AI-Driven Cybercrime Emerges as Major Security Threat for Businesses in 2023, Experts Warn
Published on: 2026-01-24
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: ‘Weaponized AI’ could be the biggest security threat facing your business this year – here’s what experts say you should be on the lookout for
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
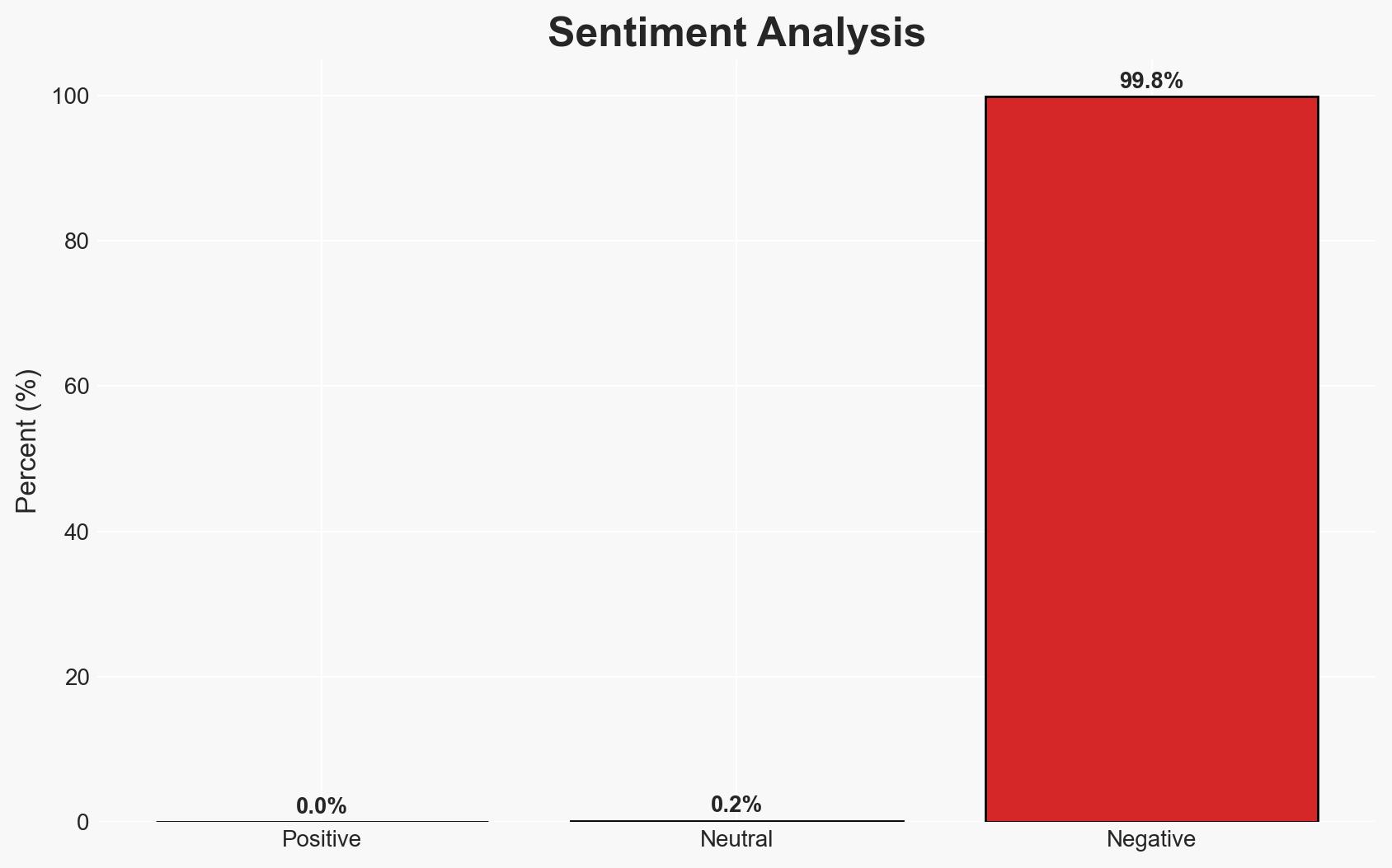
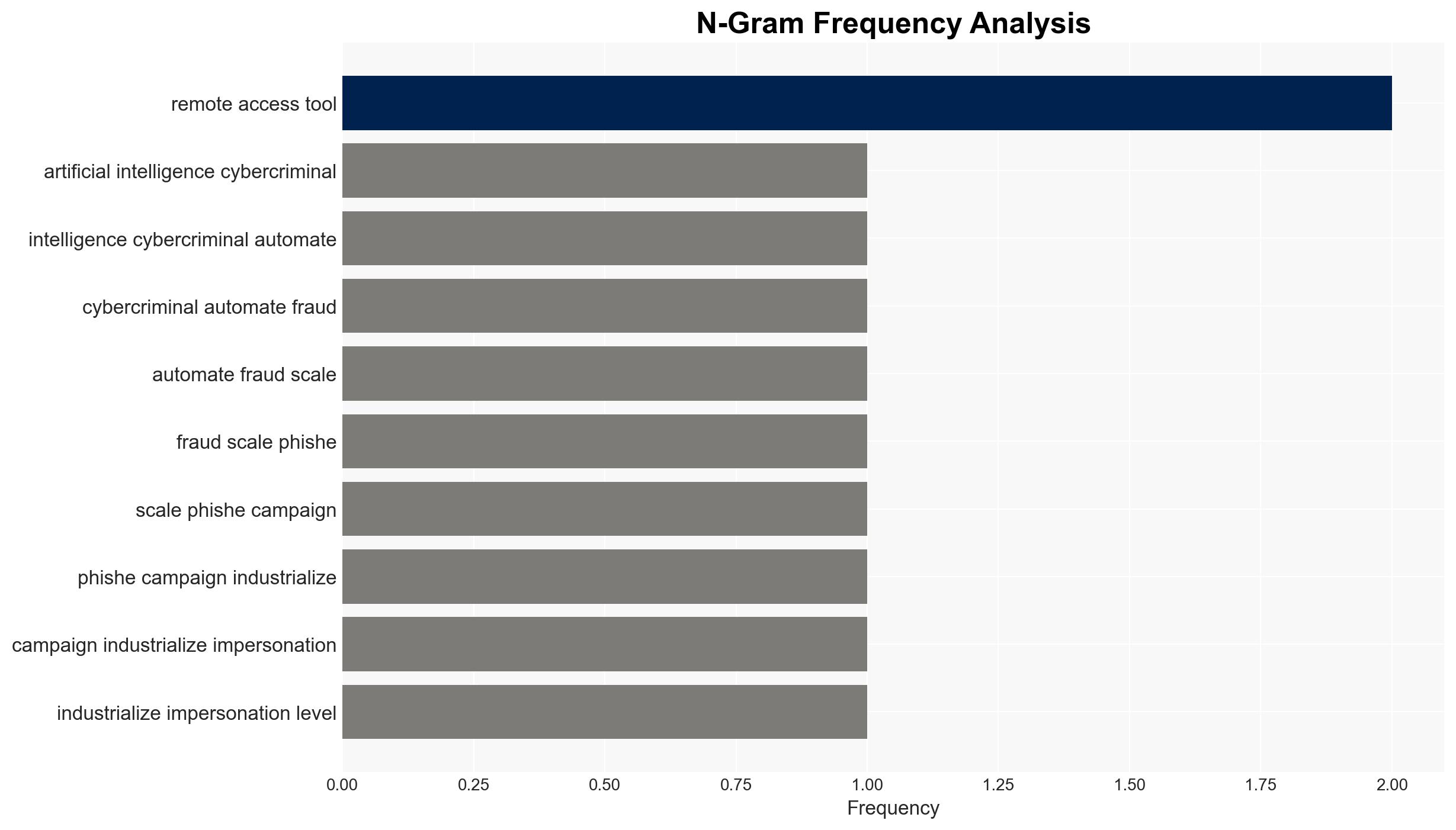
Weaponized AI is emerging as a significant cyber threat, with AI tools being used to automate and scale cybercriminal activities such as phishing and impersonation. Businesses are particularly vulnerable to these AI-assisted attacks, which are becoming increasingly sophisticated and difficult to detect. The most likely hypothesis is that the commercial availability of AI tools is driving a structured AI crimeware economy. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the current evidence and trends.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The rise in AI-assisted cybercrime is primarily driven by the commercial availability of AI tools, leading to a structured crimeware economy. This is supported by the increase in dark web activity and the emergence of vendors offering AI crimeware services. However, the extent of adoption across different criminal networks remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The increase in AI-assisted cybercrime is a temporary surge driven by initial experimentation with new AI technologies, which may stabilize or decline as defenses improve. This is contradicted by the sustained high interest and market activity observed since the release of ChatGPT.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the persistent and structured nature of the AI crimeware market and the significant increase in related dark web activity. Indicators such as a decrease in market activity or a shift in criminal focus could alter this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI tools will remain commercially available; cybercriminals will continue to exploit AI for economic gain; current defensive measures are insufficient against AI-assisted attacks.
- Information Gaps: Detailed understanding of the full scope of AI tool adoption by cybercriminals; effectiveness of current countermeasures against AI-assisted attacks.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from cybersecurity firms with vested interests; possible exaggeration of threat levels to drive demand for security solutions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of weaponized AI in cybercrime is likely to evolve, impacting various sectors and necessitating adaptive strategies. The integration of AI in cybercriminal activities could lead to more sophisticated and widespread attacks.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international tensions as states may accuse each other of harboring or supporting cybercriminals using AI.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat landscape with AI-enabled attacks potentially targeting critical infrastructure and national security assets.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased complexity in cybersecurity operations, requiring advanced AI-based defenses and continuous monitoring.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic losses from cybercrime could destabilize businesses and erode trust in digital systems, impacting social cohesion.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of dark web activities; implement AI-driven anomaly detection systems; conduct awareness training for employees on AI-enabled threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for intelligence sharing; invest in AI-based defensive technologies; establish protocols for rapid response to AI-assisted attacks.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Effective defenses reduce the impact of AI-assisted cybercrime, with improved international cooperation on cybersecurity.
- Worst Case: AI-enabled attacks overwhelm defenses, causing significant economic and security disruptions.
- Most Likely: Continued evolution of AI crimeware with incremental improvements in defensive capabilities, maintaining a dynamic threat landscape.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
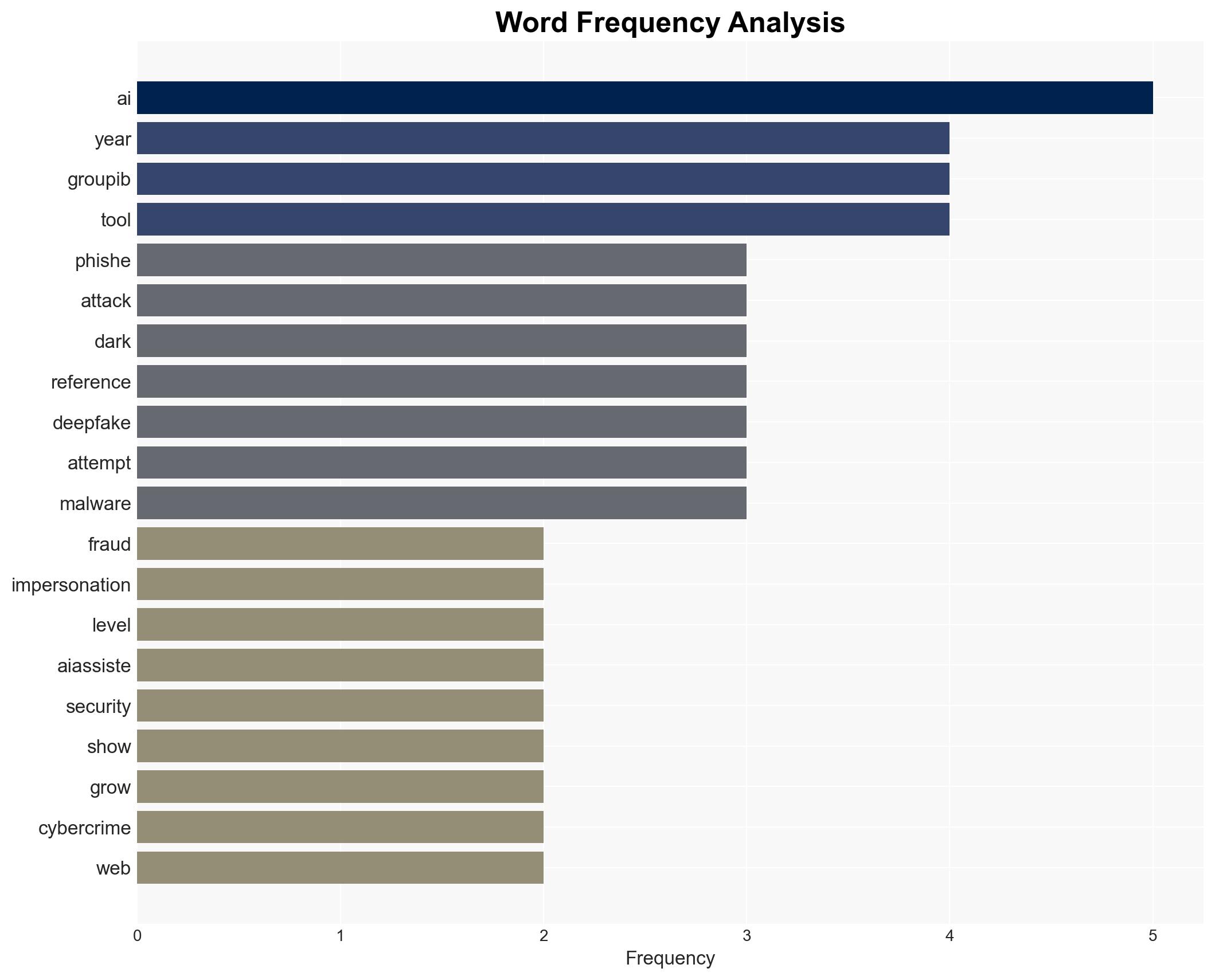
cybersecurity, AI crimeware, dark web, phishing, deepfake, cyber defense, economic impact
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us