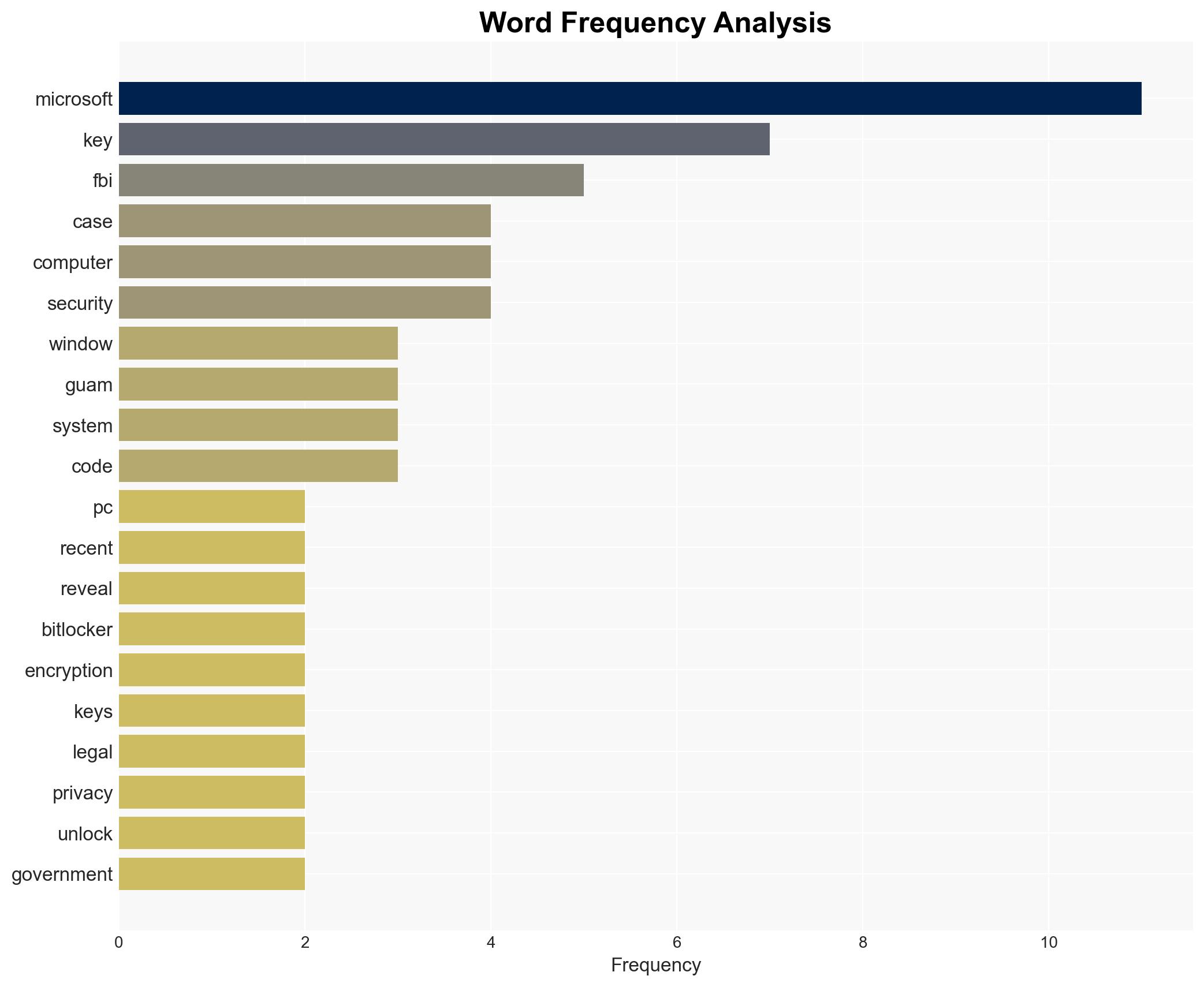
FBI Unlocked Windows Laptops Using BitLocker Keys Provided by Microsoft in Guam Investigation
Published on: 2026-01-24
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: FBI Accessed Windows Laptops After Microsoft Shared BitLocker Recovery Keys
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The FBI accessed encrypted laptops by obtaining BitLocker recovery keys from Microsoft, highlighting a significant privacy vulnerability. This incident affects users who store recovery keys in their Microsoft accounts, with moderate confidence in the assessment that this practice may undermine perceived data security. The situation underscores the tension between privacy and law enforcement needs.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Microsoft’s cooperation with the FBI is a standard legal compliance measure, reflecting a balance between user privacy and legal obligations. Supporting evidence includes Microsoft’s policy of providing keys upon valid legal orders. However, the extent of user awareness about this policy is uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: Microsoft’s actions represent a broader trend of tech companies prioritizing government cooperation over user privacy, potentially leading to increased surveillance. This is contrasted by Apple’s refusal in a similar case, suggesting variability in corporate policies.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to Microsoft’s transparent policy and legal framework compliance. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in user privacy policies or increased public backlash.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Users are generally unaware of the implications of storing recovery keys online; Microsoft’s cooperation is limited to legal requests; the FBI’s actions are within legal boundaries.
- Information Gaps: The extent of user consent and awareness regarding key storage; details on how frequently such keys are accessed by law enforcement.
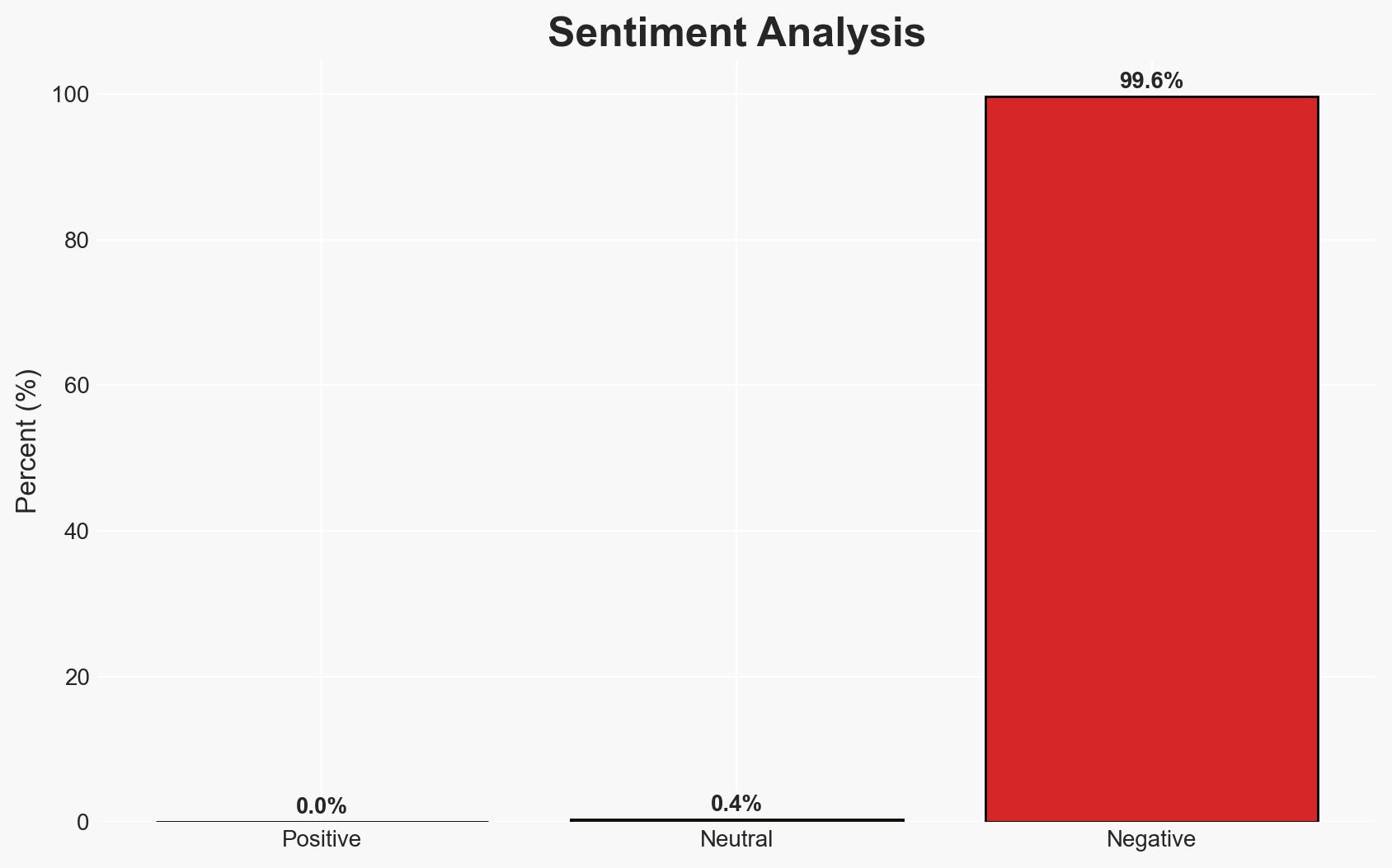
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting favoring privacy concerns; risk of misinterpretation of legal compliance as overreach.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of tech companies’ data privacy practices and influence future regulatory measures. It may also affect user trust and corporate reputations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for policy debates on data privacy and government access to encrypted data.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced law enforcement capabilities in accessing encrypted data could improve investigation outcomes but may also provoke privacy advocacy backlash.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased awareness of digital vulnerabilities could lead to changes in user behavior and cybersecurity practices.
- Economic / Social: Potential impact on Microsoft’s market position and user trust; broader implications for tech industry standards.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor public and legal reactions; assess user awareness and consent mechanisms for key storage.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop strategies to enhance transparency in data handling; engage with stakeholders on privacy standards.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Improved user trust through enhanced transparency and privacy measures.
- Worst: Escalating privacy concerns leading to regulatory challenges and diminished user trust.
- Most-Likely: Gradual adaptation of privacy policies with ongoing public discourse on data security.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Microsoft
- FBI
- Kathleen Peredo
- Marleen Pinaula
- Charissa Tenorio
- Frankie Rosalin
- Guam Department of Labour
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data privacy, law enforcement, encryption, tech policy, user consent, corporate compliance
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us