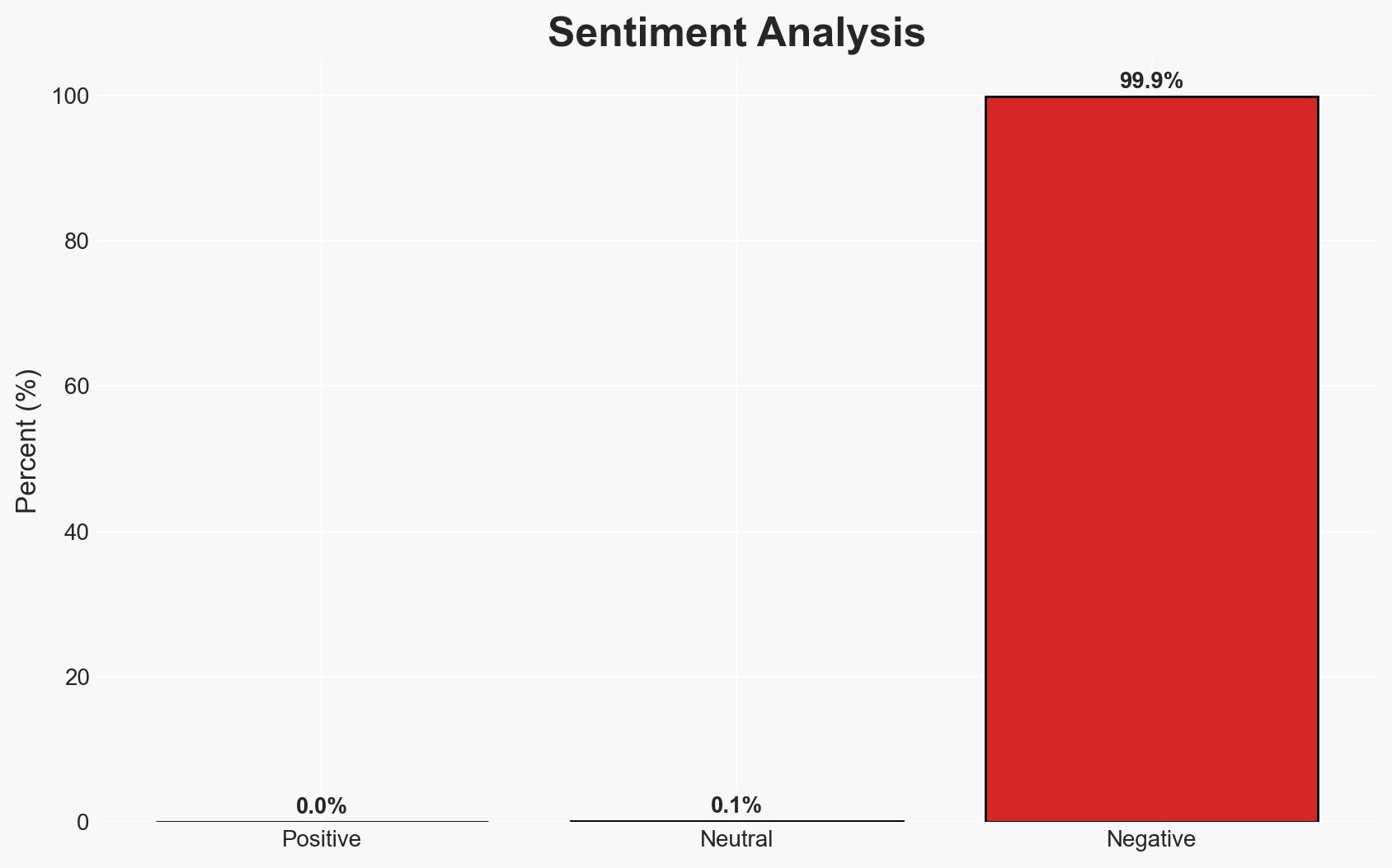
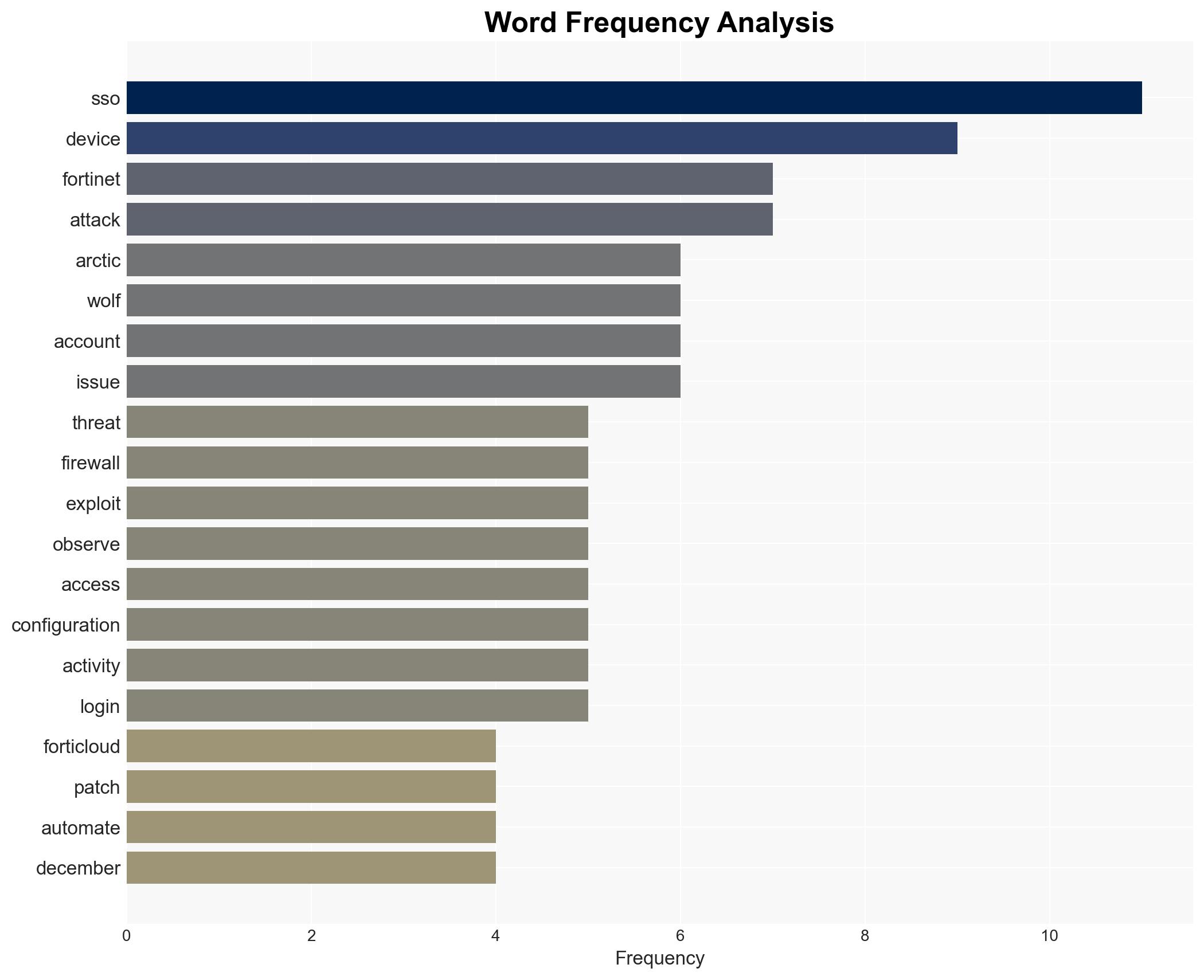
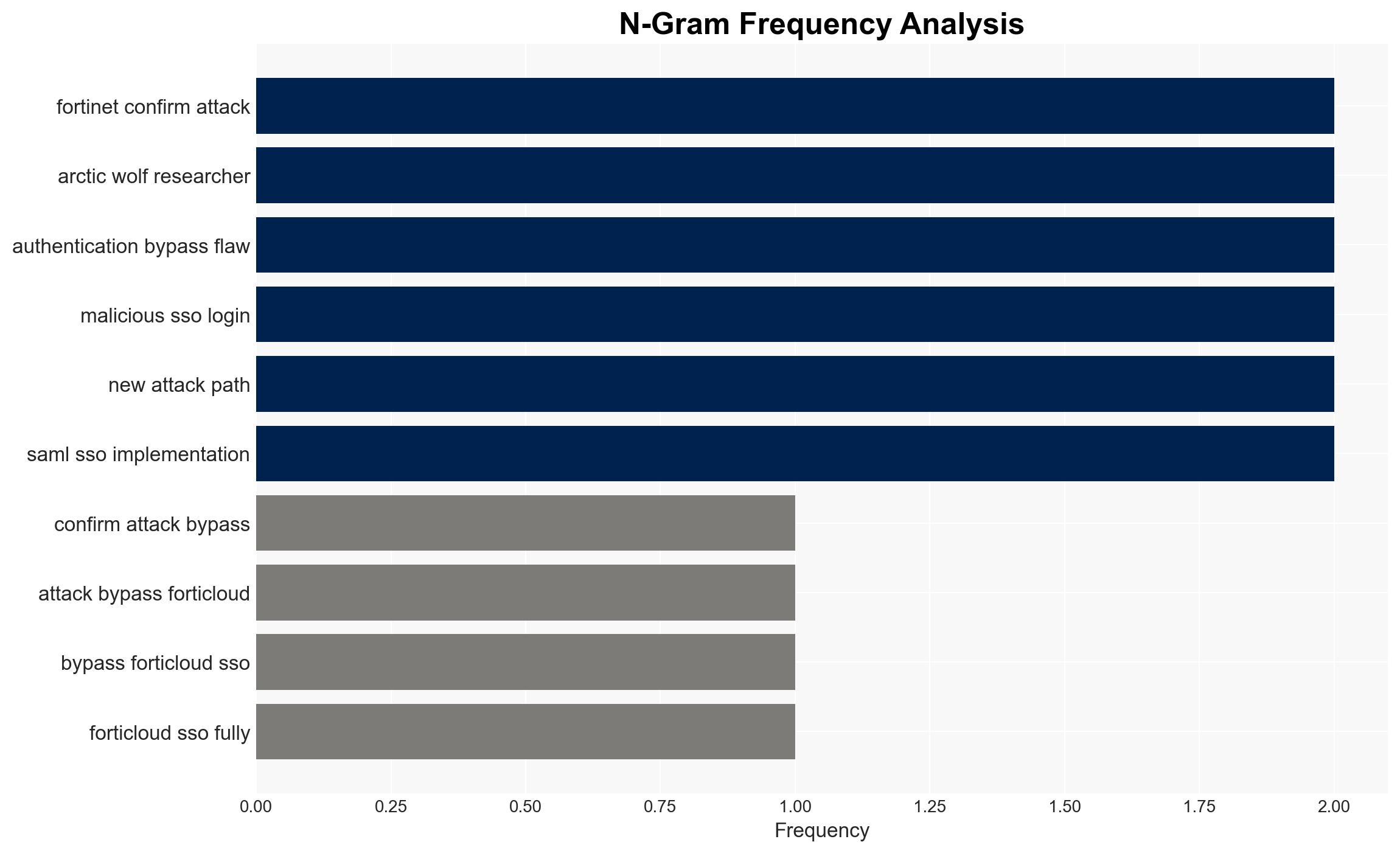
Recent cyber attacks have successfully bypassed FortiCloud SSO on fully patched FortiGate devices, indicating a new vulnerability path. The attacks are highly automated and target administrative accounts, posing significant risks to network security. The most likely hypothesis is that threat actors have discovered a new method to exploit FortiCloud SSO, affecting organizations using Fortinet products. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Threat actors have discovered a new vulnerability in FortiCloud SSO that allows them to bypass security measures on fully patched devices. This is supported by the evidence of successful attacks on updated devices and the rapid automation of these attacks. Key uncertainty includes the exact nature of the new vulnerability.
- Hypothesis B: The attacks are exploiting a previously unknown flaw in the implementation of security patches, rather than a new vulnerability. This is less supported as Fortinet has confirmed the attacks on fully patched devices, suggesting a new exploit path.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the confirmation of successful attacks on fully patched devices and the identification of a new attack path by Fortinet. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new information on patch implementation flaws or further technical details on the exploit.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The new attack path is distinct from previously patched vulnerabilities; threat actors have the capability to automate complex attacks; Fortinet’s detection and reporting are accurate and timely.
- Information Gaps: Detailed technical specifics of the new vulnerability; the identity and motivations of the threat actors; the full scope of affected devices and organizations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in relying on vendor-provided information; risk of threat actors using deception to obscure true attack vectors.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased cyber threat activity targeting Fortinet users, potentially affecting global network security. If unresolved, it may impact trust in Fortinet’s security solutions and could prompt regulatory scrutiny.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored actors are involved; possible diplomatic repercussions if critical infrastructure is affected.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for organizations using Fortinet products; increased demand for cybersecurity measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for broader exploitation of similar vulnerabilities in other products; increased focus on SSO security.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial losses for affected organizations; reputational damage to Fortinet and affected entities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of Fortinet devices for unusual activity; apply any interim security measures advised by Fortinet; engage with cybersecurity partners for threat intelligence sharing.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures including alternative security solutions; strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity firms; invest in capability development for rapid response to emerging threats.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Fortinet rapidly patches the new vulnerability, restoring confidence and security.
- Worst: Exploits spread to other systems, causing widespread disruption and financial loss.
- Most-Likely: Continued targeted attacks until a patch is released, with moderate impact on affected organizations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Fortinet
- Arctic Wolf
- Threat actors (not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability exploitation, Fortinet, SSO bypass, network security, threat intelligence, automated attacks
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us