AI-Driven Cyberattacks Become Inexpensively Accessible, Transforming Business Security Landscape
Published on: 2026-01-29
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: AI has made hacking cheap That changes everything for business
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The integration of AI into cyberattack methodologies has significantly reduced the cost and increased the accessibility of executing sophisticated cyberattacks. This development poses a heightened threat to businesses, particularly those with inadequate cybersecurity measures. The most likely hypothesis is that AI will continue to democratize cyber capabilities, increasing the frequency and scale of attacks. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to the rapid evolution of AI capabilities and the current lack of comprehensive data on long-term impacts.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI-driven cyberattacks will become the norm, significantly increasing the volume and sophistication of attacks. This is supported by the evidence that AI can perform complex hacking tasks at a fraction of the cost and time required by human hackers. However, the extent to which this will affect global cybersecurity dynamics remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The impact of AI on cyberattacks will be limited by countermeasures and regulatory frameworks that will evolve to mitigate these threats. While there is potential for regulatory adaptation, current evidence suggests that AI capabilities are advancing faster than defensive measures.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the demonstrated ability of AI to execute complex tasks cheaply and effectively. Indicators such as increased AI integration in cybersecurity tools or significant regulatory changes could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI capabilities will continue to advance; businesses will not uniformly enhance their cybersecurity measures; AI-driven attacks will remain economically viable.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the long-term effectiveness of AI-driven attacks and comprehensive statistics on their frequency and success rate.
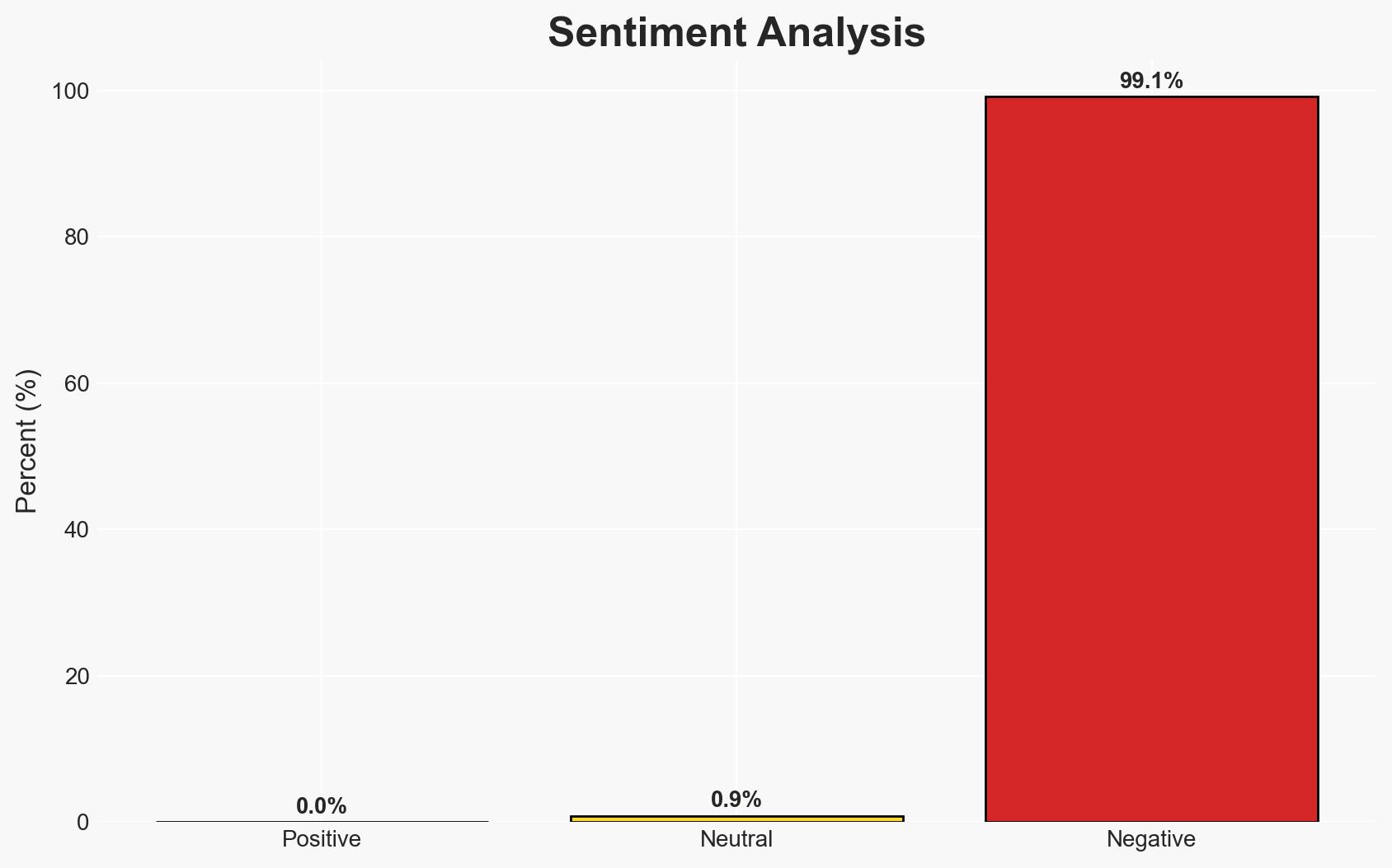
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from AI security labs with vested interests; lack of independent verification of AI capabilities in cyberattacks.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The proliferation of AI-driven cyberattacks could lead to increased economic and operational disruptions across various sectors. This development may also influence geopolitical dynamics and national security strategies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions as states may attribute cyberattacks to rival nations, complicating diplomatic relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Expanded attack surfaces and increased vulnerabilities could be exploited by terrorist organizations or hostile state actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Enhanced AI capabilities may lead to more sophisticated misinformation campaigns and data breaches.
- Economic / Social: Potential for significant economic losses and disruptions in business operations, affecting social stability and trust in digital systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of AI-driven cyber threats, enhance cybersecurity awareness among non-technical staff, and review existing security protocols.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with AI security firms, invest in AI-driven defensive technologies, and advocate for regulatory frameworks addressing AI in cybersecurity.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective countermeasures and regulations mitigate AI-driven threats.
- Worst: Unchecked AI-driven attacks lead to widespread economic and security crises.
- Most-Likely: Gradual increase in AI-driven attacks with intermittent regulatory and technological responses.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Gal Nagli, Head of Threat Exposure at Wiz
- Omer Nevo, Cofounder and CTO at Irregular
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
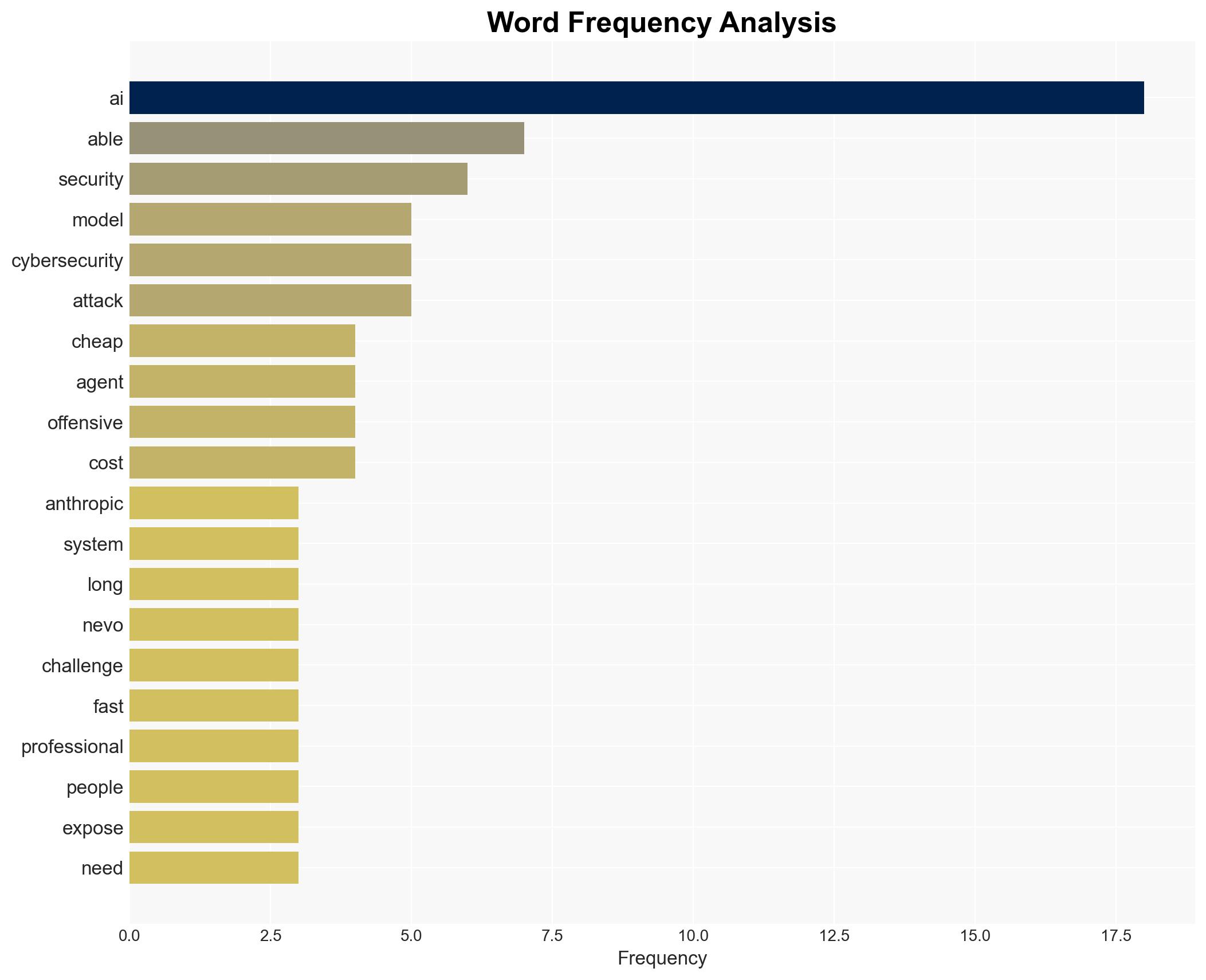
cybersecurity, AI, cyberattacks, economic impact, regulatory challenges, technological advancement, national security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us