Database Leak Exposes 149 Million Logins, Including 900,000 Apple Accounts
Published on: 2026-01-26
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: 149M logins exposed in unsecured database inc 900k Apple accounts
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
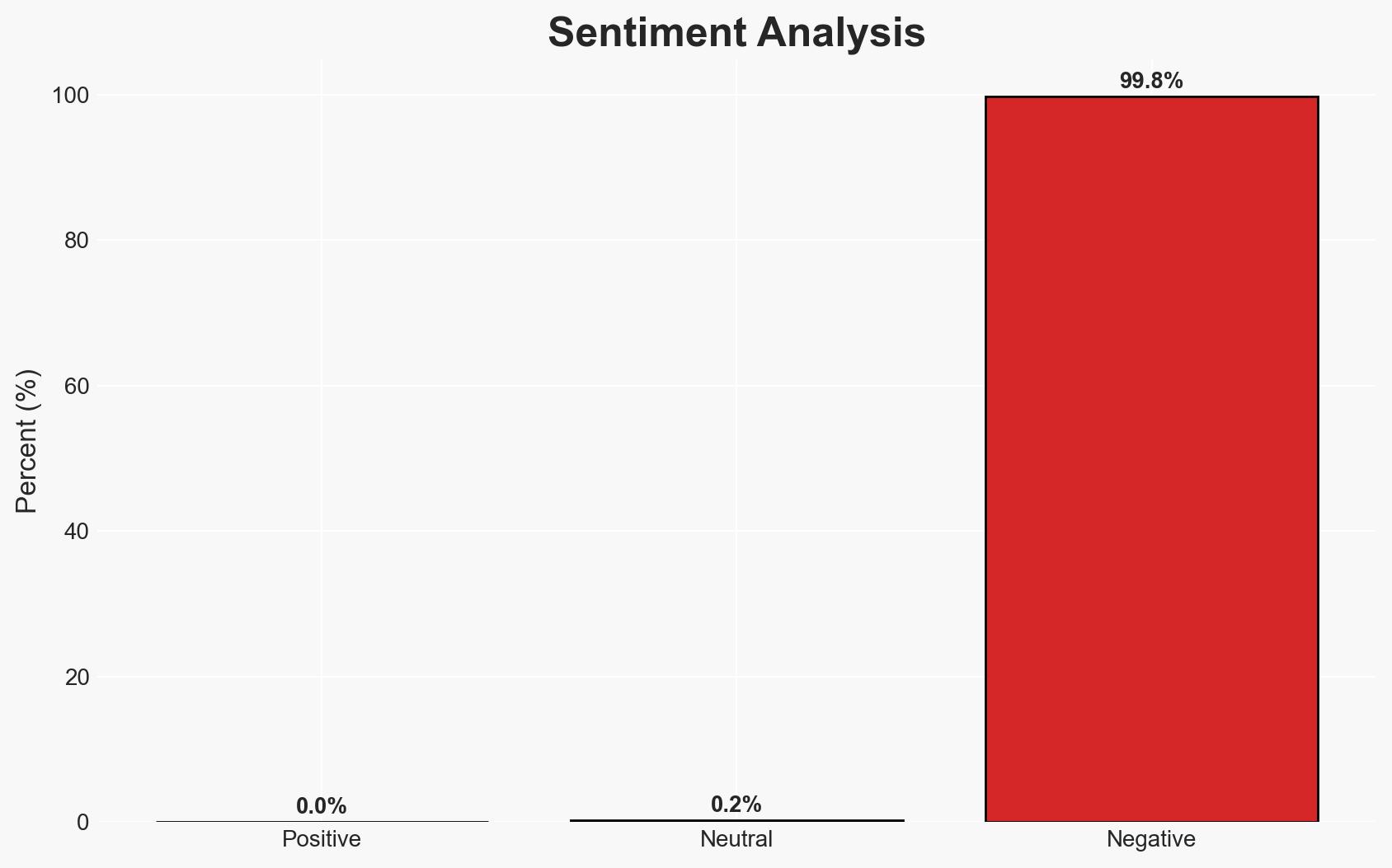
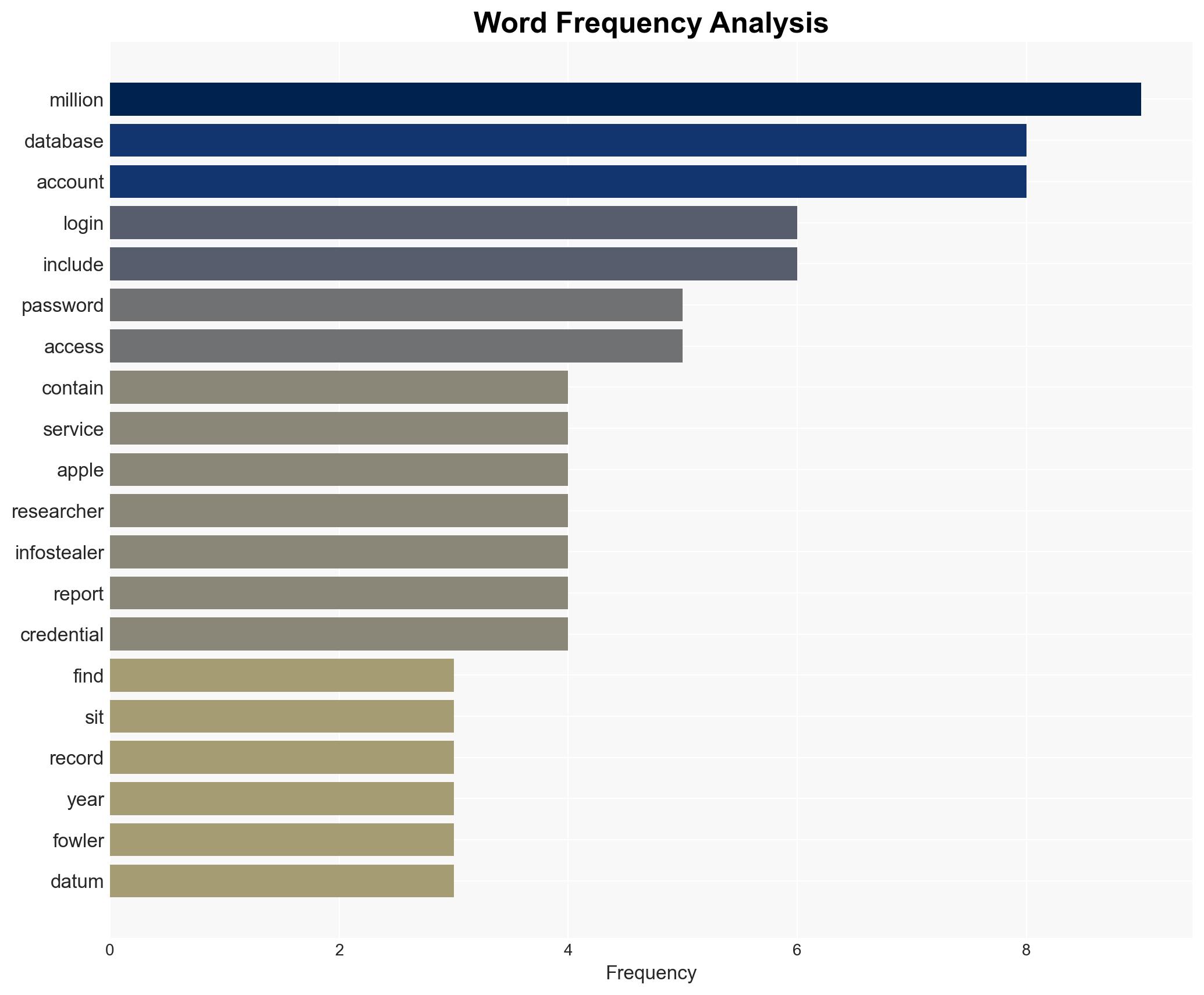
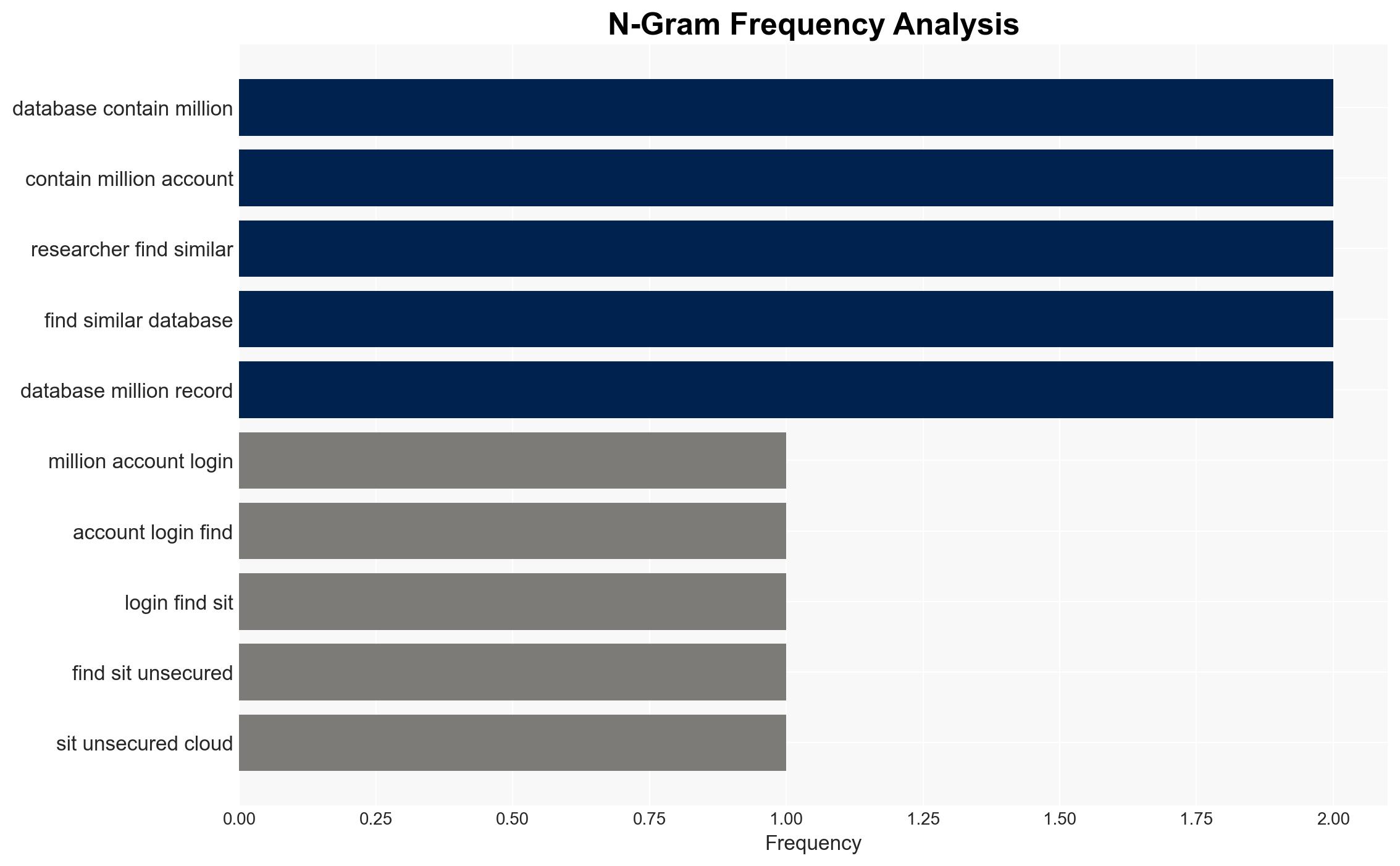
The exposure of 149 million login credentials, including 900,000 Apple accounts, in an unsecured database poses a significant cybersecurity threat. This incident highlights vulnerabilities in data storage and the increasing prevalence of infostealer malware. The most likely hypothesis is that these credentials were harvested through malware and aggregated over time. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to the recurring nature of such incidents and the involvement of known infostealer tactics.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The database was compiled from credentials harvested by infostealer malware, as indicated by the presence of multiple service logins and the history of similar incidents. Key uncertainties include the exact timeline of data aggregation and the full scope of affected services.
- Hypothesis B: The database was created through unauthorized access to multiple service providers’ systems, rather than through malware. This is less supported due to the lack of evidence of breaches in the service providers’ systems and the known use of infostealers.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the pattern of data collection consistent with infostealer malware and the previous discovery of similar databases. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of breaches in service providers’ systems or new data on the methods of data aggregation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The database was accessible to unauthorized users; infostealer malware was used to collect the data; the hosting provider was unaware of the database’s contents.
- Information Gaps: The identity of the actors responsible for compiling the database; the specific malware variants used; the timeline of data aggregation.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in relying on a single researcher’s findings; risk of deception if the database was intentionally exposed to mislead or distract from other activities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased cyber threats as exposed credentials are used for further attacks. It may also prompt regulatory scrutiny on data protection practices.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state actors are suspected of involvement or if affected entities are critical infrastructure.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of identity theft and unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased need for cybersecurity measures and monitoring of infostealer malware activity.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact from identity theft and loss of consumer trust in digital services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of exposed credentials, inform affected users, and enforce password resets.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for information sharing on infostealer threats, enhance public awareness campaigns on cybersecurity hygiene.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid containment and mitigation of the threat, leading to improved cybersecurity practices.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation of exposed credentials, resulting in significant financial and reputational damage.
- Most-Likely: Continued sporadic exploitation of credentials with incremental improvements in cybersecurity measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Jeremiah Fowler, Security Researcher
- Google, Service Provider
- Apple, Service Provider
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for other entities.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data breach, infostealer malware, identity theft, digital security, information protection, cyber hygiene
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us