New National Police Service to Enhance Crime-Fighting Capabilities in England and Wales
Published on: 2026-01-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How the British FBI will work
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The establishment of the National Police Service (NPS), dubbed the “British FBI,” aims to centralize efforts against serious crimes such as terrorism, fraud, and organized crime, while enabling local forces to focus on community-level offenses. This restructuring is expected to enhance law enforcement efficiency in England and Wales. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the current lack of detailed operational plans and potential implementation challenges.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The NPS will significantly improve the UK’s capacity to tackle serious crime by consolidating expertise and resources, leading to more effective crime prevention and resolution. This is supported by the consensus among law enforcement experts and the integration of advanced technology. However, uncertainties remain regarding the execution of reforms and inter-agency cooperation.
- Hypothesis B: The NPS may face operational challenges and resistance from existing agencies, potentially resulting in inefficiencies and limited impact on crime rates. This hypothesis considers the complexities of merging multiple agencies and the potential for bureaucratic inertia.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to broad institutional support and the strategic focus on modernizing policing capabilities. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include delays in implementation, resistance from local forces, or failure to integrate new technologies effectively.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The NPS will receive adequate funding and political support; existing agencies will cooperate in the transition; advanced technologies will be effectively integrated; public support will be maintained.
- Information Gaps: Detailed operational plans for the NPS; specific metrics for success; potential resistance from local police forces; public opinion data on the reforms.
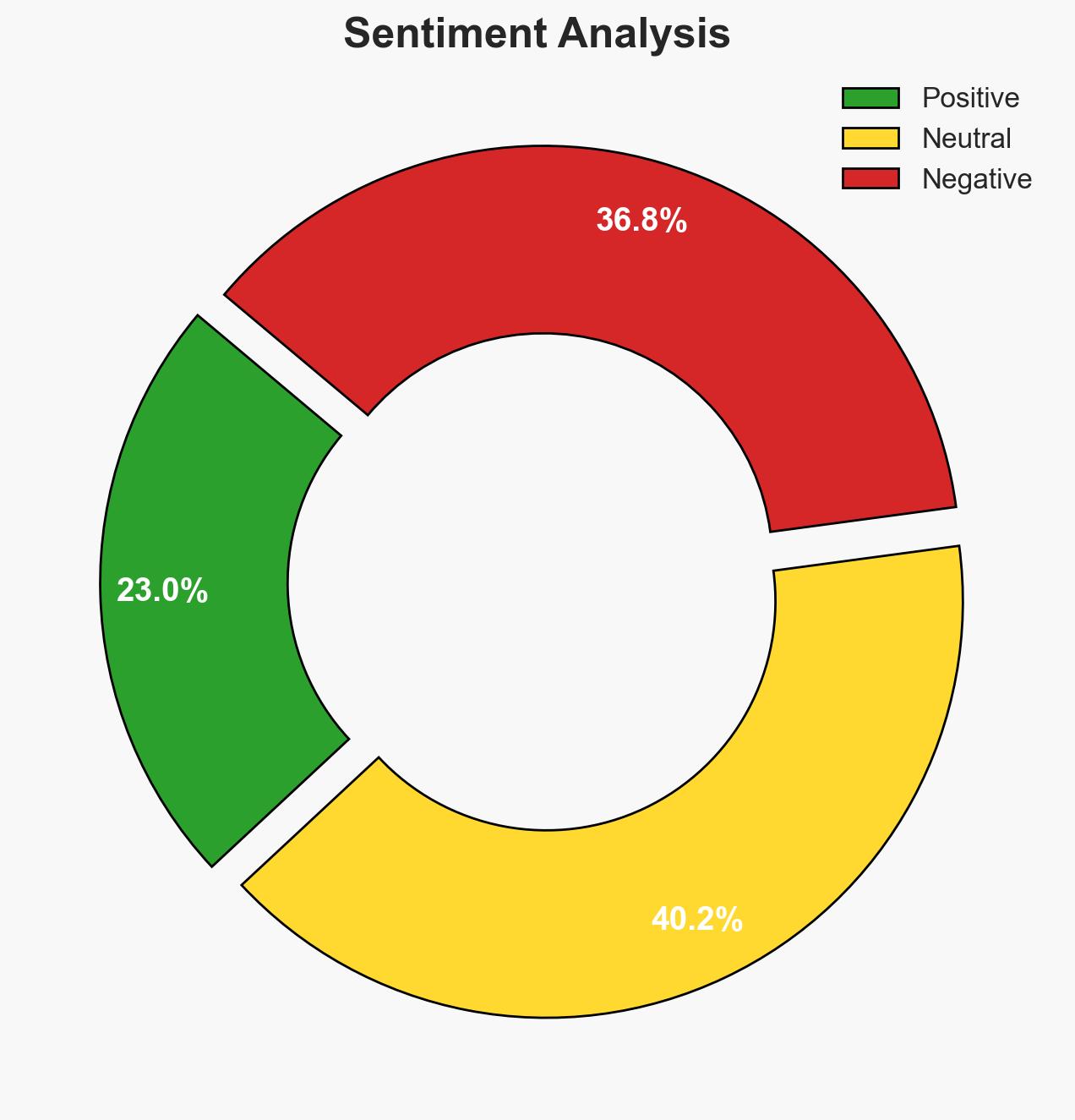
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in expert consensus; government overstatement of reform benefits; lack of transparency in technology deployment, particularly facial recognition.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The NPS could redefine the UK’s law enforcement landscape, impacting crime rates and public trust in policing. However, the transition may encounter resistance and operational hurdles.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased centralization of power in law enforcement, affecting regional autonomy in Scotland and Northern Ireland.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced capability to address cross-border and complex crimes, but risks of coordination failures during the transition.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased use of digital tools like facial recognition may raise privacy concerns and require robust cyber defenses.
- Economic / Social: Potential for improved public safety and economic stability, but social tensions could arise from perceived overreach or privacy violations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Establish a clear communication strategy to manage public expectations; initiate stakeholder engagement to address concerns and gather input.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop robust training programs for NPS personnel; monitor integration progress and adapt strategies as needed; foster inter-agency collaboration.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Smooth integration leads to significant crime reduction and enhanced public trust.
- Worst: Implementation failures result in increased crime rates and public dissatisfaction.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvements with intermittent challenges, requiring ongoing adjustments.
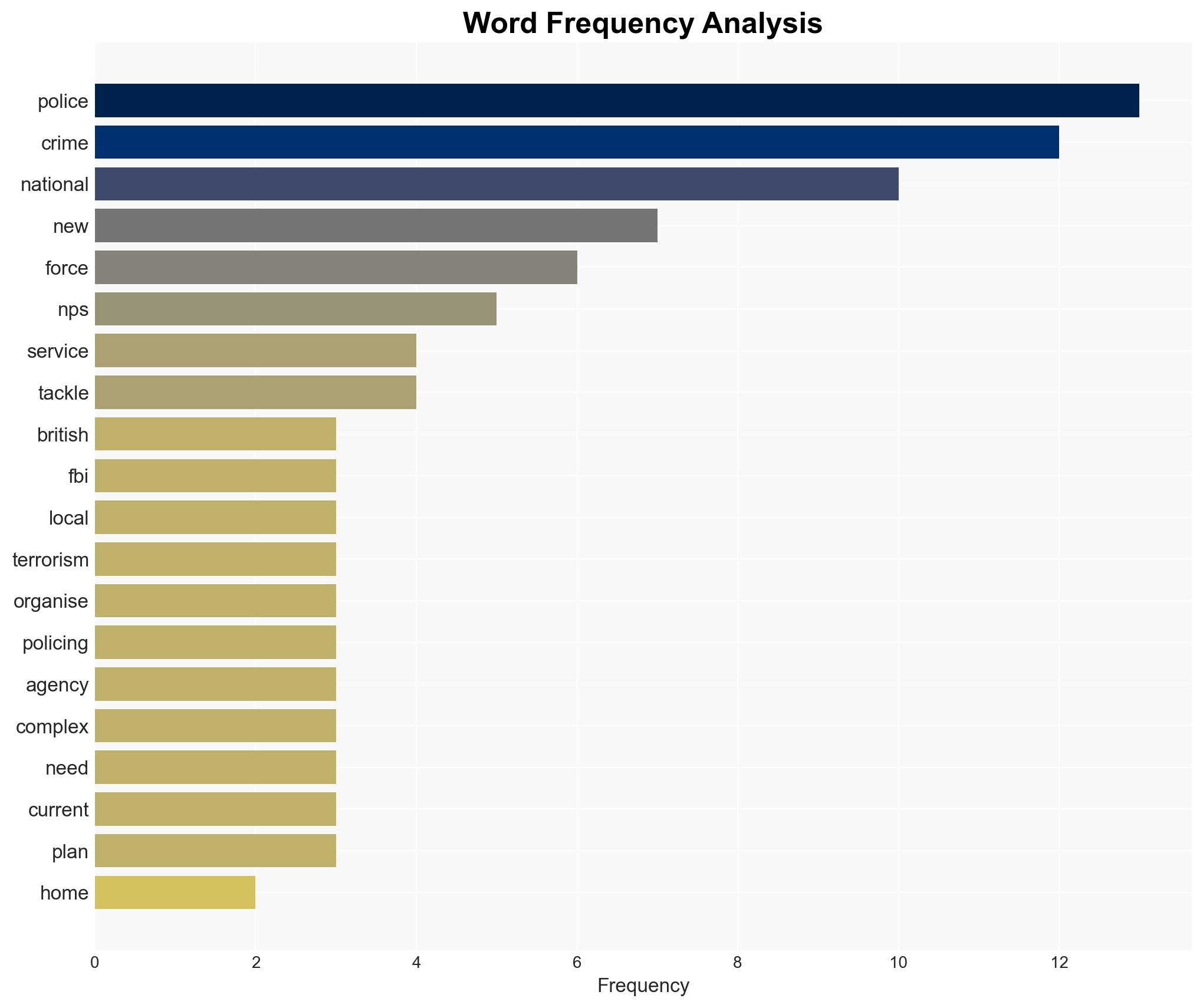
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Shabana Mahmood, Home Secretary
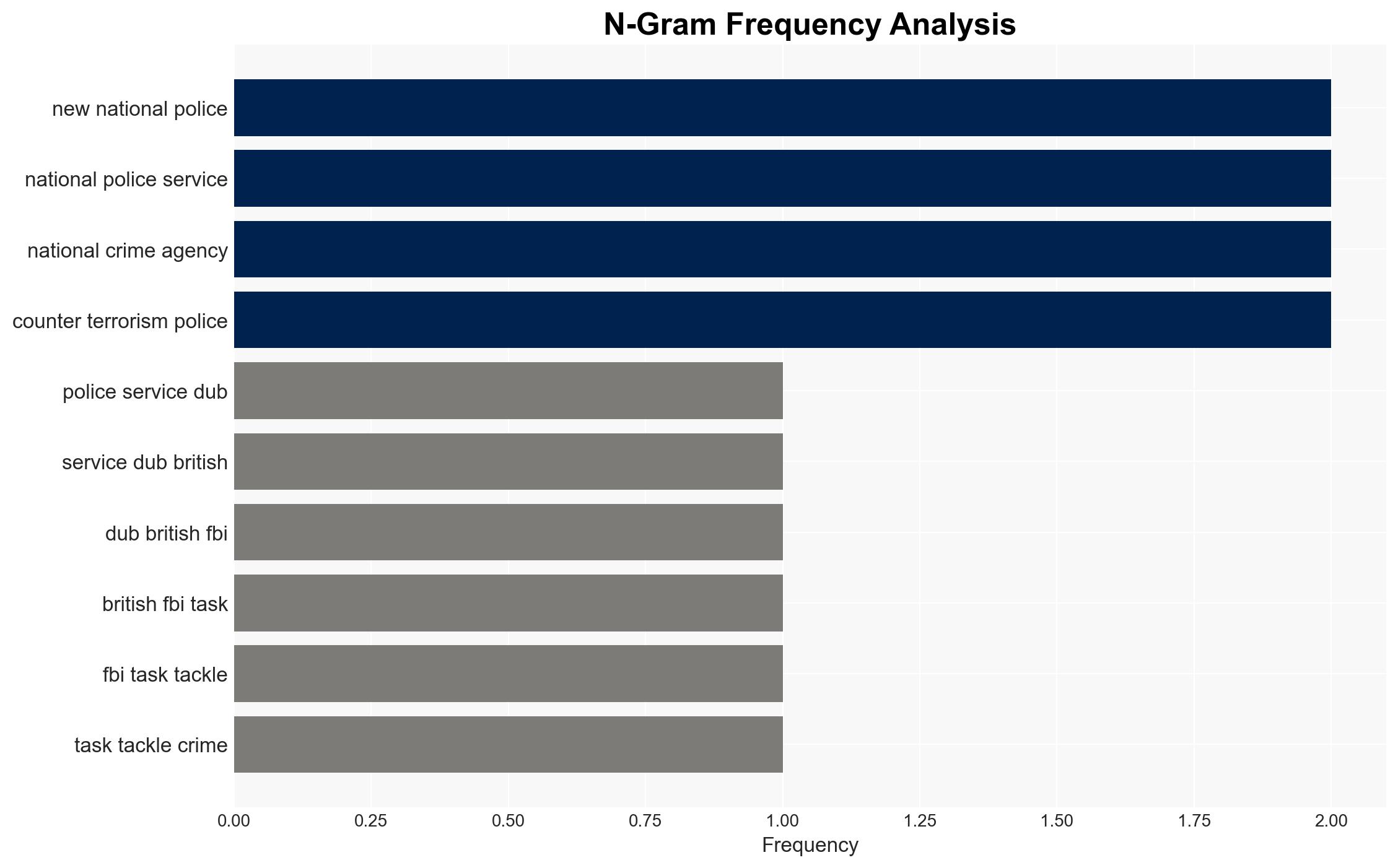
- National Police Service (NPS)
- National Crime Agency
- Counter Terrorism Policing
- National Police Chiefs’ Council
- College of Policing
- Metropolitan Police
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, law enforcement reform, organized crime, policing technology, public safety, inter-agency cooperation, privacy concerns
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us