Families of Hostages Criticize Aid Policy, Claim Support for Hamas Amid Ongoing Conflict in Gaza
Published on: 2026-01-29
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Hostages’ families Every additional aid truck helps Hamas
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
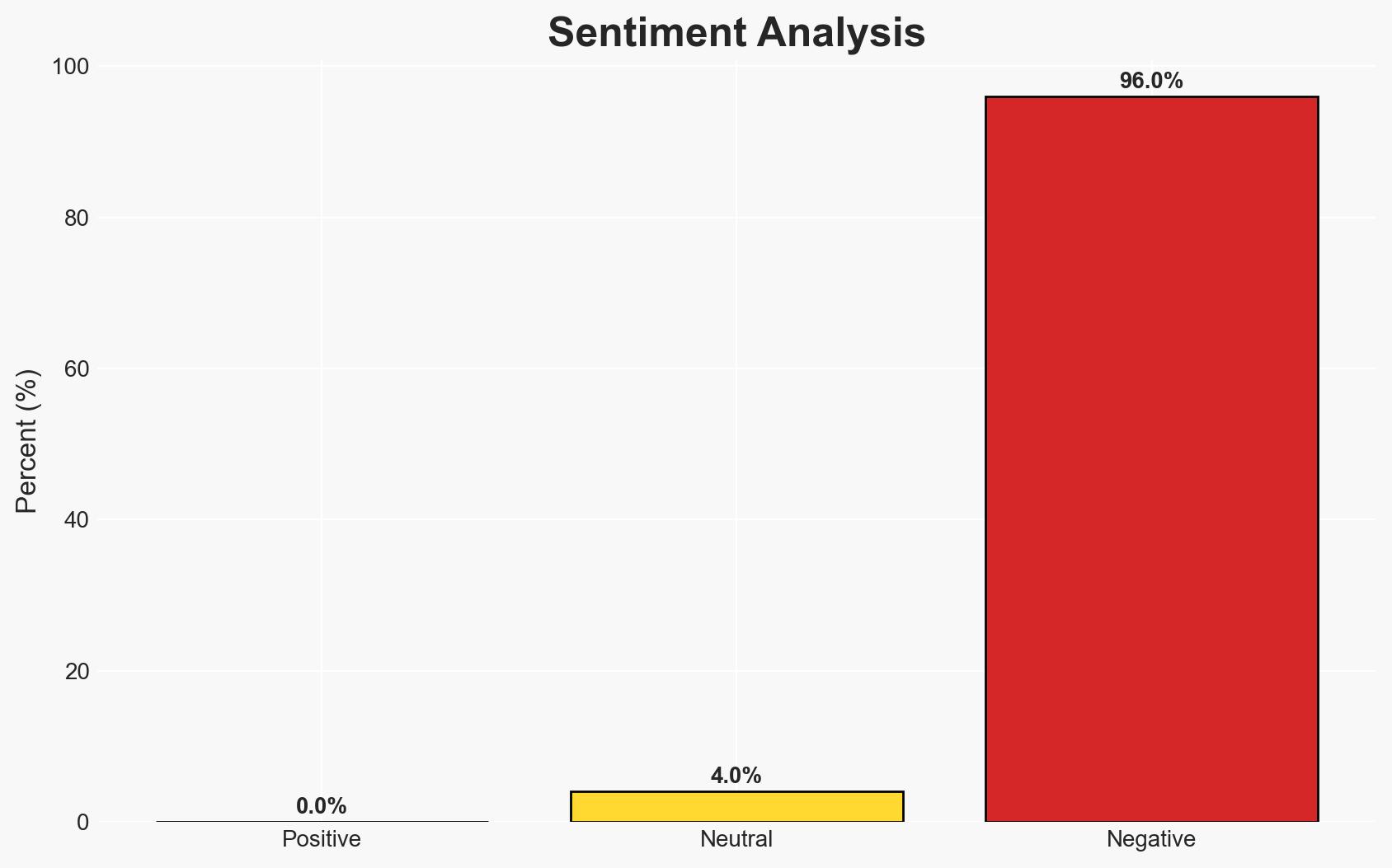
The current humanitarian aid policy to the Gaza Strip is perceived to inadvertently strengthen Hamas by exceeding necessary aid levels, potentially undermining Israeli security efforts. The most likely hypothesis is that excessive aid is being exploited by Hamas for operational gains. This situation affects Israeli national security and regional stability, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The volume of humanitarian aid entering Gaza is excessive and is being exploited by Hamas to strengthen its operational capabilities. Evidence includes IDF reports of aid exceeding UN standards and smuggling activities. Key uncertainties include the exact proportion of aid being diverted to Hamas.
- Hypothesis B: The aid provided is necessary to prevent a humanitarian crisis and does not significantly bolster Hamas. Supporting evidence includes the absence of a prominent humanitarian crisis and the structured aid system in place. Contradicting evidence includes IDF concerns about aid volume and smuggling.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to IDF warnings and the reported excess in aid volume. Indicators that could shift this judgment include verified data on the actual use of aid within Gaza and independent assessments of humanitarian needs.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The IDF’s data on aid volumes is accurate; Hamas has the capability to exploit aid for operational gains; the humanitarian needs in Gaza are accurately represented by UN standards.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the distribution and end-use of aid within Gaza; independent verification of smuggling routes and volumes.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in IDF reporting due to internal policy disagreements; risk of Hamas propaganda manipulating perceptions of aid effectiveness.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate regional tensions and complicate Israeli military operations, while affecting international perceptions of the humanitarian situation in Gaza.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased diplomatic pressure on Israel regarding humanitarian policies; potential for international criticism or sanctions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced operational capabilities for Hamas could lead to increased attacks or destabilization efforts.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting aid logistics or information campaigns by Hamas.
- Economic / Social: Strain on Israeli resources and potential social unrest due to perceived policy failures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive audit of aid distribution; enhance monitoring of smuggling routes; engage with international partners for independent assessments.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to counter Hamas exploitation; strengthen partnerships with humanitarian organizations for transparent aid delivery.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Aid is effectively monitored, reducing Hamas exploitation, leading to improved security (trigger: successful audit and monitoring systems).
- Worst: Aid continues to bolster Hamas, resulting in increased conflict (trigger: failure to address smuggling and aid diversion).
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in aid monitoring with ongoing challenges (trigger: partial implementation of recommendations).
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Hamas
- IDF (Israel Defense Forces)
- Hagvura Forum
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, humanitarian aid, Israeli security, Gaza conflict, smuggling, regional stability, military operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us