ReversingLabs Reports 73% Surge in Malicious Open-Source Packages in 2025 Amid Rising Supply Chain Threats
Published on: 2026-01-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
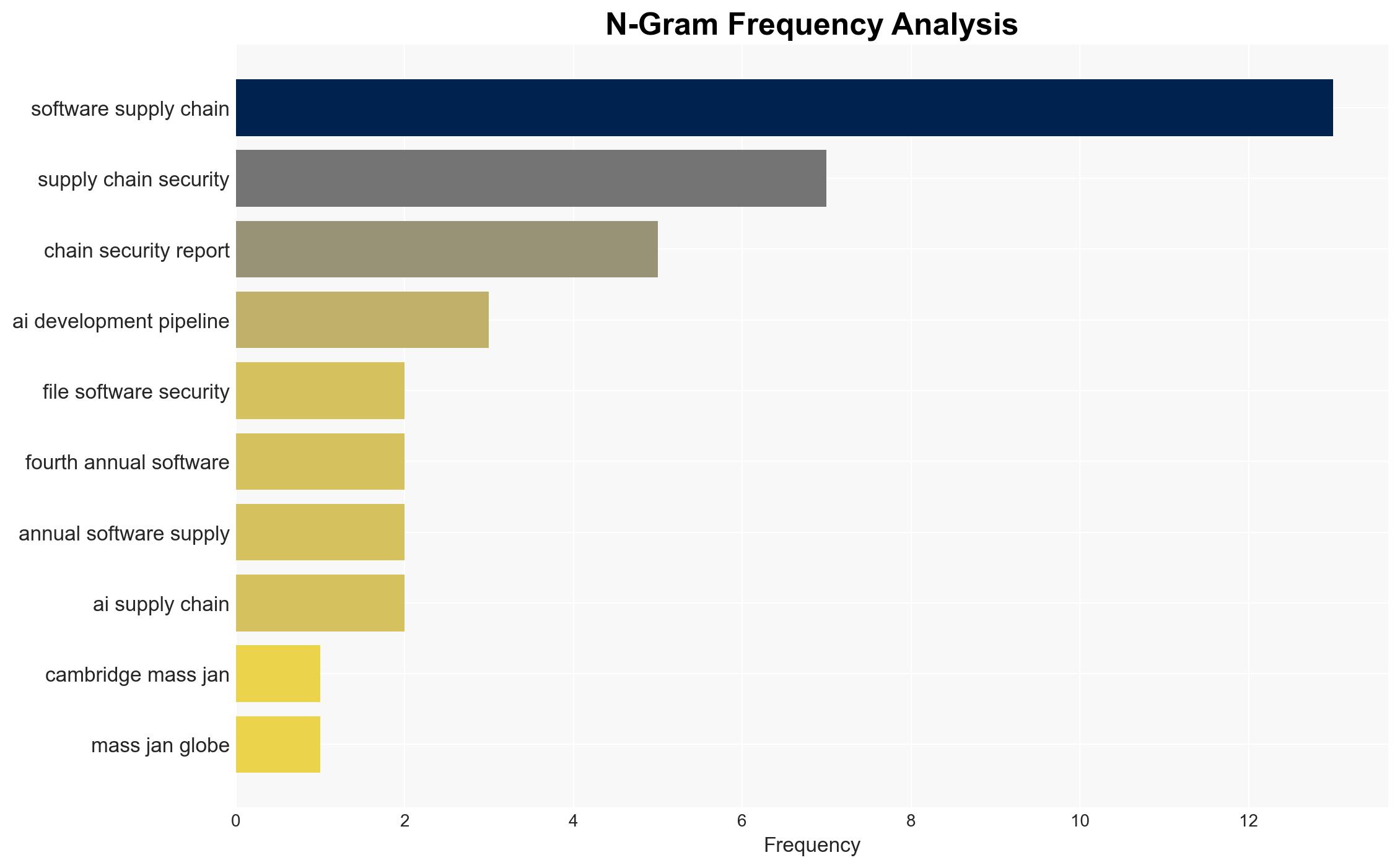
Intelligence Report: ReversingLabs 2026 Software Supply Chain Security Report Identifies 73 Increase in Malicious Open-Source Packages
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
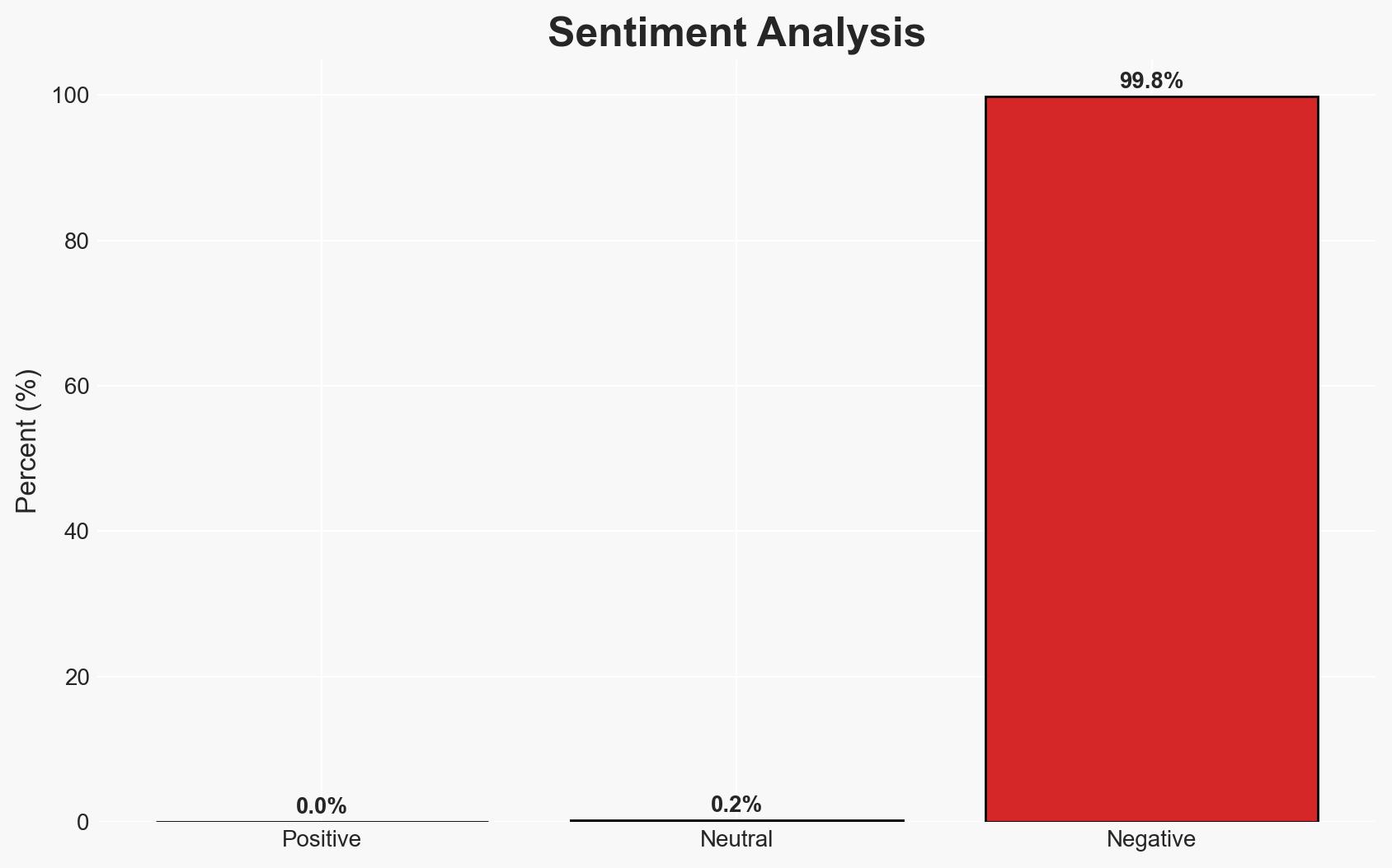
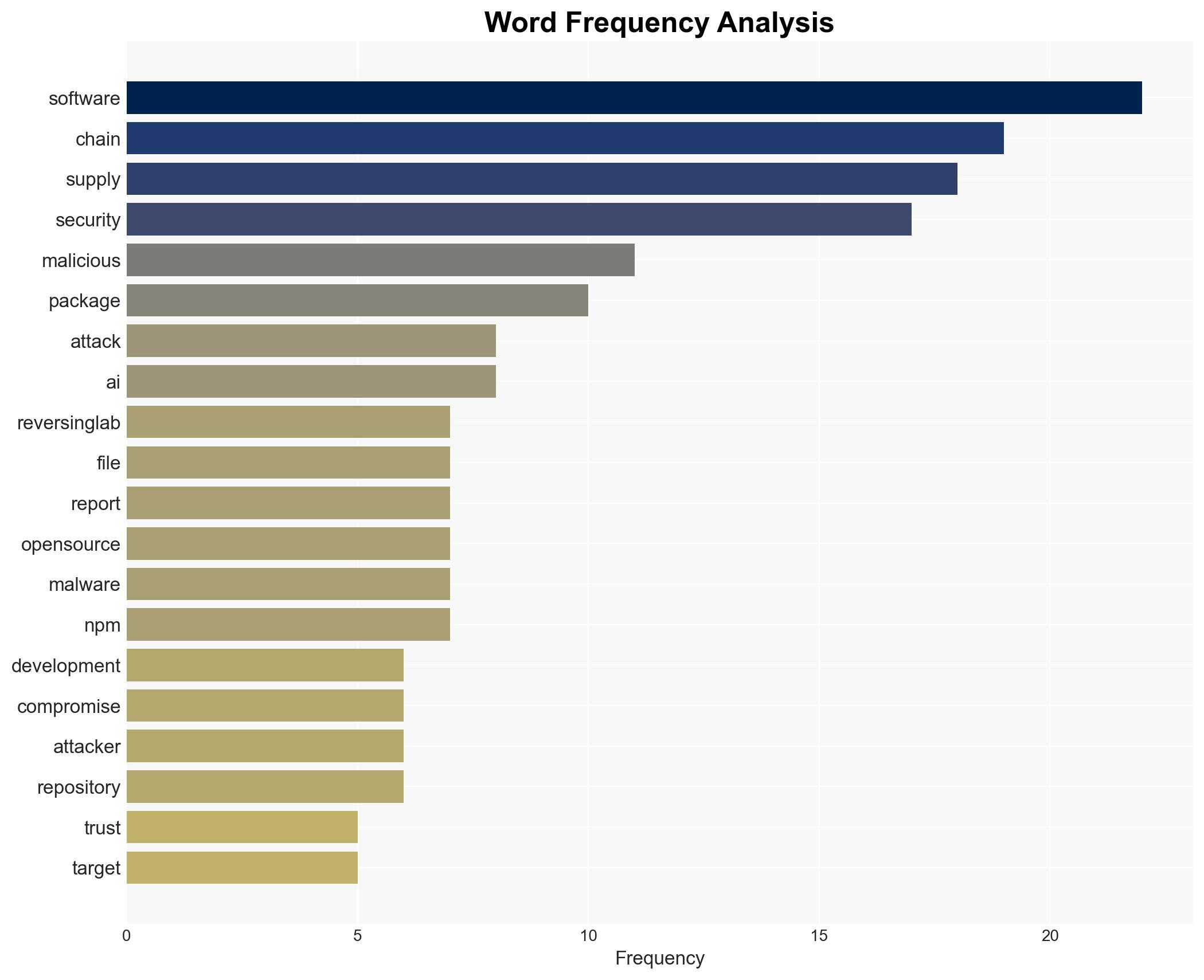
The ReversingLabs 2026 report highlights a significant 73% increase in malicious open-source packages, indicating a strategic shift by cybercriminals and state-sponsored actors towards exploiting software supply chains. This trend poses a substantial threat to organizations relying on open-source software, with a moderate confidence level in the assessment due to the comprehensive data presented. The focus on npm and AI development pipelines suggests a broadening attack surface that requires immediate attention from cybersecurity stakeholders.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The increase in malicious open-source packages is primarily driven by cybercriminals exploiting weak security controls and the inherent trust in open-source ecosystems. Evidence includes the significant rise in npm-related attacks and the use of techniques like dependency confusion. However, the exact motivations and affiliations of the attackers remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: State-sponsored actors are the primary drivers of this increase, using open-source vulnerabilities as a strategic tool for broader geopolitical objectives. While the report mentions state-sponsored actors, there is less direct evidence linking specific state actions to the observed trends.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the detailed evidence of cybercriminal techniques and the specific targeting of npm. Indicators such as increased attribution to specific state actors or geopolitical tensions could shift this judgment towards Hypothesis B.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Open-source ecosystems will continue to be a primary target; npm’s security posture will not significantly improve in the short term; AI development pipelines will remain vulnerable due to rapid adoption and integration.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of attacks to specific actors; comprehensive data on the impact of these attacks on affected organizations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing attacks primarily to cybercriminals without considering state-sponsored motives; reliance on data from a single source (ReversingLabs) could limit perspective.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The increase in malicious open-source packages could lead to widespread disruptions in software development and deployment, affecting various sectors. This trend may exacerbate existing cybersecurity challenges and necessitate a reevaluation of trust models in software supply chains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions between states if state-sponsored involvement is confirmed, leading to retaliatory cyber actions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of supply chain attacks being used as vectors for broader cyber-espionage or sabotage campaigns.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing CI/CD pipelines and enhancing open-source security practices; potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting these vulnerabilities.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact due to disruptions in software services and increased costs for implementing enhanced security measures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of open-source repositories; implement stricter security controls in CI/CD pipelines; conduct awareness campaigns for developers.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with open-source communities to improve security practices; invest in automated threat detection and response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid adoption of security measures reduces attack success rates.
- Worst: Continued increase in attacks leads to major disruptions and loss of trust in open-source software.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security posture mitigate some risks, but attackers continue to exploit vulnerabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- ReversingLabs
- npm
- Mario Vuksan, CEO of ReversingLabs
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, software supply chain, open-source vulnerabilities, state-sponsored actors, npm, AI development, malware
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us