Critical n8n Vulnerabilities Enable Authenticated Users to Execute Remote Code Remotely
Published on: 2026-01-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Two High-Severity n8n Flaws Allow Authenticated Remote Code Execution
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The discovery of two high-severity vulnerabilities in the n8n workflow automation platform poses a significant risk of remote code execution by authenticated users, potentially compromising entire organizational infrastructures. The most likely hypothesis is that these vulnerabilities will be exploited by cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to the presence of known vulnerabilities and the potential for widespread impact.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Cybercriminals will exploit these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to sensitive organizational data and systems. Supporting evidence includes the high CVSS scores of the vulnerabilities and the potential for complete system takeover. However, the requirement for authentication may limit the pool of potential attackers.
- Hypothesis B: Organizations will quickly patch these vulnerabilities, minimizing the risk of exploitation. This is supported by the availability of patches and advisories urging updates. Contradicting evidence includes the historical lag in patch adoption and the large number of unpatched instances.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the high number of unpatched instances and the significant impact of potential exploitation. Indicators that could shift this judgment include widespread adoption of patches and increased security awareness among n8n users.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations will prioritize patching these vulnerabilities; Cybercriminals have the capability to exploit these flaws; n8n instances are integral to organizational operations.
- Information Gaps: The exact number of organizations that have applied the patches; The specific motivations and capabilities of potential attackers.
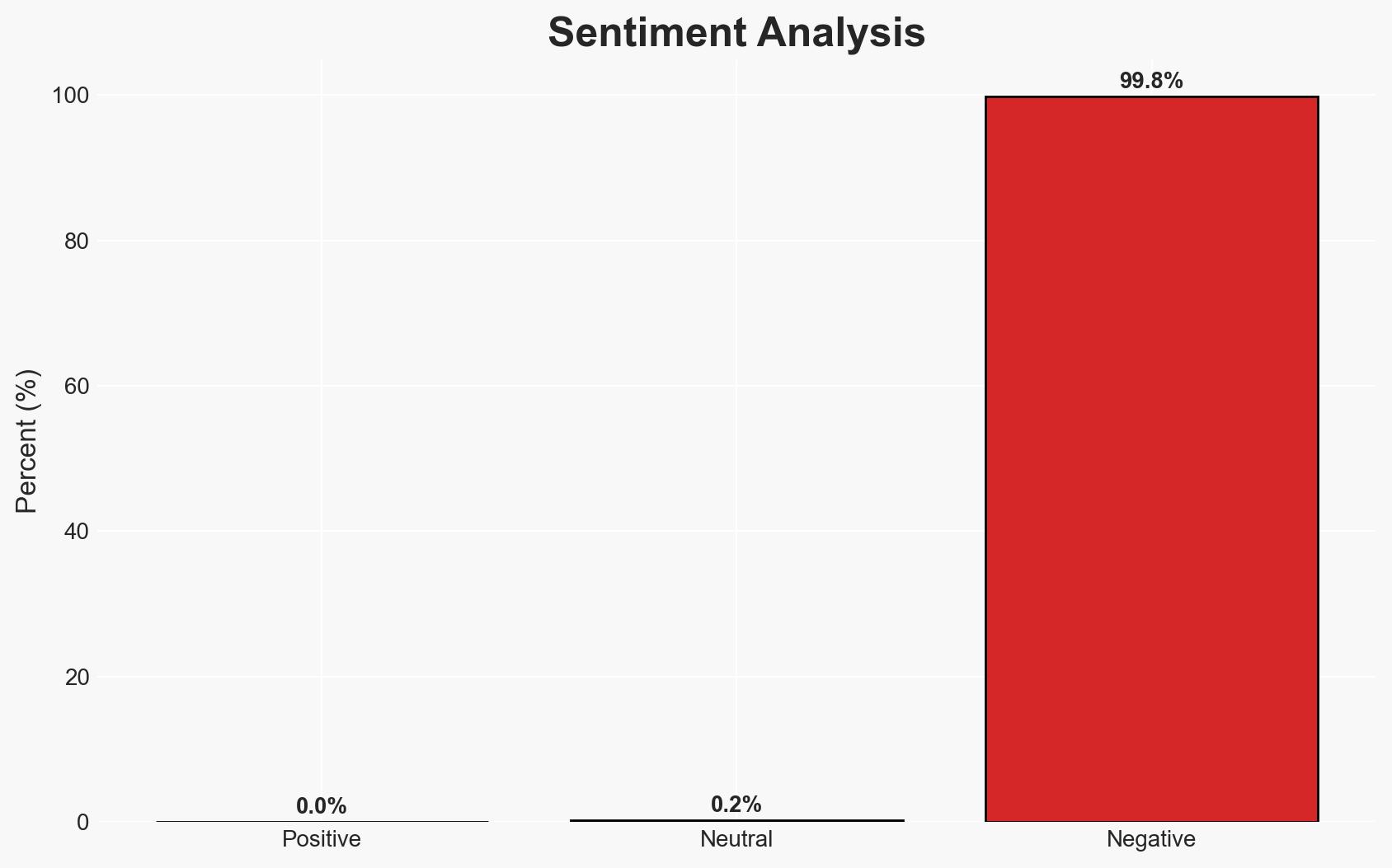
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underreporting of exploitation incidents; Overreliance on vendor-provided information without independent verification.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of these vulnerabilities could lead to significant disruptions in organizational operations and data breaches, affecting trust and economic stability. Over time, this could prompt regulatory scrutiny and changes in cybersecurity practices.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between nations if state-sponsored actors are involved in exploiting these vulnerabilities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment as cybercriminals leverage compromised systems for further attacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber espionage activities and data theft.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses for affected organizations and potential impacts on consumer trust and market stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgently apply available patches; Conduct security audits to identify and mitigate potential exploitation; Increase monitoring of n8n instances for suspicious activities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for information sharing on vulnerabilities; Enhance organizational cybersecurity training and awareness programs.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid patch adoption prevents major incidents. Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant data breaches. Most-Likely: Mixed patch adoption results in isolated but impactful breaches.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Shachar Menashe, JFrog’s Vice President of Security Research
- JFrog Security Research Team
- Shadowserver Foundation
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, remote code execution, vulnerability management, patch management, cyber threat, information security, organizational risk
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us