Trump threatens to withdraw US support for Iraq if former PM al-Maliki regains power amid Iran concerns
Published on: 2026-01-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Trump warns Iraq against returning former PM al-Maliki to power amid worries about Iran influence
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
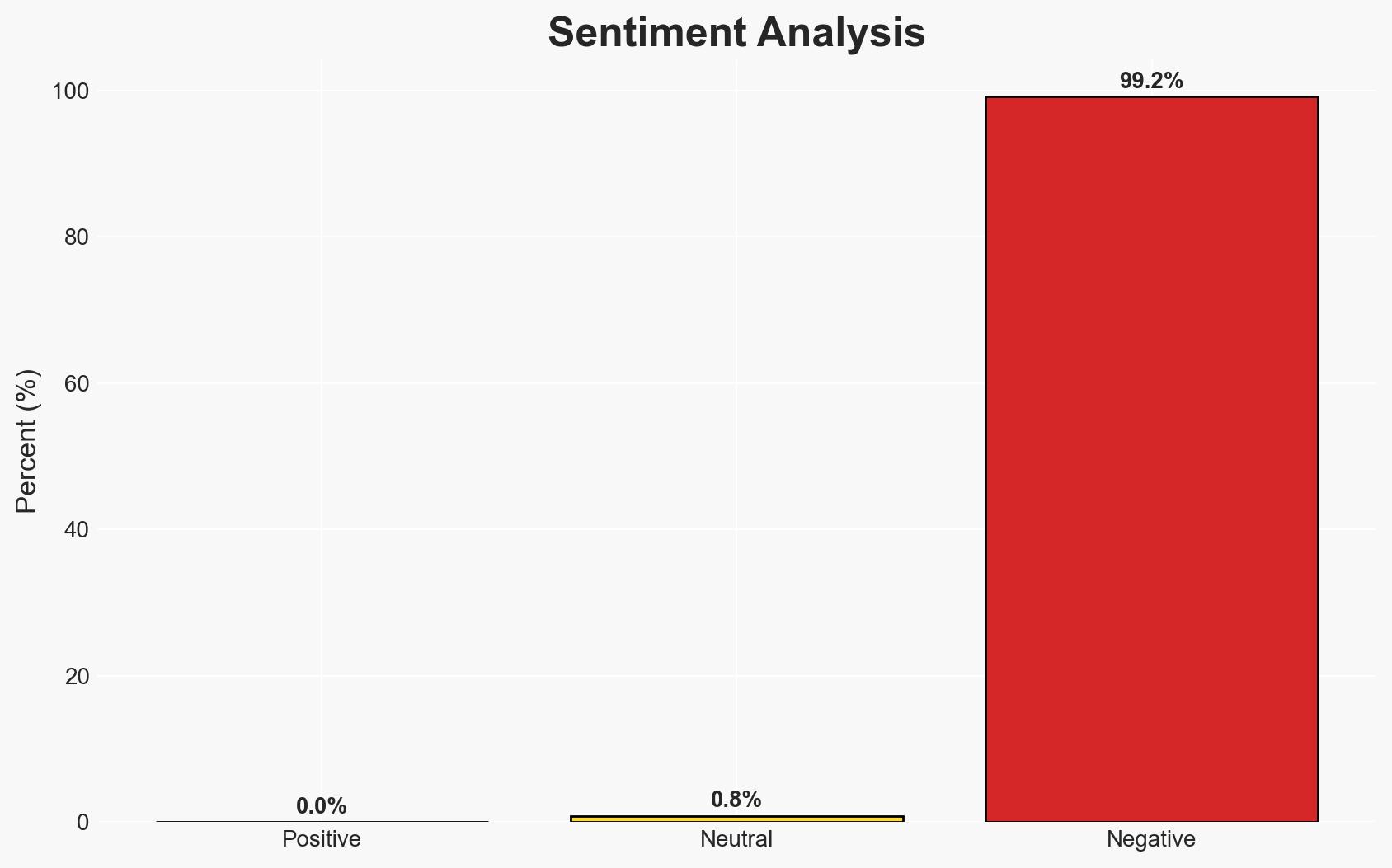
President Trump’s warning against Nouri al-Maliki’s potential return to power in Iraq highlights U.S. concerns over Iranian influence in the region. The situation presents a risk of increased instability in Iraq, potentially affecting U.S. interests and regional security. The most likely hypothesis is that Trump’s warning aims to deter al-Maliki’s candidacy and reduce Iranian influence, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Trump’s warning is a strategic move to prevent al-Maliki’s return to power, thereby limiting Iranian influence in Iraq. Supporting evidence includes Trump’s explicit statements and historical U.S. concerns about al-Maliki’s ties to Iran. Contradicting evidence is limited but includes the possibility that Trump’s statements may not significantly influence Iraqi political dynamics.
- Hypothesis B: Trump’s warning is primarily a domestic political maneuver aimed at reinforcing his administration’s stance against Iran. Supporting evidence includes Trump’s broader Middle East policy and recent tensions with Iran. However, this hypothesis is less supported due to the direct focus on Iraqi political developments.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct link between Trump’s statements and the ongoing political developments in Iraq. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in Iraqi political alignments or shifts in U.S.-Iran relations.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. has significant leverage over Iraqi political processes; Iranian influence is a primary concern for U.S. policy in Iraq; al-Maliki’s return would increase Iranian influence.
- Information Gaps: Details on the Coordination Framework’s internal dynamics and the extent of Iranian influence on al-Maliki’s candidacy.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in assessing Iranian influence; source bias from U.S. political statements; possible manipulation by Iraqi political actors to influence U.S. perceptions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The potential return of al-Maliki could exacerbate sectarian tensions in Iraq and strengthen Iranian influence, complicating U.S. strategic interests in the region. This development could lead to increased instability and security challenges.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential realignment of Iraqi political factions and increased Iranian influence could alter regional power dynamics.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: A shift in power could lead to increased sectarian violence and a resurgence of extremist groups.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased Iranian cyber operations targeting U.S. and Iraqi interests.
- Economic / Social: Political instability could undermine economic recovery efforts and exacerbate social divisions in Iraq.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase diplomatic engagement with Iraqi political actors to discourage al-Maliki’s candidacy; enhance intelligence monitoring of Iranian activities in Iraq.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen partnerships with regional allies to counterbalance Iranian influence; develop contingency plans for potential security escalations.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Al-Maliki does not return to power, reducing Iranian influence. Worst: Al-Maliki returns, increasing instability and Iranian influence. Most-Likely: Continued political uncertainty with moderate Iranian influence.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Nouri al-Maliki
- Donald Trump
- Coordination Framework
- Mohammed Shia al-Sudani
- Iranian Government (Tehran)
7. Thematic Tags
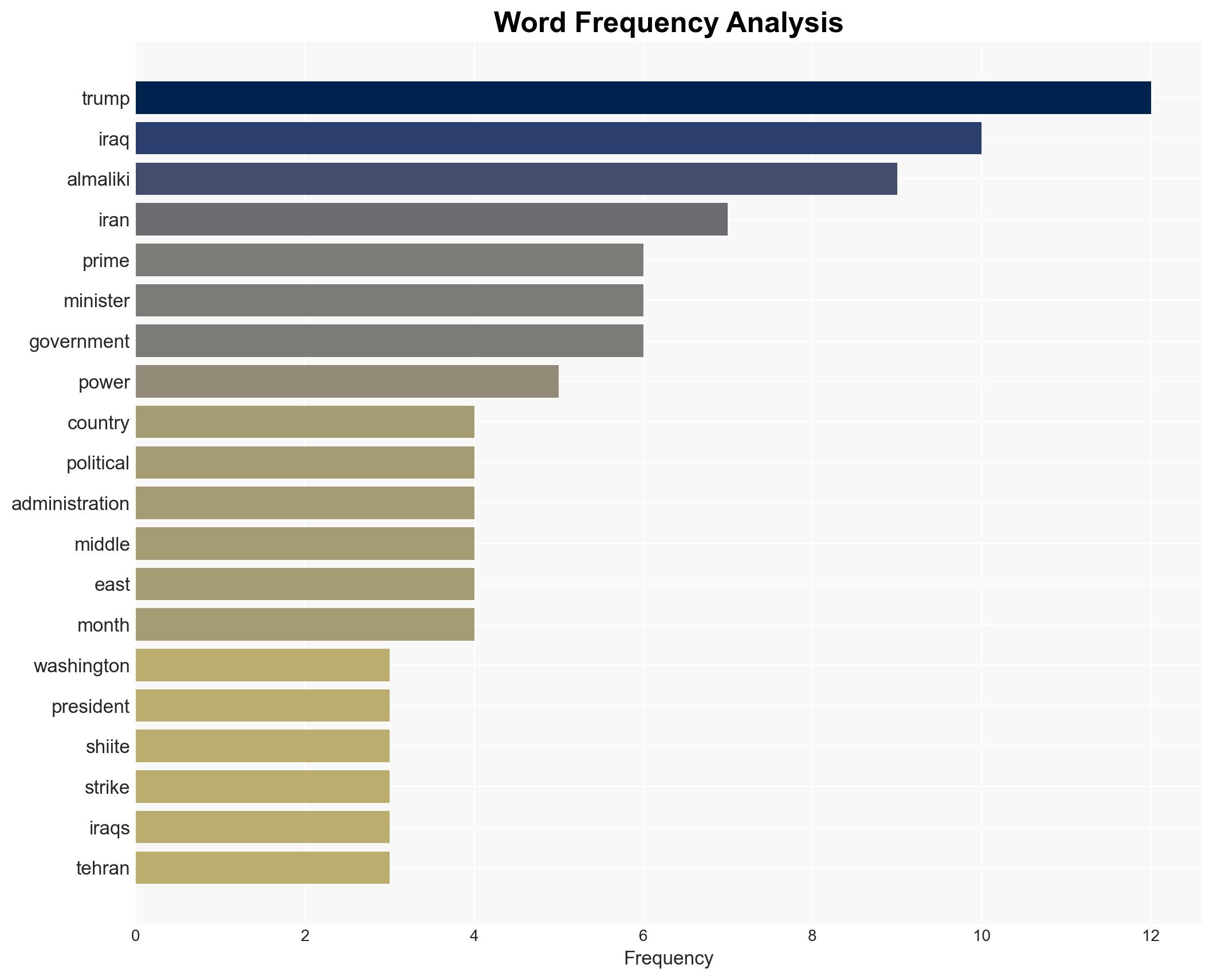
regional conflicts, Iranian influence, Iraqi politics, U.S. foreign policy, sectarian tensions, regional security, Middle East stability, geopolitical strategy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us