Oxfam declines to share Palestinian staff details with Israel, citing humanitarian concerns amid Gaza conflic…
Published on: 2026-01-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Oxfam refuses to provide Israel with details of Palestinian staff in Gaza
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
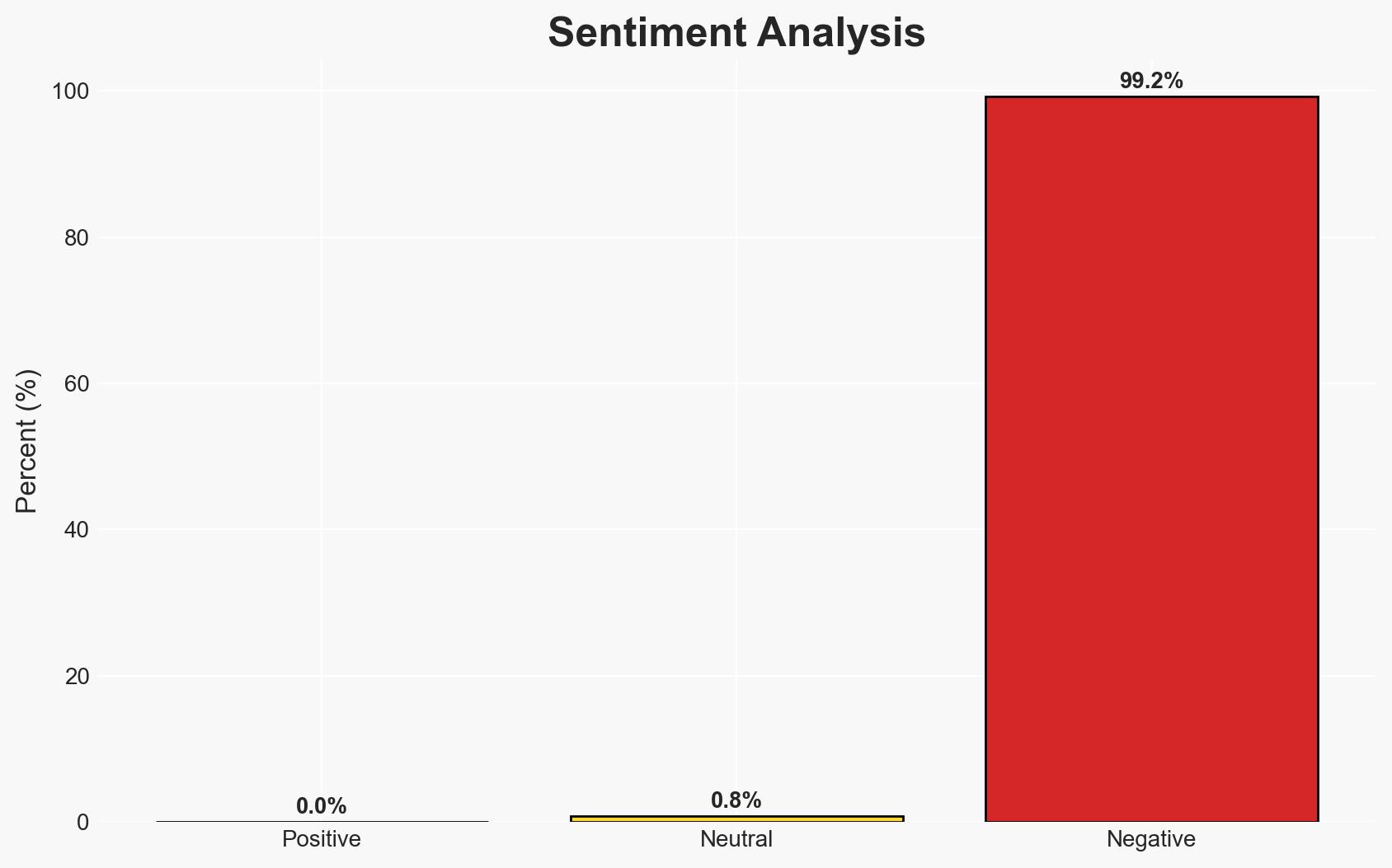
Oxfam’s refusal to comply with Israel’s demand for personal details of Palestinian staff highlights a significant tension between humanitarian principles and national security measures. This development affects international NGOs operating in Gaza and the West Bank, potentially impacting aid delivery. The most likely hypothesis is that Oxfam’s stance will lead to increased scrutiny and potential operational restrictions by Israel. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate due to limited visibility into Israel’s enforcement mechanisms and potential NGO responses.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Oxfam’s refusal is primarily driven by adherence to humanitarian principles and data protection obligations. Supporting evidence includes Oxfam’s public statements and the cited risk to staff safety. Contradicting evidence is the lack of a unified stance among NGOs, as some are complying under specific conditions.
- Hypothesis B: Oxfam’s decision is a strategic move to pressure Israel and international stakeholders to reconsider the new regulations. Supporting evidence includes Oxfam’s call for donor governments to leverage influence. However, the lack of immediate international response weakens this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to Oxfam’s consistent emphasis on humanitarian principles and data protection. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in international diplomatic engagement or a unified NGO response strategy.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Oxfam’s public statements accurately reflect its internal motivations; Israel will enforce its regulations uniformly; NGOs have the capacity to resist or comply based on strategic priorities.
- Information Gaps: Detailed understanding of Israel’s enforcement mechanisms and timelines; internal deliberations within NGOs regarding compliance; potential diplomatic interventions by third-party states.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in NGO public statements to gain international sympathy; risk of Israeli information operations framing NGOs as security threats.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a protracted standoff between Israel and international NGOs, affecting humanitarian operations and regional stability. Over time, this may influence broader geopolitical dynamics and international perceptions of Israel’s policies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic friction between Israel and countries supporting NGOs; increased international scrutiny of Israel’s policies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Possible increase in security measures by Israel, impacting NGO operations and local populations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for cyber operations targeting NGOs or Israeli entities to influence public opinion or disrupt operations.
- Economic / Social: Disruption in aid delivery could exacerbate humanitarian conditions, leading to social unrest or economic instability in affected areas.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor NGO compliance trends and Israeli enforcement actions; engage with diplomatic channels to assess potential interventions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for NGOs operating under restrictive conditions; explore partnerships to mitigate operational risks.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Israel revises regulations, allowing NGOs to operate without data disclosure, triggered by international diplomatic pressure.
- Worst: NGOs are forced to cease operations, leading to a humanitarian crisis, triggered by strict enforcement and lack of international intervention.
- Most-Likely: A mixed compliance landscape with ongoing negotiations, triggered by incremental diplomatic engagements and selective enforcement.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
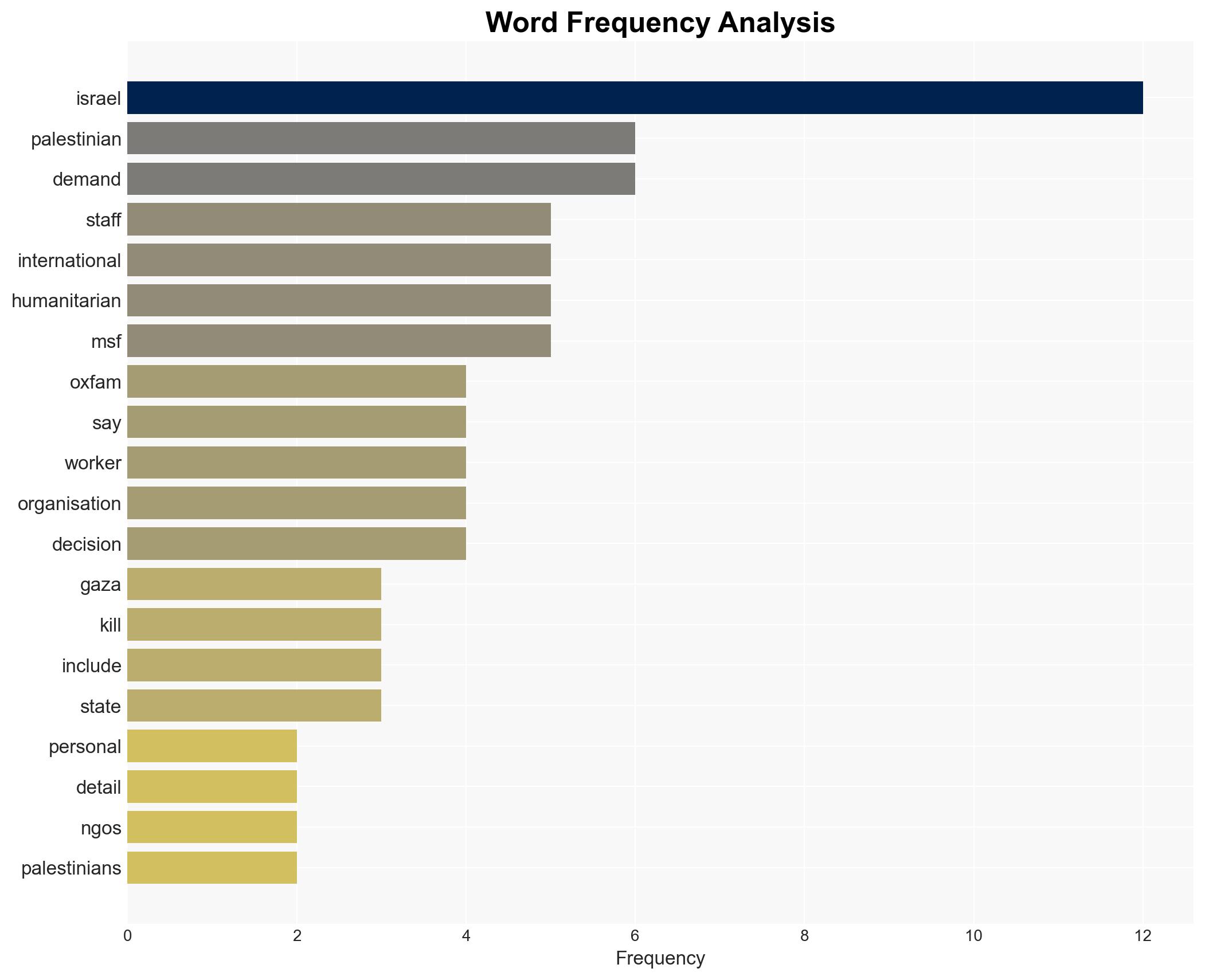
- Oxfam
- Israel’s Ministry for Diaspora Affairs
- Norwegian Refugee Council
- International Rescue Committee
- Doctors Without Borders (MSF)
- Palestinian NGOs Network (PNGO)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, humanitarian aid, NGO compliance, Israel-Palestine conflict, data protection, international diplomacy, security regulations, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us