Germany to Enhance Protection of Critical Infrastructure Amid Rising Tensions with Russia
Published on: 2026-01-29
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Germany to strengthen critical infrastructure as Russia fears spike
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
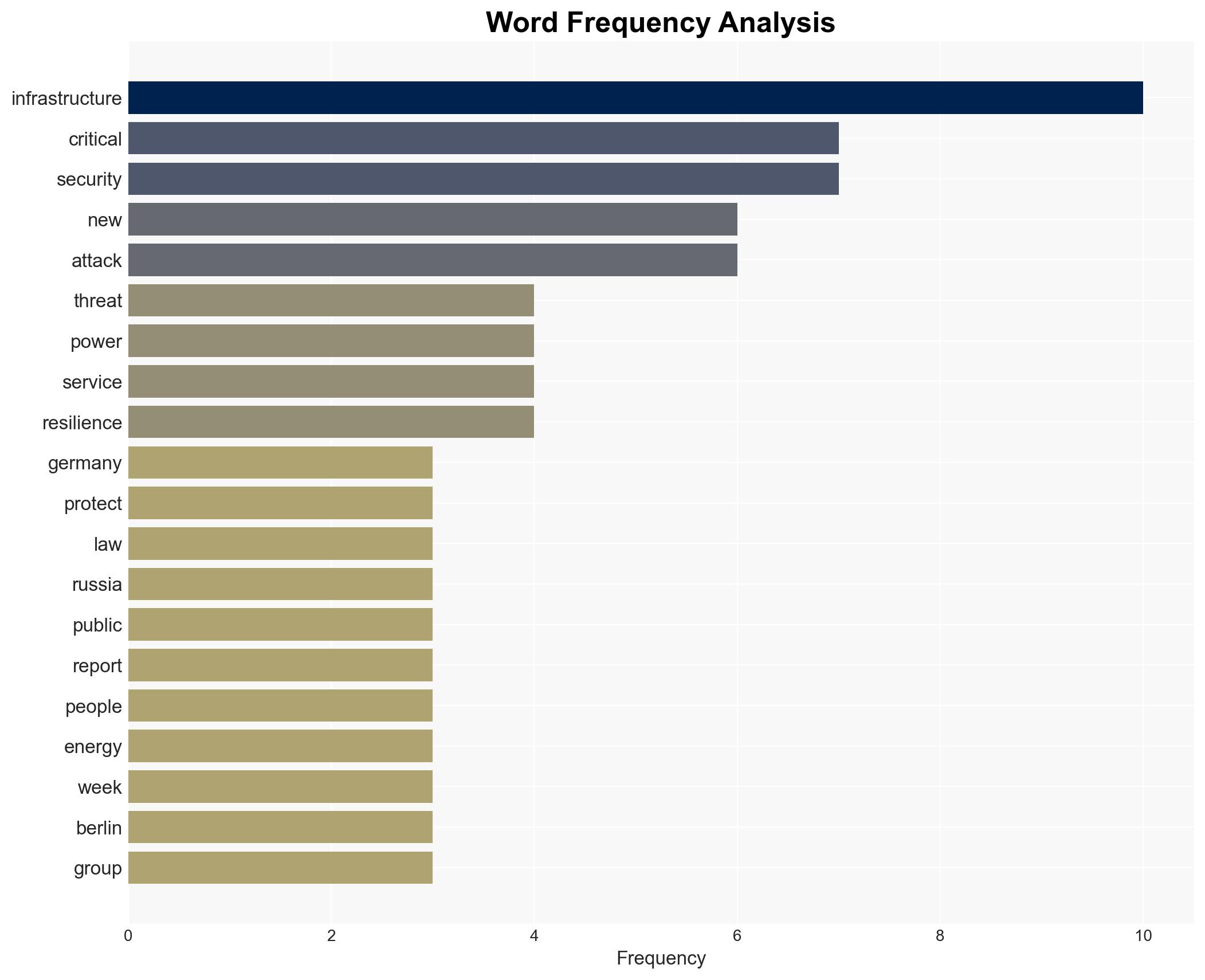
Germany is advancing legislation to enhance the protection of its critical infrastructure amid heightened tensions with Russia and recent domestic sabotage incidents. This move is primarily driven by the need to align with EU directives and to mitigate vulnerabilities exposed by recent attacks. The most likely hypothesis is that these measures will incrementally improve resilience but may face implementation challenges. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Germany’s new legislation will significantly enhance the resilience of its critical infrastructure against both domestic and foreign threats. Supporting evidence includes the comprehensive scope of the law covering multiple sectors and the alignment with EU directives. However, uncertainties remain regarding the speed and effectiveness of implementation.
- Hypothesis B: The legislative measures will have limited impact due to inadequate resources, bureaucratic inertia, and potential resistance from private sector stakeholders. This hypothesis is supported by criticisms from political figures and experts who deem the response as insufficient and delayed.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the structured legislative approach and the urgency driven by recent incidents. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the pace of legislative adoption, resource allocation, and private sector compliance.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The German government has the political will and resources to enforce the new legislation; EU directives will provide a coherent framework for implementation; private sector stakeholders will comply with new security requirements.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on resource allocation for enforcement, private sector readiness to implement changes, and the timeline for full legislative adoption.
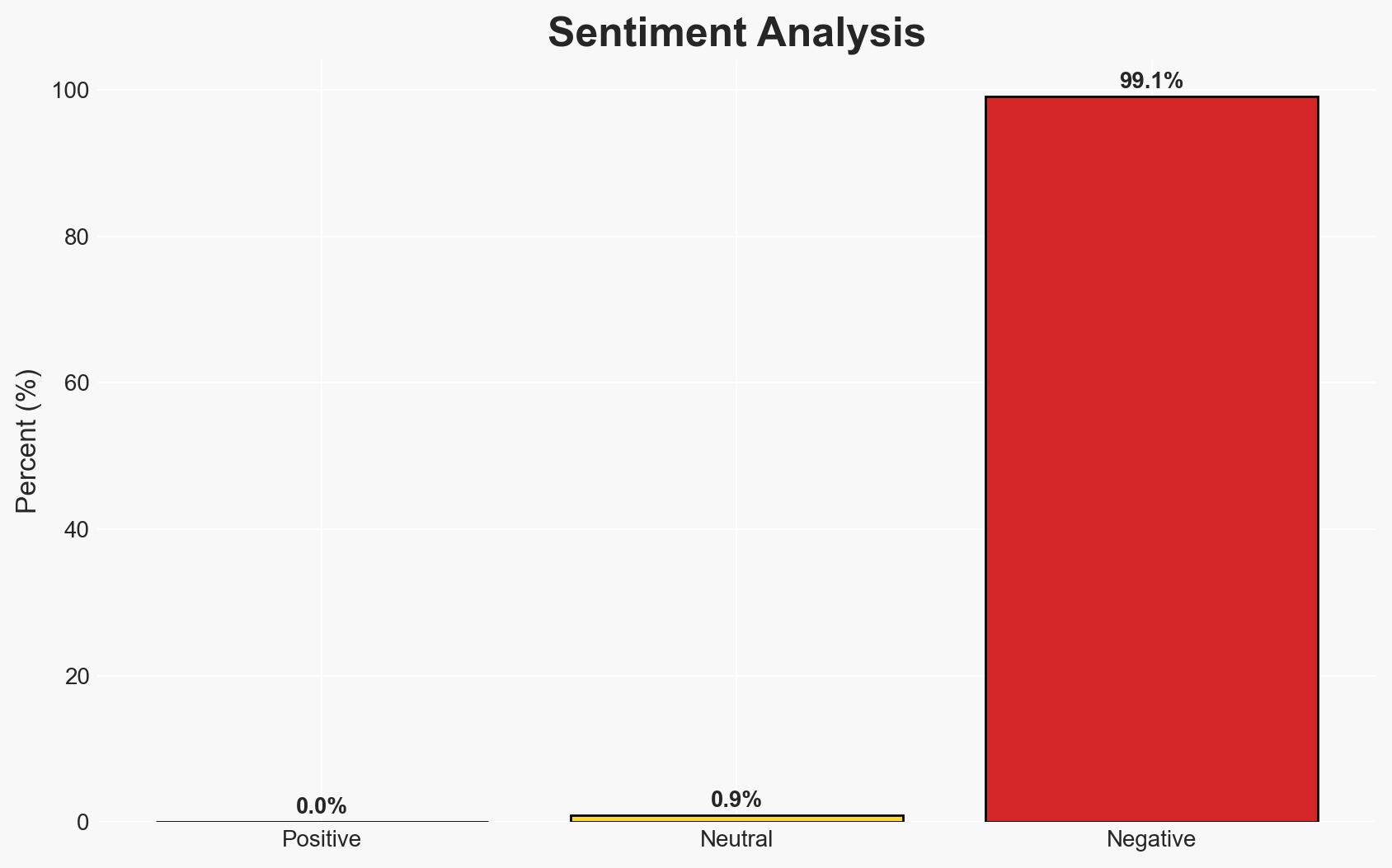
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on government and media sources may introduce bias; risk of underestimating the adaptability of threat actors to new security measures.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a gradual strengthening of Germany’s critical infrastructure, potentially deterring future attacks. However, incomplete implementation or inadequate enforcement could leave vulnerabilities unaddressed.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strengthened infrastructure may reduce leverage for foreign actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities, potentially stabilizing regional security dynamics.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced infrastructure security could deter domestic and international threat actors but may also prompt them to seek alternative methods of attack.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on cybersecurity could lead to improved defenses against cyber-attacks, but also necessitates vigilance against evolving cyber threats.
- Economic / Social: Improved infrastructure security could bolster public confidence and economic stability, though initial costs and disruptions may pose challenges.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor legislative progress and stakeholder responses; enhance intelligence sharing with EU partners; initiate public-private partnerships for rapid implementation.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures and conduct regular security audits; invest in cybersecurity capabilities; engage in regional security dialogues to address hybrid threats.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Full implementation leads to robust infrastructure security and deterrence of threats.
- Worst: Legislative measures falter, leaving critical vulnerabilities exposed.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements with ongoing challenges in enforcement and compliance.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
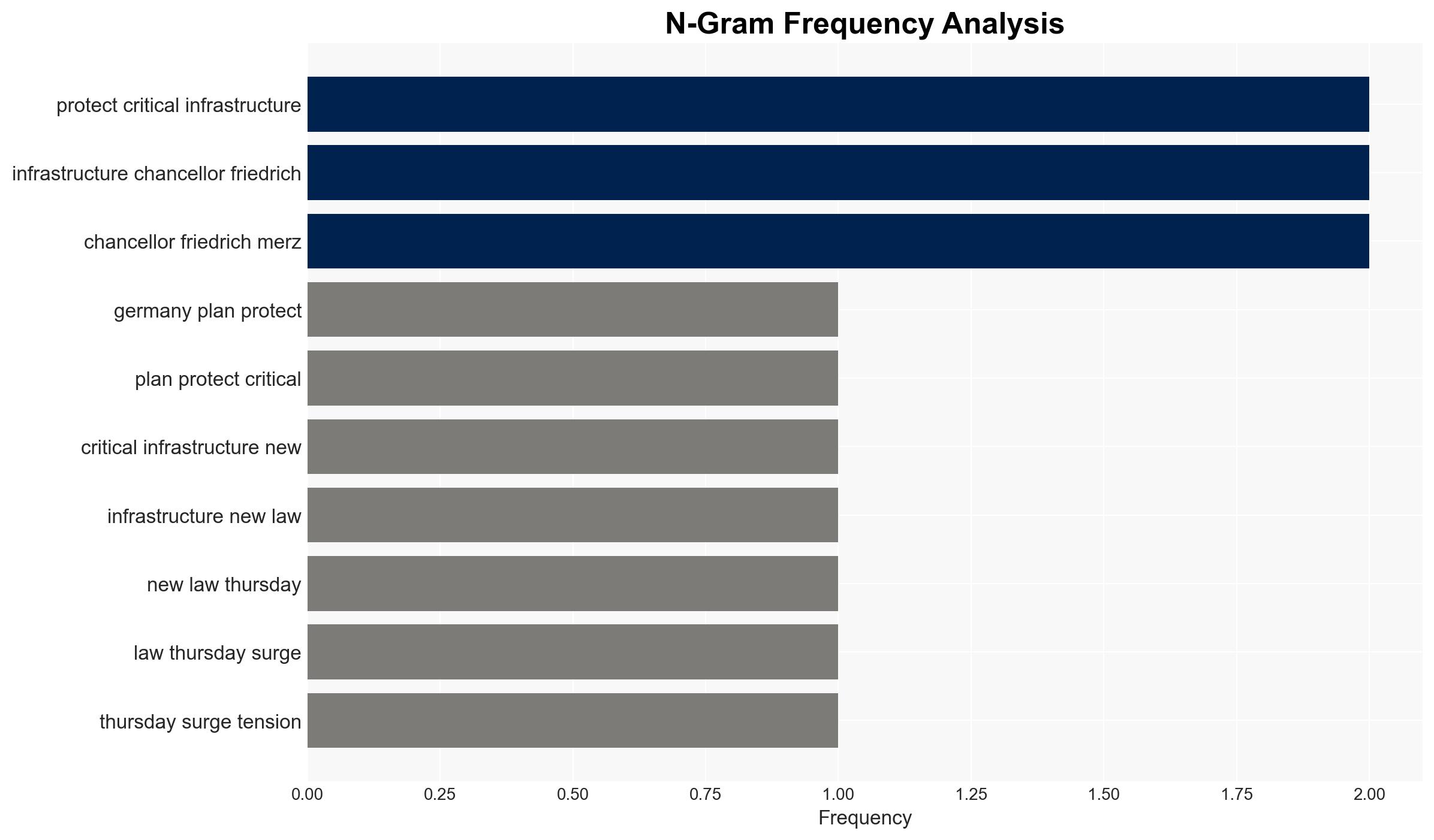
- Chancellor Friedrich Merz
- Defence Minister Boris Pistorius
- Greens MP Konstantin von Notz
- Vulkangruppe (Vulcan Group)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, critical infrastructure, national security, cyber threats, EU directives, hybrid warfare, public-private partnerships, legislative measures
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us