US Proposes International Buyback Program for Gaza Demilitarization Amidst Ongoing Hamas Control
Published on: 2026-01-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: US tells UN Gaza demilitarization to include internationally funded buyback program
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The United States has proposed a demilitarization plan for Gaza, involving an internationally funded weapons buyback program, aimed at disarming Hamas. This initiative is part of a broader peace effort but faces significant challenges due to Hamas’s current armament levels and lack of detailed disarmament proposals. The overall confidence in the successful implementation of this plan is moderate, given the complexities and uncertainties involved.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The demilitarization plan will succeed, leading to a reduction in Hamas’s military capabilities and increased stability in Gaza. This is supported by international backing and pressure from the U.S. and allied countries. However, the lack of detailed proposals and Hamas’s current armament levels are significant uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: The plan will fail due to Hamas’s resistance and the absence of concrete disarmament proposals. This is supported by statements from Hamas officials and the historical difficulty of disarming militant groups in the region.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the absence of detailed disarmament proposals and Hamas’s significant armament. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the presentation of a concrete disarmament plan and increased international pressure on Hamas.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The international community will maintain pressure on Hamas; Hamas is open to negotiation; the buyback program is adequately funded and effectively implemented.
- Information Gaps: Details on the buyback program’s funding and implementation, Hamas’s internal decision-making processes, and the role of international monitors.
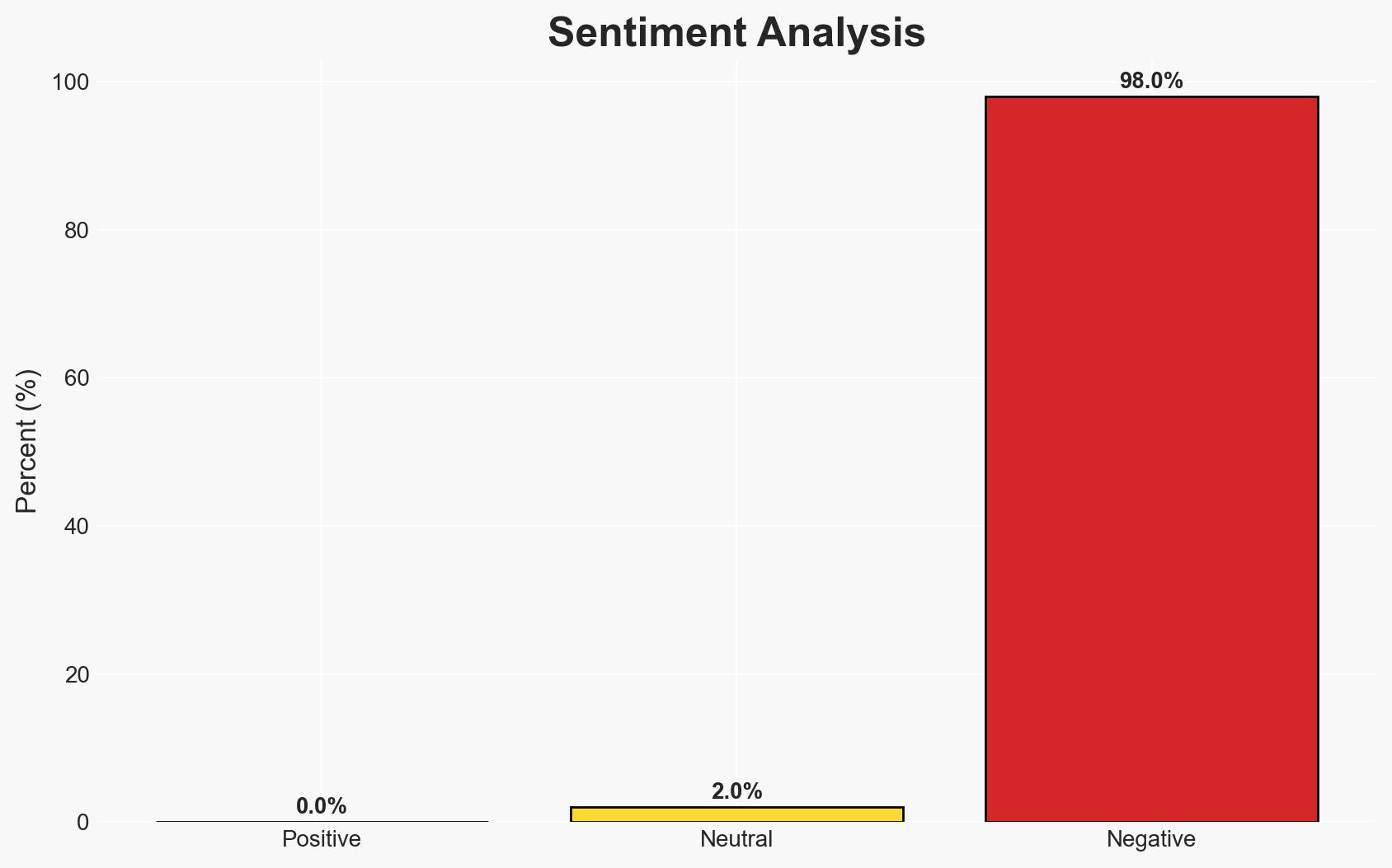
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in U.S. reporting; Hamas’s public statements may not reflect internal strategies; risk of misinformation from involved parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The proposed demilitarization plan could significantly impact regional stability and the balance of power in Gaza. Its success or failure will have wide-ranging effects on political, security, and economic dynamics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential shifts in power dynamics within Gaza and between Israel and Palestine; possible changes in international diplomatic relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Changes in the threat landscape in Gaza; potential for increased violence if disarmament efforts fail.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased propaganda or misinformation campaigns by involved parties.
- Economic / Social: Economic impact of demilitarization efforts; potential social unrest if disarmament is perceived as unjust or ineffective.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor developments closely; engage with international partners to ensure cohesive strategy; prepare for potential escalation.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential fallout; strengthen partnerships with regional allies; enhance intelligence capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful disarmament and stabilization; Worst: Increased conflict and regional instability; Most-Likely: Partial disarmament with ongoing tensions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Mike Waltz, U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations
- Hamas leadership
- Israeli U.N. Ambassador Danny Danon
- Trump’s Board of Peace
- Palestinian National Committee
7. Thematic Tags
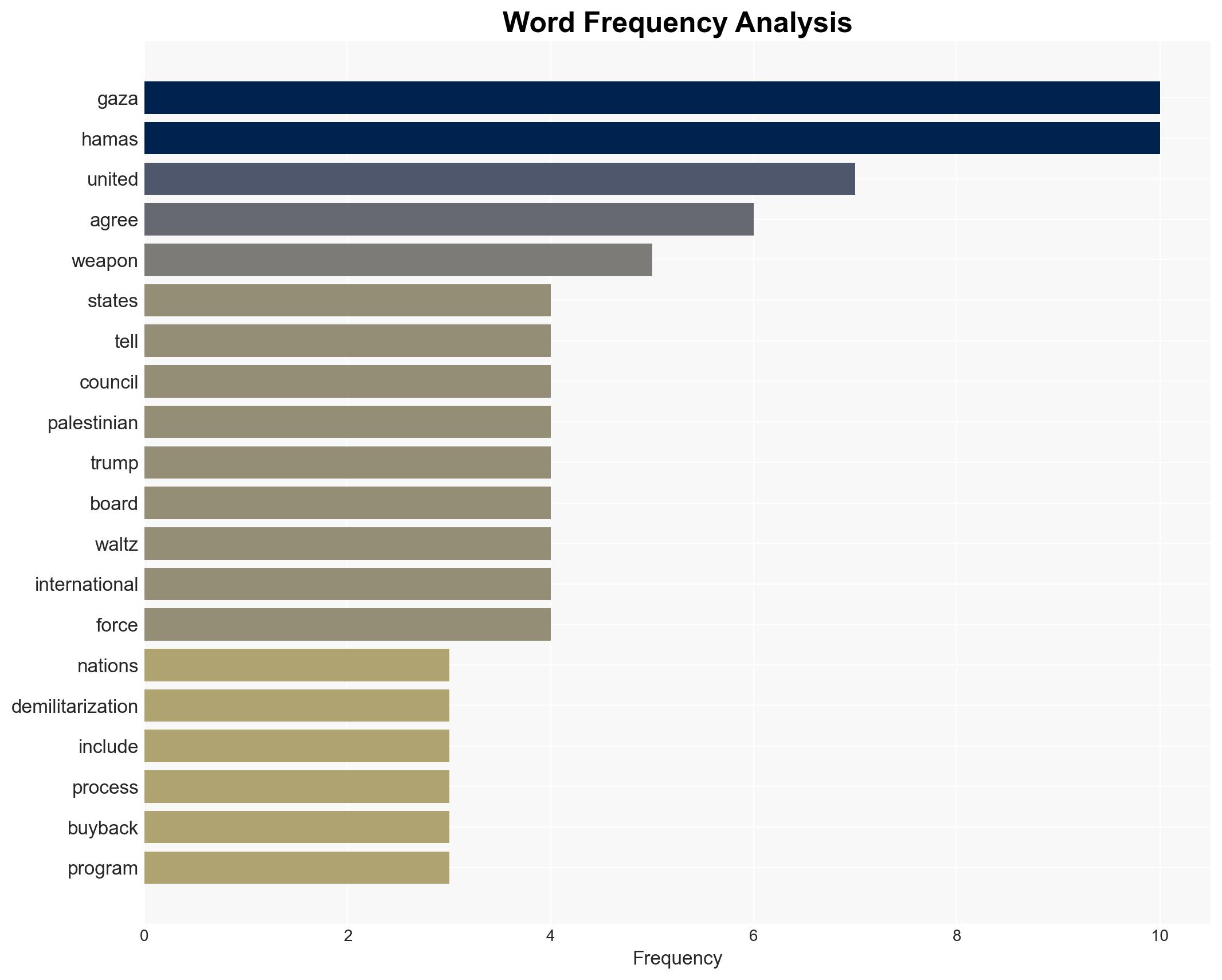
Counter-Terrorism, demilitarization, international relations, Middle East peace process, arms control, Gaza conflict, U.S. foreign policy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us