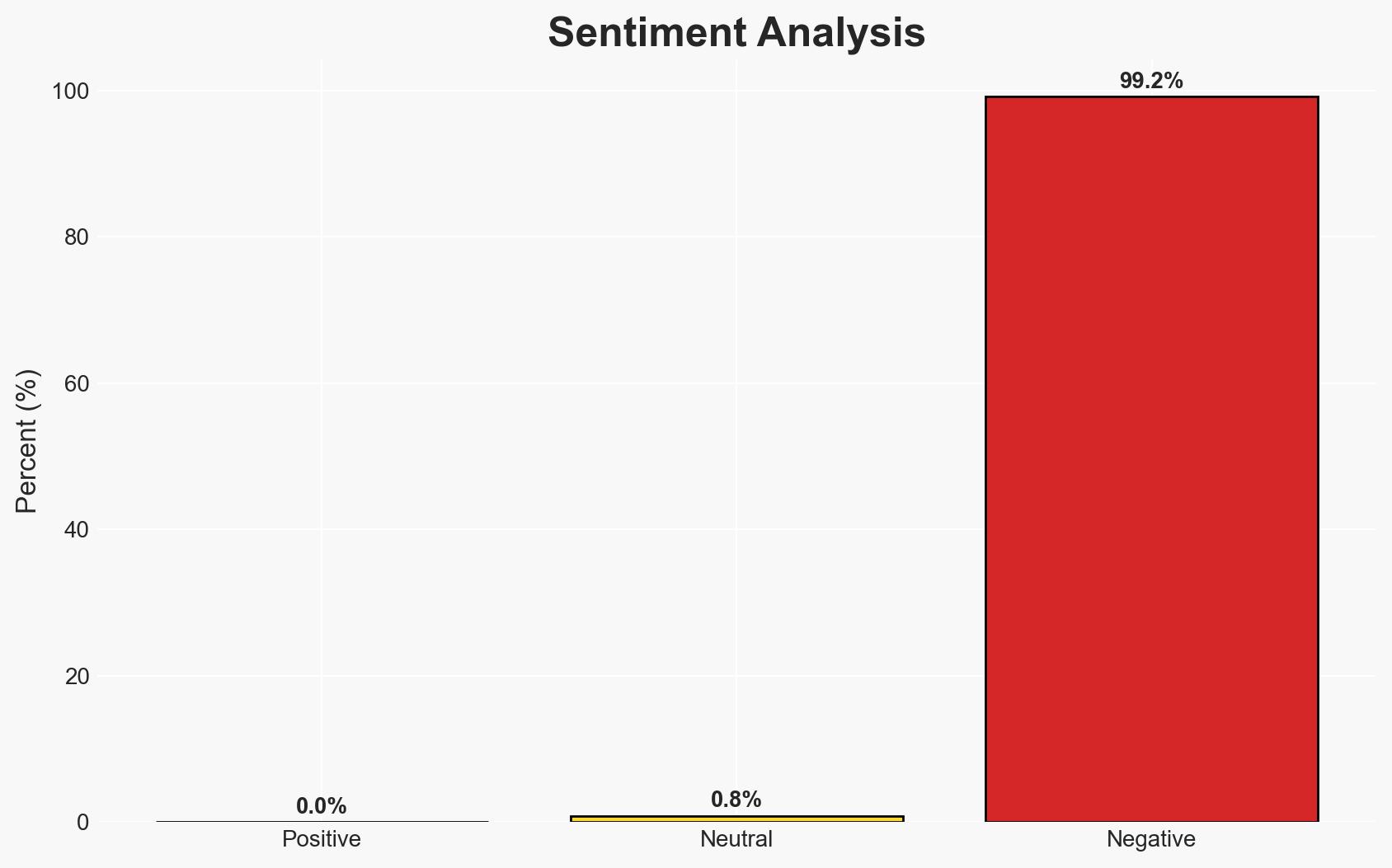
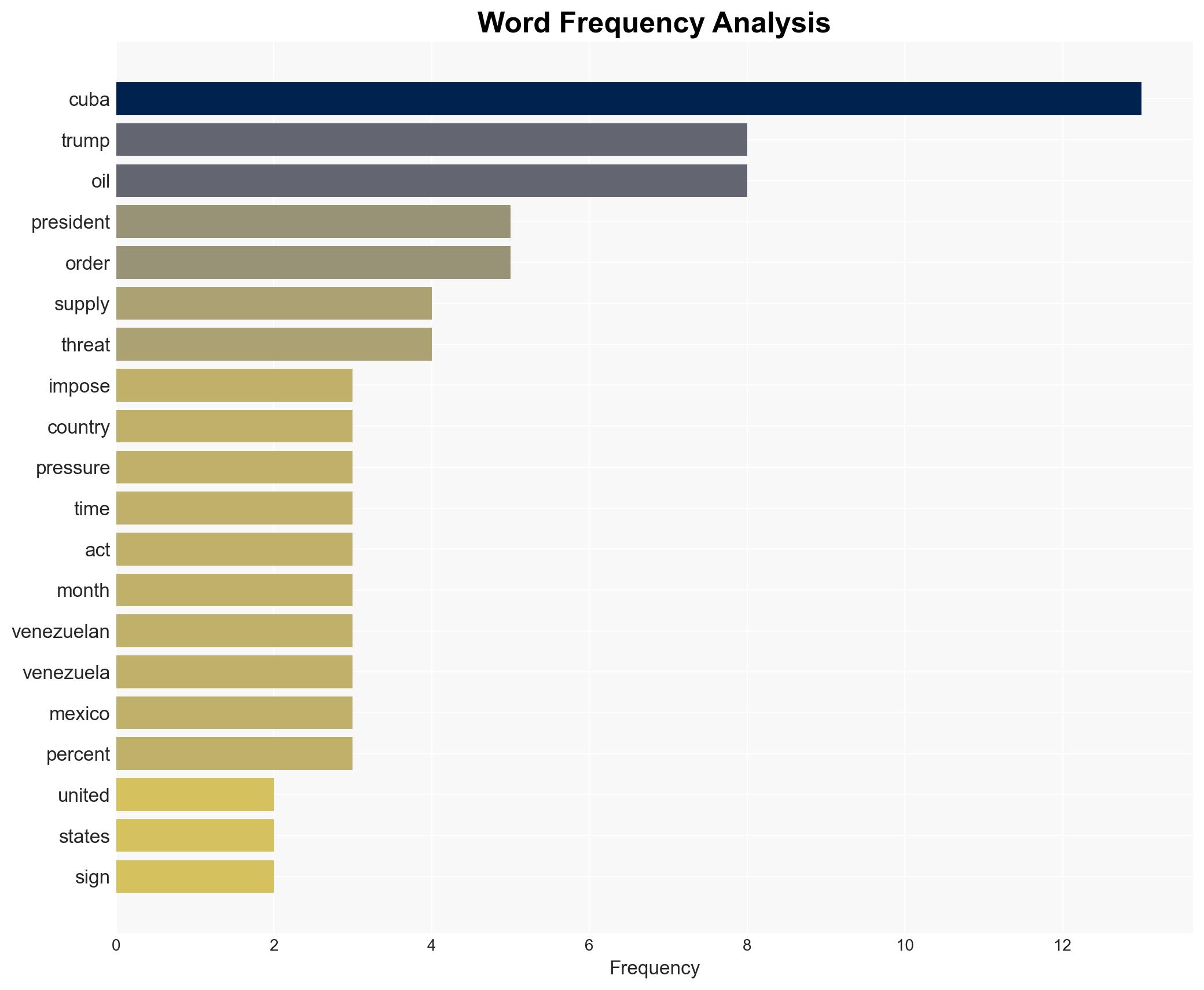
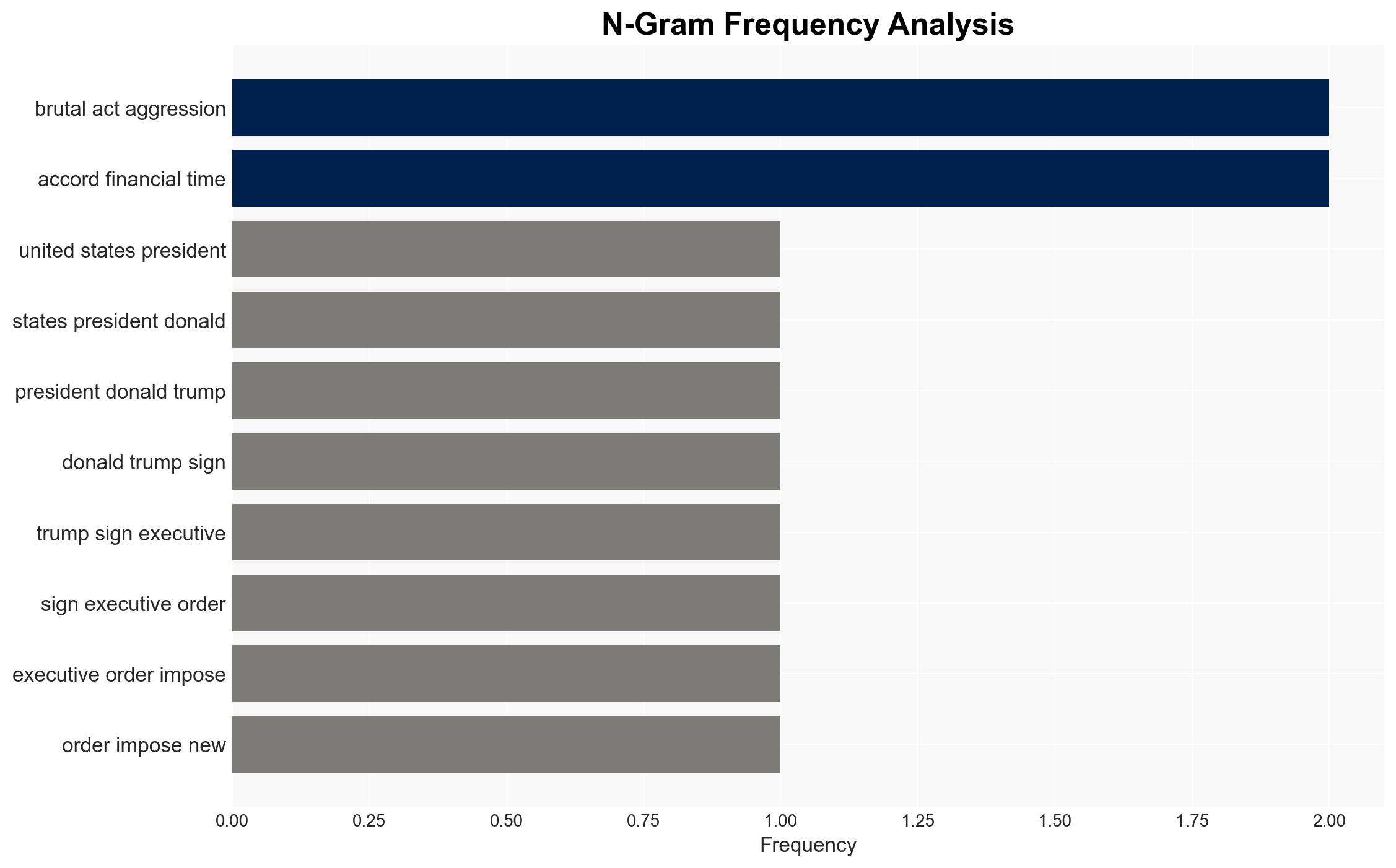
Trump signs order to impose tariffs on nations supplying oil to Cuba, citing national security concerns.
Published on: 2026-01-30
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Trump threatens tariffs on countries supplying Cuba with much-needed oil
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The United States, under President Trump’s directive, is imposing tariffs on countries supplying oil to Cuba, aiming to pressure the Cuban government by cutting off its energy supplies. This move primarily affects Mexico and potentially other countries involved in Cuba’s oil imports. The most likely hypothesis is that the US seeks to destabilize Cuba economically to force political concessions. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the complexity of international responses and potential for unforeseen consequences.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The US is using economic pressure to force Cuba into political concessions, leveraging its control over Venezuela’s oil sector to cut off a critical energy supply to Cuba. Supporting evidence includes the imposition of tariffs and the explicit mention of Cuba as a threat. Key uncertainties include the potential for international backlash and Cuba’s ability to find alternative oil sources.
- Hypothesis B: The US aims to isolate Cuba diplomatically by pressuring its oil suppliers, thereby weakening Cuba’s alliances with countries like Mexico and Russia. This hypothesis is supported by the US’s pressure on Mexico and the broader geopolitical context. However, the effectiveness of this strategy is uncertain due to Mexico’s assertion of sovereign decision-making and potential resistance from other countries.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct economic impact of cutting off oil supplies and the explicit US strategy to destabilize Cuba. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in international diplomatic alignments or Cuba securing alternative energy sources.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The US has sufficient leverage over oil-supplying countries; Cuba cannot quickly secure alternative oil sources; international backlash will be limited or manageable.
- Information Gaps: Detailed responses from other major oil suppliers to Cuba, such as Russia and Algeria, and their potential countermeasures.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential US overestimation of its influence on Mexico and other countries; Cuban and allied narratives may exaggerate or downplay impacts for strategic purposes.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased geopolitical tensions, particularly if other countries perceive the US actions as overreach. The economic strain on Cuba might lead to internal instability or increased migration pressures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic rifts between the US and countries like Mexico and Russia; increased alignment among Cuba’s allies against US policies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Possible increase in regional instability, which could be exploited by transnational terrorist groups.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely increase in propaganda and information operations from both US and Cuban-aligned entities to sway international opinion.
- Economic / Social: Economic hardship in Cuba could lead to social unrest, impacting regional stability and potentially increasing refugee flows.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor oil supply routes to Cuba and diplomatic communications from affected countries; engage in dialogue with Mexico to assess its stance and potential shifts.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop contingency plans for increased migration flows; strengthen alliances with regional partners to mitigate geopolitical fallout.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Cuba concedes to US demands, leading to improved relations.
- Worst Case: Heightened geopolitical tensions lead to broader regional instability.
- Most Likely: Continued economic pressure on Cuba with limited immediate political concessions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Donald Trump – US President
- Bruno Rodriguez – Cuban Foreign Minister
- Claudia Sheinbaum – Mexican President
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for other key individuals.
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, sanctions, geopolitical tension, energy security, US-Cuba relations, economic pressure, international diplomacy, regional stability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us